Vegan cheese offers a plant-based alternative to dairy cheese, made from ingredients like nuts, soy, and coconut oil, making it suitable for lactose-intolerant individuals and vegans. Unlike traditional dairy cheese, vegan cheese is free from cholesterol and often contains fewer saturated fats, promoting heart health. While taste and texture vary, advancements in food technology have significantly improved the flavor profiles and meltability of vegan cheese compared to earlier versions.
Table of Comparison
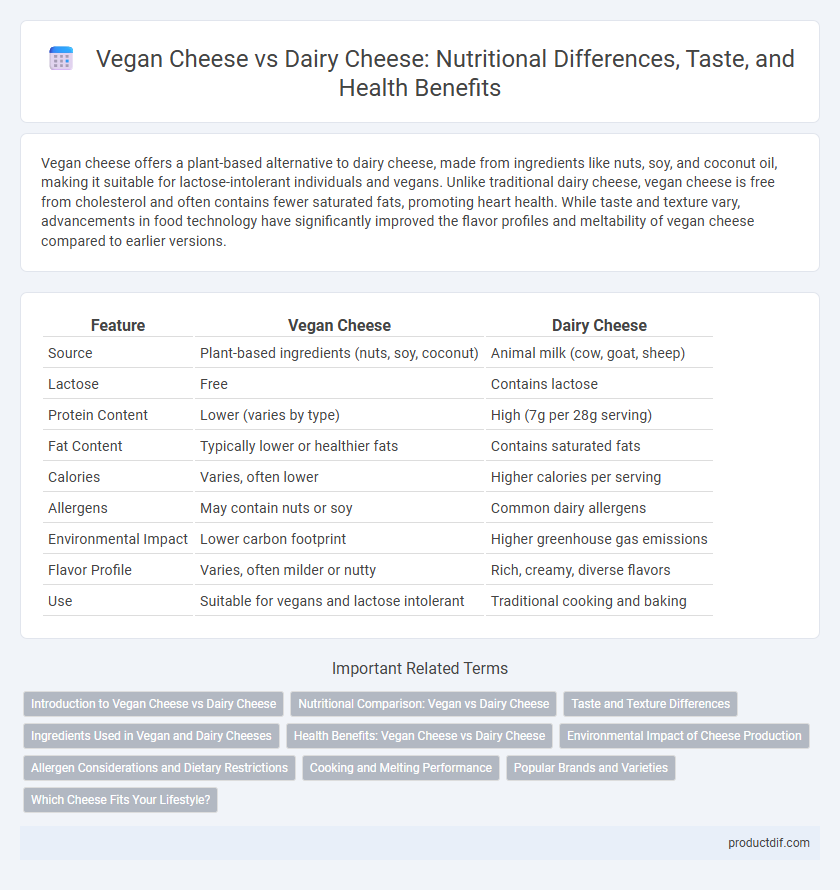
| Feature | Vegan Cheese | Dairy Cheese |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-based ingredients (nuts, soy, coconut) | Animal milk (cow, goat, sheep) |
| Lactose | Free | Contains lactose |
| Protein Content | Lower (varies by type) | High (7g per 28g serving) |
| Fat Content | Typically lower or healthier fats | Contains saturated fats |
| Calories | Varies, often lower | Higher calories per serving |
| Allergens | May contain nuts or soy | Common dairy allergens |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint | Higher greenhouse gas emissions |
| Flavor Profile | Varies, often milder or nutty | Rich, creamy, diverse flavors |
| Use | Suitable for vegans and lactose intolerant | Traditional cooking and baking |
Introduction to Vegan Cheese vs Dairy Cheese
Vegan cheese is crafted from plant-based ingredients such as nuts, soy, or coconut oil, offering a lactose-free alternative to traditional dairy cheese made from cow, goat, or sheep milk. This shift addresses dietary restrictions, lactose intolerance, and environmental concerns linked to dairy farming. Nutritional profiles vary widely, with vegan cheeses often containing less saturated fat and cholesterol but differing significantly in protein content compared to dairy cheese.
Nutritional Comparison: Vegan vs Dairy Cheese
Vegan cheese typically contains lower saturated fat and cholesterol than dairy cheese, making it a heart-healthier option. While dairy cheese is naturally rich in calcium and protein, vegan alternatives are often fortified with these nutrients to match their nutritional profile. Some vegan cheeses provide added fiber and antioxidants from plant-based ingredients, offering unique health benefits compared to traditional dairy cheese.
Taste and Texture Differences
Vegan cheese often features a creamy or nutty flavor profile derived from ingredients like nuts, soy, or coconut oil, differing significantly from the rich, umami taste of traditional dairy cheese made from animal milk. Texture in vegan cheese can range from soft and spreadable to firm and sliceable, but it generally lacks the elasticity and meltability of dairy cheese, which owes its smooth stretchiness to casein proteins. Many consumers note that while dairy cheese offers a complex, savory experience with a satisfying mouthfeel, vegan alternatives are continually improving in mimicking these sensory characteristics, appealing to plant-based and lactose-intolerant individuals.
Ingredients Used in Vegan and Dairy Cheeses
Vegan cheese primarily uses plant-based ingredients such as nuts, soy, coconut oil, and nutritional yeast to mimic the texture and flavor of traditional cheese, avoiding animal derivatives entirely. Dairy cheese is made from animal milk, typically cow, goat, or sheep, and relies on natural fermentation and enzymes like rennet to develop its distinct taste and consistency. The absence of lactose and cholesterol in vegan cheese offers a dairy-free alternative, while dairy cheese provides a complex nutrient profile including calcium, protein, and vitamins derived from milk.
Health Benefits: Vegan Cheese vs Dairy Cheese
Vegan cheese offers health benefits such as lower cholesterol and reduced saturated fat compared to dairy cheese, making it heart-friendly. Rich in plant-based ingredients like nuts and seeds, vegan cheese provides antioxidants and essential nutrients without lactose, benefiting those with dairy intolerance. While dairy cheese contains calcium and protein, its saturated fat content can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, highlighting vegan cheese as a healthier alternative.
Environmental Impact of Cheese Production
Vegan cheese production typically generates significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to dairy cheese, as it avoids methane release from cows. Dairy cheese requires extensive water usage and land resources for livestock farming, contributing to deforestation and soil degradation. Plant-based cheese alternatives reduce environmental strain by utilizing crops like nuts and soy, which demand less energy and produce fewer pollutants during cultivation.
Allergen Considerations and Dietary Restrictions
Vegan cheese eliminates common allergens such as lactose and casein found in dairy cheese, making it suitable for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Dairy cheese contains milk proteins that can trigger allergic reactions, limiting its consumption among individuals with specific dietary restrictions. Choosing vegan cheese supports diverse dietary needs, including vegan, lactose-intolerant, and allergy-sensitive consumers.
Cooking and Melting Performance
Vegan cheese often contains plant-based oils and starches that influence its melting behavior, resulting in a texture that is sometimes softer and less elastic compared to dairy cheese. Dairy cheese, rich in casein proteins and fats, typically melts smoothly and stretches well, making it ideal for cooking applications like pizza and grilled cheese. Chefs aiming for optimal meltability in vegan options often select brands with coconut oil or tapioca starch, which improve flexibility and melt quality under heat.
Popular Brands and Varieties
Popular vegan cheese brands such as Daiya, Miyoko's Creamery, and Violife offer a variety of plant-based options including cashew-based, almond-based, and coconut oil blends that mimic the flavors and textures of traditional cheese. In contrast, dairy cheese brands like Tillamook, Cabot, and Kraft provide a wide range of varieties including cheddar, mozzarella, and gouda made from cow's milk. Consumer demand drives innovation in both sectors, with vegan cheeses gaining traction for their allergy-friendly, lactose-free, and sustainable ingredients while dairy cheese maintains popularity for its rich taste and established varieties.
Which Cheese Fits Your Lifestyle?
Vegan cheese offers a plant-based alternative free from lactose and cholesterol, making it ideal for those with dietary restrictions or ethical preferences. Dairy cheese provides essential nutrients like calcium and protein, supporting bone health but can trigger lactose intolerance in sensitive individuals. Choosing between vegan and dairy cheese depends on your lifestyle goals, dietary needs, and environmental values.
Vegan Cheese vs Dairy Cheese Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com