Hydroponics offers precise control over nutrient delivery and water usage, resulting in faster plant growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil-grown methods. Soil-grown crops rely on natural microbial activity and soil quality, which can influence flavor complexity and nutrient profiles. Both methods have unique advantages, with hydroponics excelling in efficiency and soil cultivation enhancing plant resilience and taste.
Table of Comparison
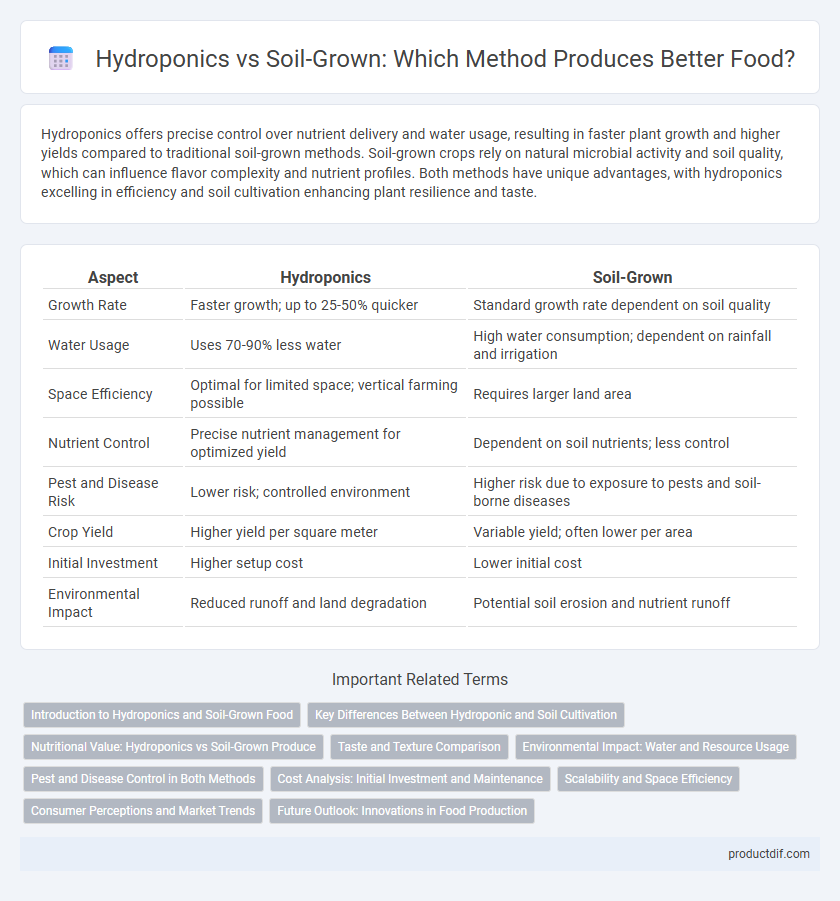
| Aspect | Hydroponics | Soil-Grown |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Faster growth; up to 25-50% quicker | Standard growth rate dependent on soil quality |
| Water Usage | Uses 70-90% less water | High water consumption; dependent on rainfall and irrigation |
| Space Efficiency | Optimal for limited space; vertical farming possible | Requires larger land area |
| Nutrient Control | Precise nutrient management for optimized yield | Dependent on soil nutrients; less control |
| Pest and Disease Risk | Lower risk; controlled environment | Higher risk due to exposure to pests and soil-borne diseases |
| Crop Yield | Higher yield per square meter | Variable yield; often lower per area |
| Initial Investment | Higher setup cost | Lower initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced runoff and land degradation | Potential soil erosion and nutrient runoff |
Introduction to Hydroponics and Soil-Grown Food
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants using nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, enabling precise control over nutrient delivery and reducing water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional farming. Soil-grown food relies on natural soil ecosystems, where plants absorb nutrients from decomposed organic matter and microorganisms, supporting biodiversity and soil health. Both methods impact crop yield and quality differently, with hydroponics offering faster growth rates and soil-grown crops often praised for their complex flavor profiles.
Key Differences Between Hydroponic and Soil Cultivation
Hydroponic cultivation uses nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, enabling precise control over nutrient delivery and faster growth cycles compared to traditional soil-grown methods. Soil cultivation relies on natural soil ecosystems, which influence plant health through organic matter and microbial activity but can lead to variability in nutrient availability and longer growth times. Hydroponic systems often yield higher crop density and reduced water usage, while soil-grown crops benefit from natural biodiversity and lower initial setup costs.
Nutritional Value: Hydroponics vs Soil-Grown Produce
Hydroponically grown produce often exhibits higher concentrations of essential vitamins and minerals due to controlled nutrient delivery, optimizing growth conditions. Soil-grown crops benefit from natural microbial interactions that can enhance the bioavailability of certain nutrients but may also vary due to soil quality and climate factors. Comparative studies reveal hydroponics can achieve consistent nutrient profiles, while soil-grown produce offers greater diversity in phytochemicals influenced by soil ecology.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Hydroponically grown produce often exhibits a cleaner, more consistent texture due to controlled nutrient delivery and water availability, which can enhance crispness in leafy greens and tenderness in fruits. Soil-grown crops develop more complex flavor profiles influenced by natural soil microbiomes and organic matter, often resulting in richer, earthier tastes. While hydroponic methods optimize growth conditions for uniformity and freshness, soil cultivation promotes diverse sensory qualities that many consumers associate with traditional taste and texture satisfaction.
Environmental Impact: Water and Resource Usage
Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water compared to soil-grown agriculture by recycling nutrient solutions and minimizing evaporation. Soil-grown farming relies heavily on irrigation, often leading to significant water runoff and soil degradation. Designing controlled environments in hydroponics reduces the need for pesticides and fertilizers, thus lowering the overall environmental footprint.
Pest and Disease Control in Both Methods
Hydroponics systems significantly reduce pest infestations due to the absence of soil, which often harbors common pests and soil-borne diseases. Soil-grown crops face higher risks of fungal infections, nematodes, and insect damage, necessitating regular pesticide applications. Effective disease control in hydroponics relies on maintaining sterile water and nutrient solutions, while soil-grown techniques depend heavily on crop rotation and soil treatment methods.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Hydroponic systems require a higher initial investment due to costs for equipment like grow trays, pumps, and nutrient solutions, while soil-grown methods typically have lower startup expenses limited to seeds, soil, and basic tools. Maintenance costs for hydroponics can be more consistent and controlled, involving periodic nutrient replenishment and system monitoring, whereas soil-grown crops may incur variable expenses related to pest control, soil amendments, and water usage. Over time, hydroponics can offer cost savings through increased yield efficiency and reduced water consumption compared to traditional soil cultivation.
Scalability and Space Efficiency
Hydroponics systems enable vertical farming and higher crop density, maximizing space utilization in urban environments while supporting year-round production independent of soil quality. Soil-grown agriculture requires larger land areas and is limited by soil fertility and seasonal cycles, reducing scalability in constrained spaces. Controlled hydroponic environments enhance scalability and resource efficiency, making them ideal for meeting increasing food demand in space-limited settings.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Consumer perceptions of hydroponically grown produce emphasize freshness, sustainability, and pesticide-free qualities, driving increased market demand. Soil-grown crops continue to appeal due to traditional flavor profiles and perceived naturalness, maintaining strong market presence. Market trends indicate a growing acceptance of hydroponics in urban and health-conscious demographics, with sales expanding in specialty grocery and organic product sectors.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Food Production
Hydroponics offers precise nutrient delivery and water efficiency, positioning it as a leading method for future urban and space farming innovations. Advances in sensor technology and AI integration are enhancing crop yields and reducing resource consumption compared to traditional soil-grown agriculture. These innovations are driving sustainable food production, addressing challenges of climate change and land scarcity.
Hydroponics vs Soil-grown Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com