Biodynamic farming emphasizes holistic practices that integrate spiritual and ecological principles, enhancing soil fertility and plant health through natural composts and lunar cycles. Sustainable farming prioritizes resource efficiency and long-term ecosystem balance by reducing chemical inputs and preserving biodiversity. Both approaches aim to create resilient food systems but differ in their methodologies and philosophical foundations.
Table of Comparison
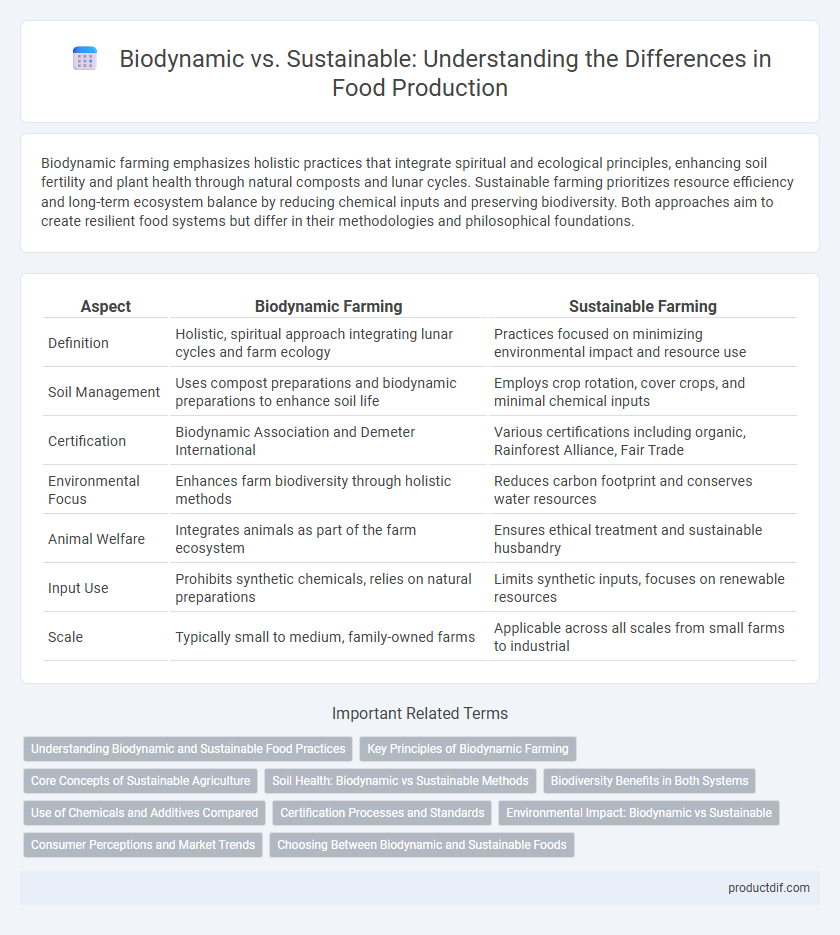
| Aspect | Biodynamic Farming | Sustainable Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Holistic, spiritual approach integrating lunar cycles and farm ecology | Practices focused on minimizing environmental impact and resource use |
| Soil Management | Uses compost preparations and biodynamic preparations to enhance soil life | Employs crop rotation, cover crops, and minimal chemical inputs |
| Certification | Biodynamic Association and Demeter International | Various certifications including organic, Rainforest Alliance, Fair Trade |
| Environmental Focus | Enhances farm biodiversity through holistic methods | Reduces carbon footprint and conserves water resources |
| Animal Welfare | Integrates animals as part of the farm ecosystem | Ensures ethical treatment and sustainable husbandry |
| Input Use | Prohibits synthetic chemicals, relies on natural preparations | Limits synthetic inputs, focuses on renewable resources |
| Scale | Typically small to medium, family-owned farms | Applicable across all scales from small farms to industrial |
Understanding Biodynamic and Sustainable Food Practices
Biodynamic food practices integrate organic farming methods with holistic approaches, emphasizing soil health, biodiversity, and cosmic rhythms to enhance crop vitality and ecosystem balance. Sustainable food practices prioritize minimizing environmental impact through resource conservation, waste reduction, and fair labor standards, aiming to support long-term agricultural resilience. Both methods contribute to eco-friendly food production but differ in philosophical foundations and specific agricultural techniques.
Key Principles of Biodynamic Farming
Biodynamic farming emphasizes holistic soil health through crop rotation, composting, and planting calendars aligned with lunar cycles to enhance vitality. It integrates ecological diversity by incorporating livestock, cover crops, and wildlife habitats to create a self-sustaining ecosystem. This approach extends beyond sustainable practices by treating the farm as a living organism, fostering interconnectedness between soil, plants, animals, and cosmic rhythms.
Core Concepts of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture prioritizes soil health, water conservation, and biodiversity to maintain ecosystem balance and ensure long-term productivity. It integrates techniques like crop rotation, organic fertilization, and reduced chemical usage to minimize environmental impact while supporting economic viability. Core concepts emphasize resource efficiency, ecological resilience, and social responsibility to create a sustainable food system.
Soil Health: Biodynamic vs Sustainable Methods
Biodynamic farming enhances soil health through holistic practices like composting with specific herbal preparations and crop rotations aligned with lunar phases, promoting microbial biodiversity and nutrient-rich soil. Sustainable methods focus on minimizing chemical inputs and maintaining soil organic matter by using cover crops, reduced tillage, and integrated pest management to prevent erosion and degradation. Both approaches prioritize long-term soil fertility, but biodynamic farming integrates spiritual and cosmic principles to boost soil vitality beyond conventional sustainability techniques.
Biodiversity Benefits in Both Systems
Biodynamic and sustainable farming methods both enhance biodiversity by promoting diverse plant and animal species within agricultural ecosystems. Biodynamic practices incorporate holistic techniques such as crop rotation, composting, and the use of natural preparations to enrich soil health and foster microbial diversity. Sustainable agriculture prioritizes habitat conservation and minimizes chemical inputs, supporting pollinators and beneficial insects critical for ecosystem resilience.
Use of Chemicals and Additives Compared
Biodynamic farming strictly prohibits synthetic chemicals and additives, relying instead on natural preparations and composts to enhance soil health and plant growth. Sustainable agriculture permits limited use of approved synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, aiming to balance environmental impact with crop productivity. The key distinction lies in biodynamics' holistic, chemical-free approach versus sustainable farming's regulated, minimal chemical use for ecological balance.
Certification Processes and Standards
Biodynamic certification requires adherence to strict guidelines established by the Demeter Association, emphasizing holistic farm management, cosmic rhythms, and closed-loop fertility practices. Sustainable certification standards vary widely but generally focus on minimizing environmental impact, conserving resources, and promoting social responsibility, often verified by organizations like Rainforest Alliance or USDA Organic. Both certification processes involve rigorous audits and compliance measures, yet biodynamic certification integrates spiritual and ecological principles beyond conventional sustainable practices.
Environmental Impact: Biodynamic vs Sustainable
Biodynamic agriculture enhances soil fertility through holistic methods integrating cosmic rhythms and organic compost, resulting in improved biodiversity and reduced chemical inputs. Sustainable farming prioritizes resource efficiency and long-term ecosystem health by minimizing water use, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and maintaining soil quality. Both approaches aim to mitigate environmental impact, but biodynamic practices emphasize ecological harmony and regenerative cycles beyond conventional sustainability standards.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Consumer perceptions increasingly differentiate biodynamic food for its holistic approach, incorporating lunar cycles and soil health, which appeals to niche markets valuing purity and ecological harmony. Sustainable food practices gain broader market traction by emphasizing resource efficiency, carbon footprint reduction, and social equity, resonating with environmentally conscious and mainstream consumers alike. Market trends reveal rising demand for transparent labeling, driving both biodynamic and sustainable products to innovate in certifications and storytelling to capture health-focused and eco-aware demographics.
Choosing Between Biodynamic and Sustainable Foods
Choosing between biodynamic and sustainable foods involves understanding their distinct agricultural practices and environmental impacts. Biodynamic farming employs holistic, ecological, and ethical approaches integrating lunar cycles and spiritual principles, enhancing soil fertility and ecosystem health, while sustainable food prioritizes reducing environmental footprint through resource efficiency and minimal pollution. Consumers seeking organic integrity with a strong emphasis on ecological balance may prefer biodynamic options, whereas those focused on resource conservation and broader environmental sustainability might choose sustainable foods.
biodynamic vs sustainable Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com