Artisanal food emphasizes craftsmanship, using high-quality, often locally sourced ingredients to create unique flavors and textures. Mass-produced food prioritizes efficiency and consistency, utilizing standardized processes to deliver large quantities at lower costs. Consumers seeking authentic taste and traditional methods often prefer artisanal options over mass-produced alternatives.
Table of Comparison
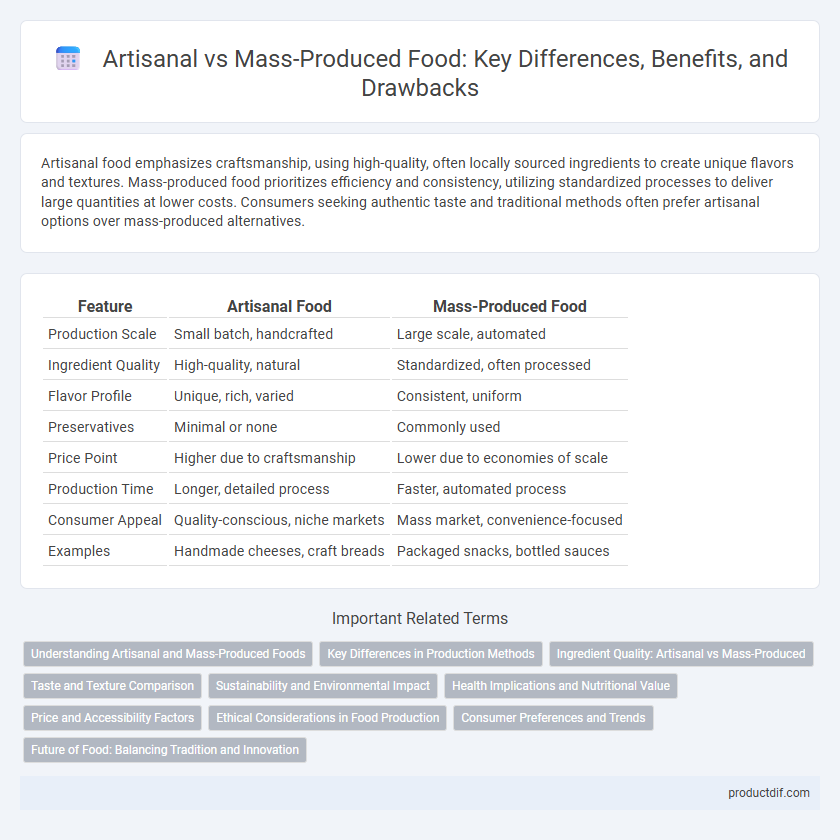
| Feature | Artisanal Food | Mass-Produced Food |
|---|---|---|
| Production Scale | Small batch, handcrafted | Large scale, automated |
| Ingredient Quality | High-quality, natural | Standardized, often processed |
| Flavor Profile | Unique, rich, varied | Consistent, uniform |
| Preservatives | Minimal or none | Commonly used |
| Price Point | Higher due to craftsmanship | Lower due to economies of scale |
| Production Time | Longer, detailed process | Faster, automated process |
| Consumer Appeal | Quality-conscious, niche markets | Mass market, convenience-focused |
| Examples | Handmade cheeses, craft breads | Packaged snacks, bottled sauces |
Understanding Artisanal and Mass-Produced Foods
Artisanal foods are crafted in small batches using traditional methods that emphasize quality, unique flavors, and natural ingredients, often sourced locally. Mass-produced foods are manufactured on a large scale with standardized processes to ensure consistency, lower costs, and widespread availability. The distinction lies in the production scale, ingredient quality, and sensory experience, where artisanal foods offer distinctive taste profiles compared to the uniformity of mass-produced products.
Key Differences in Production Methods
Artisanal food products are crafted using traditional, hands-on techniques that emphasize quality, uniqueness, and small-batch production, often incorporating locally sourced ingredients. Mass-produced food relies on automated, large-scale manufacturing processes designed for efficiency, consistency, and lower costs, frequently utilizing standardized ingredients. The key differences lie in the level of human involvement, production scale, and ingredient sourcing, impacting flavor complexity and product authenticity.
Ingredient Quality: Artisanal vs Mass-Produced
Artisanal foods are crafted using high-quality, often locally sourced ingredients that emphasize freshness and unique flavors, while mass-produced foods typically rely on standardized, cost-effective components to ensure consistency and scalability. The ingredient quality in artisanal products significantly enhances nutritional value and taste complexity, contrasting with the often processed or preserved elements found in mass-produced items. Consumers seeking premium taste and health benefits tend to prefer artisanal options due to their superior ingredient integrity and minimal additives.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Artisanal foods often boast superior taste and texture due to handcrafted methods and high-quality, natural ingredients, resulting in richer flavors and more complex textures. Mass-produced items typically have a more uniform taste and texture, achieved through standardized processes and preservatives aimed at consistency and shelf life rather than depth of flavor. Consumers seeking unique sensory experiences tend to prefer artisanal products for their authenticity and nuanced palate profiles.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Artisanal foods often utilize locally sourced, organic ingredients, reducing carbon footprints and supporting sustainable agriculture compared to mass-produced items that rely on large-scale industrial farming with higher energy consumption and waste. The smaller batch production of artisanal products minimizes packaging and food waste, contributing to lower environmental impact. Mass-produced food systems commonly involve extensive transportation and synthetic inputs, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion.
Health Implications and Nutritional Value
Artisanal foods often contain higher nutrient density due to minimal processing and the use of natural ingredients, preserving vitamins, minerals, and beneficial enzymes. Mass-produced foods commonly include additives, preservatives, and higher levels of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, which can negatively impact metabolic health and increase the risk of chronic diseases. Choosing artisanal products supports better digestion and reduced exposure to artificial chemicals, promoting overall wellbeing.
Price and Accessibility Factors
Artisanal food products often command higher prices due to handcrafted techniques and premium ingredients, reflecting limited production scales. Mass-produced foods benefit from economies of scale, enabling lower prices and wider accessibility across diverse markets. Consumer choice frequently balances cost considerations against the desire for unique flavors and quality inherent in artisanal offerings.
Ethical Considerations in Food Production
Artisanal food production prioritizes ethical considerations by emphasizing sustainable sourcing, fair labor practices, and reduced environmental impact compared to mass-produced food. Small-scale artisans often use organic ingredients and traditional methods that support biodiversity and local economies. Mass-produced food, while efficient, frequently raises concerns related to factory farming, excessive waste, and exploitative labor conditions.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor artisanal foods for their perceived higher quality, unique flavors, and authentic craftsmanship compared to mass-produced products. Trends show a growing demand for locally sourced ingredients and sustainable practices associated with artisanal brands, reflecting a shift toward health-conscious and ethical consumption. Mass-produced foods maintain appeal due to affordability and convenience, yet market analysis reveals a rising willingness among consumers to pay premium prices for artisanal goods.
Future of Food: Balancing Tradition and Innovation
Artisanal food preserves traditional craftsmanship, offering unique flavors and sustainable practices that appeal to niche markets. Mass-produced food leverages advanced technology and economies of scale to meet global demand efficiently, driving affordability and accessibility. The future of food lies in integrating artisanal quality with innovative production methods, fostering a sustainable food system that honors heritage while embracing modern efficiency.
Artisanal vs Mass-Produced Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com