Vertical farming maximizes space by stacking crops vertically in controlled environments, enabling year-round production and reducing land use. Hydroponic farming grows plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, enhancing growth rates and minimizing soil-related issues. Both methods increase sustainability by conserving water and reducing the need for pesticides compared to traditional agriculture.
Table of Comparison
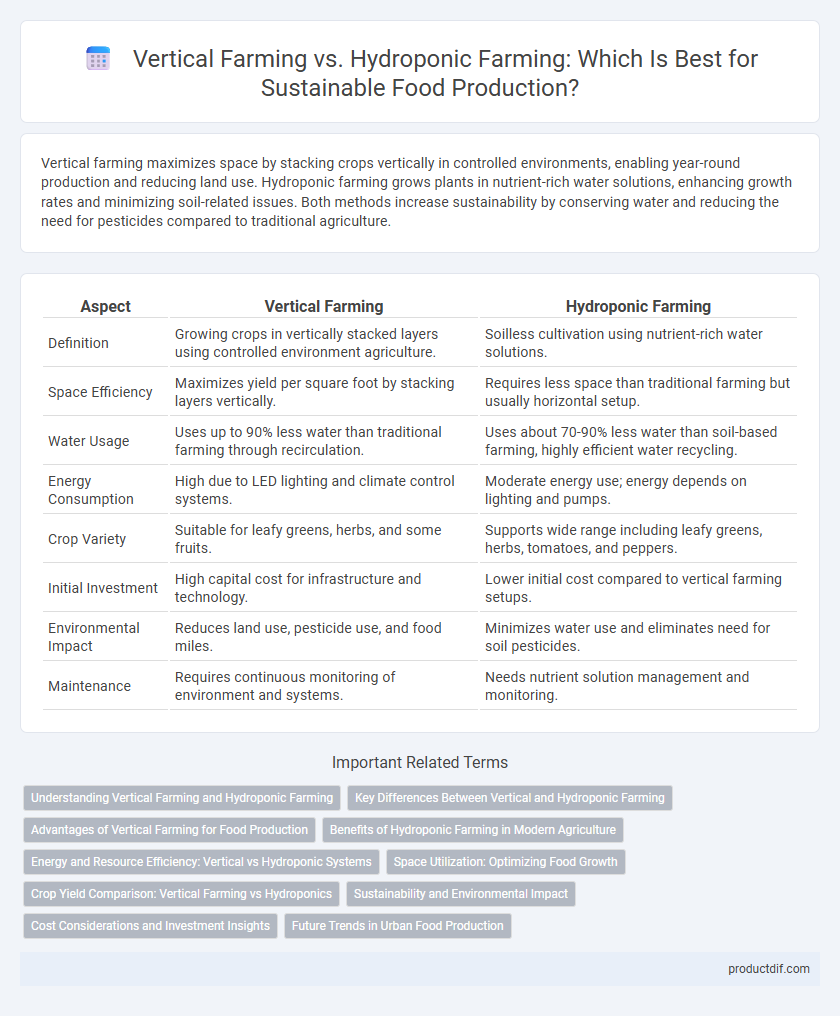
| Aspect | Vertical Farming | Hydroponic Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing crops in vertically stacked layers using controlled environment agriculture. | Soilless cultivation using nutrient-rich water solutions. |
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes yield per square foot by stacking layers vertically. | Requires less space than traditional farming but usually horizontal setup. |
| Water Usage | Uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming through recirculation. | Uses about 70-90% less water than soil-based farming, highly efficient water recycling. |
| Energy Consumption | High due to LED lighting and climate control systems. | Moderate energy use; energy depends on lighting and pumps. |
| Crop Variety | Suitable for leafy greens, herbs, and some fruits. | Supports wide range including leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, and peppers. |
| Initial Investment | High capital cost for infrastructure and technology. | Lower initial cost compared to vertical farming setups. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces land use, pesticide use, and food miles. | Minimizes water use and eliminates need for soil pesticides. |
| Maintenance | Requires continuous monitoring of environment and systems. | Needs nutrient solution management and monitoring. |
Understanding Vertical Farming and Hydroponic Farming
Vertical farming maximizes crop production by stacking layers of plants in controlled indoor environments, using artificial lighting and climate control to optimize growth conditions year-round. Hydroponic farming, a soil-less method, involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, enhancing resource efficiency and minimizing soil-related issues. Both methods reduce water usage and land dependency, offering sustainable solutions to meet increasing food demand.
Key Differences Between Vertical and Hydroponic Farming
Vertical farming utilizes stacked layers to grow crops in controlled indoor environments, maximizing space efficiency and allowing year-round production. Hydroponic farming cultivates plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, emphasizing precise control over nutrient delivery and water usage. Key differences include spatial arrangement--vertical farming prioritizes vertical space optimization, while hydroponics focuses on soil-less cultivation methods, often integrated within vertical systems.
Advantages of Vertical Farming for Food Production
Vertical farming maximizes space efficiency by stacking multiple layers of crops, allowing for higher yields per square foot compared to hydroponic farming. It offers enhanced control over environmental conditions, reducing pest exposure and minimizing water usage through closed-loop systems. This method supports urban agriculture by enabling year-round production in controlled indoor settings, leading to fresher produce with reduced transportation emissions.
Benefits of Hydroponic Farming in Modern Agriculture
Hydroponic farming offers significant water efficiency by using up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil farming and vertical farming techniques. It enables precise nutrient control, promoting faster plant growth and higher yields, making it ideal for urban agriculture and space-limited environments. The controlled environment reduces pest and disease risks, lowering the need for pesticides and contributing to sustainable food production.
Energy and Resource Efficiency: Vertical vs Hydroponic Systems
Vertical farming maximizes space by stacking crops vertically, significantly reducing land use and enabling controlled environment agriculture with efficient LED lighting systems that lower energy consumption. Hydroponic farming utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, minimizing water usage by recycling nutrient solutions and reducing wastage, offering high water-use efficiency. Both systems promote sustainable food production, yet vertical farming generally requires more energy for lighting and climate control, while hydroponics excels in water and nutrient recycling efficiency.
Space Utilization: Optimizing Food Growth
Vertical farming maximizes space by stacking multiple layers of crops in controlled environments, enabling year-round production and higher yields per square foot. Hydroponic farming uses nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, allowing dense plant arrangements and efficient vertical stacking when combined with vertical systems. Both methods significantly enhance space utilization, supporting sustainable urban agriculture and increasing food production efficiency.
Crop Yield Comparison: Vertical Farming vs Hydroponics
Vertical farming leverages multi-layered indoor environments to maximize crop yield per square foot, achieving up to 10 times higher productivity compared to traditional methods. Hydroponic farming, utilizing nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, enhances growth rates and can increase yields by approximately 25-50% over conventional soil farming. Combining vertical farming structures with hydroponic systems further intensifies output, optimizing space and resource efficiency for superior crop production.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Vertical farming reduces land use by growing crops vertically in controlled environments, significantly lowering water consumption and minimizing pesticide use compared to traditional agriculture. Hydroponic farming, a soil-less method using nutrient-rich water solutions, optimizes resource efficiency and reduces runoff pollution through precise nutrient management. Both techniques enhance sustainability by decreasing carbon footprints, conserving water, and enabling local food production, which reduces transportation emissions.
Cost Considerations and Investment Insights
Vertical farming demands higher initial capital due to infrastructure, lighting, and climate control systems, whereas hydroponic farming offers a more scalable investment with lower startup costs focused on nutrient delivery and water management systems. Operational expenses in vertical farming tend to be higher because of energy consumption for artificial lighting, while hydroponics benefits from reduced water use and faster crop cycles that improve return on investment. Investors should weigh long-term profitability of vertical farming's year-round production against hydroponics' flexibility and ease of integration with existing agricultural facilities.
Future Trends in Urban Food Production
Vertical farming and hydroponic farming are revolutionizing urban food production by maximizing space efficiency and resource conservation in densely populated areas. Innovations in LED lighting technology and nutrient delivery systems are enhancing crop yields and reducing energy consumption, making these methods more sustainable and economically viable. Integration of AI-driven monitoring and automation is further optimizing growth conditions, positioning vertical and hydroponic farming as key components in the future of resilient urban agriculture.
Vertical farming vs Hydroponic farming Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com