Sprouted grains offer enhanced nutritional benefits compared to regular grains, including higher levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The sprouting process breaks down starches, making these grains easier to digest and improving protein availability. Incorporating sprouted grains into your diet can support better blood sugar control and promote gut health.
Table of Comparison
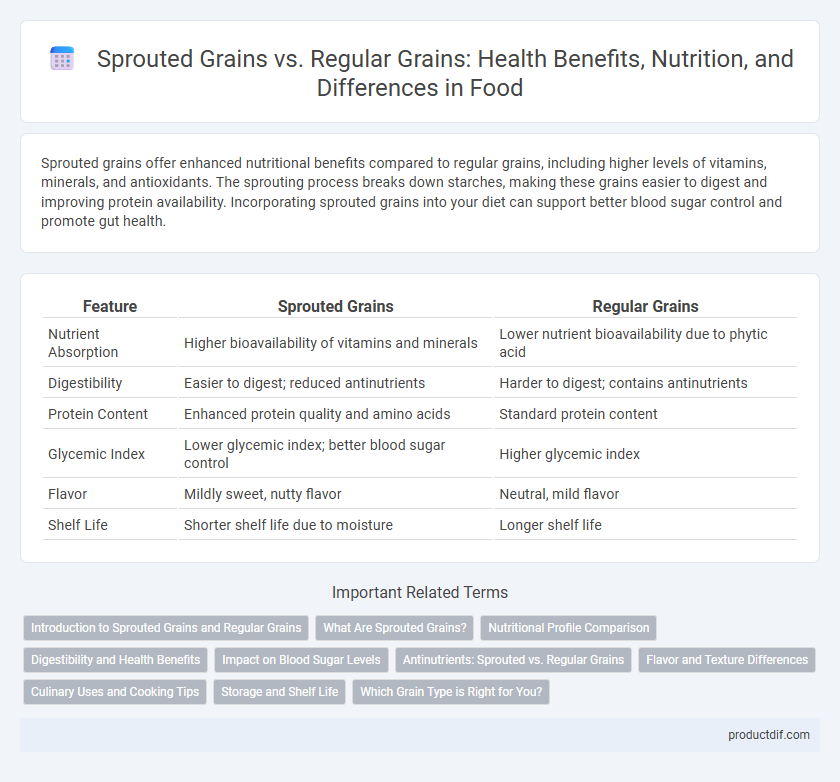
| Feature | Sprouted Grains | Regular Grains |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Absorption | Higher bioavailability of vitamins and minerals | Lower nutrient bioavailability due to phytic acid |
| Digestibility | Easier to digest; reduced antinutrients | Harder to digest; contains antinutrients |
| Protein Content | Enhanced protein quality and amino acids | Standard protein content |
| Glycemic Index | Lower glycemic index; better blood sugar control | Higher glycemic index |
| Flavor | Mildly sweet, nutty flavor | Neutral, mild flavor |
| Shelf Life | Shorter shelf life due to moisture | Longer shelf life |
Introduction to Sprouted Grains and Regular Grains
Sprouted grains are whole grains that have begun to germinate, activating enzymes that enhance nutrient availability and improve digestibility compared to regular grains. Regular grains are harvested kernels that have not sprouted, maintaining their original nutrient composition but often containing higher levels of antinutrients like phytic acid. Incorporating sprouted grains in diets can increase intake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants while reducing compounds that inhibit nutrient absorption.
What Are Sprouted Grains?
Sprouted grains are whole grains that have been soaked and allowed to germinate, activating enzymes and increasing nutrient availability such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This germination process reduces anti-nutrients like phytic acid, making the grains easier to digest compared to regular grains. Sprouted grains include varieties like sprouted wheat, barley, and quinoa, which offer enhanced protein content and improved flavor profiles.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
Sprouted grains exhibit higher levels of vitamins B and C, increased antioxidants, and improved digestibility compared to regular grains, which often contain antinutrients inhibiting nutrient absorption. The sprouting process enhances protein quality and boosts fiber content, contributing to better blood sugar regulation and gut health. Regular grains typically have a denser starch profile and lower bioavailability of minerals such as iron and zinc, making sprouted grains a nutritionally superior option.
Digestibility and Health Benefits
Sprouted grains enhance digestibility by breaking down starches and proteins during germination, making nutrients like B vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants more bioavailable compared to regular grains. These grains often contain higher levels of essential amino acids and enzymes that support gut health and reduce anti-nutrients like phytic acid, improving mineral absorption. Consuming sprouted grains is linked to better blood sugar regulation and may reduce inflammation, providing significant health benefits over conventional whole grains.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Sprouted grains have a lower glycemic index compared to regular grains, leading to a slower and more stable increase in blood sugar levels. The sprouting process increases fiber content and reduces starch, which helps improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control. Consuming sprouted grains can be beneficial for managing blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
Antinutrients: Sprouted vs. Regular Grains
Sprouted grains exhibit significantly lower levels of antinutrients such as phytic acid and tannins compared to regular grains, enhancing mineral bioavailability and digestive efficiency. Enzymatic activity during sprouting breaks down compounds that inhibit nutrient absorption, making sprouted grains a superior choice for nutrient uptake. Regular grains retain higher antinutrient concentrations, which can impair the body's ability to absorb essential minerals like iron, zinc, and calcium.
Flavor and Texture Differences
Sprouted grains have a nuttier flavor and a slightly sweeter taste compared to regular grains, which tend to have a more neutral or bland profile. The texture of sprouted grains is softer and chewier due to the germination process breaking down starches, while regular grains are often denser and firmer. This difference in flavor and texture makes sprouted grains a preferred choice for baked goods and salads seeking enhanced complexity and moisture.
Culinary Uses and Cooking Tips
Sprouted grains offer a nuttier flavor and softer texture compared to regular grains, making them ideal for baking bread, muffins, and pancakes with enhanced moisture and digestibility. When cooking sprouted grains, reduce soaking and cooking times by 20-30% to preserve their nutrients and tender structure. Regular grains require longer soaking and boiling, but they provide a denser texture perfect for pilafs, risottos, and hearty soups.
Storage and Shelf Life
Sprouted grains have higher moisture content than regular grains, which requires more careful storage to prevent mold and spoilage. They should be kept in airtight containers and stored in cool, dry environments or refrigerated to extend shelf life. Regular grains, with lower moisture levels, have a longer shelf life and can be stored at room temperature for up to a year when kept dry and sealed.
Which Grain Type is Right for You?
Sprouted grains offer enhanced nutrient absorption and easier digestibility compared to regular grains, making them ideal for individuals with sensitive digestion or seeking higher protein and vitamin content. Regular grains retain more fiber and a familiar texture, which benefits those prioritizing whole grain intake for sustained energy and heart health. Choosing between sprouted and regular grains depends on personal health goals, digestive tolerance, and nutritional preferences.
sprouted grains vs regular grains Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com