Fermented foods contain beneficial probiotics that enhance gut health and improve digestion by introducing live microorganisms. Pasteurized foods undergo heat treatment to eliminate harmful bacteria, extending shelf life but reducing some nutritional value and beneficial microbes. Choosing fermented foods supports a balanced microbiome, whereas pasteurized foods prioritize safety and longer preservation.
Table of Comparison
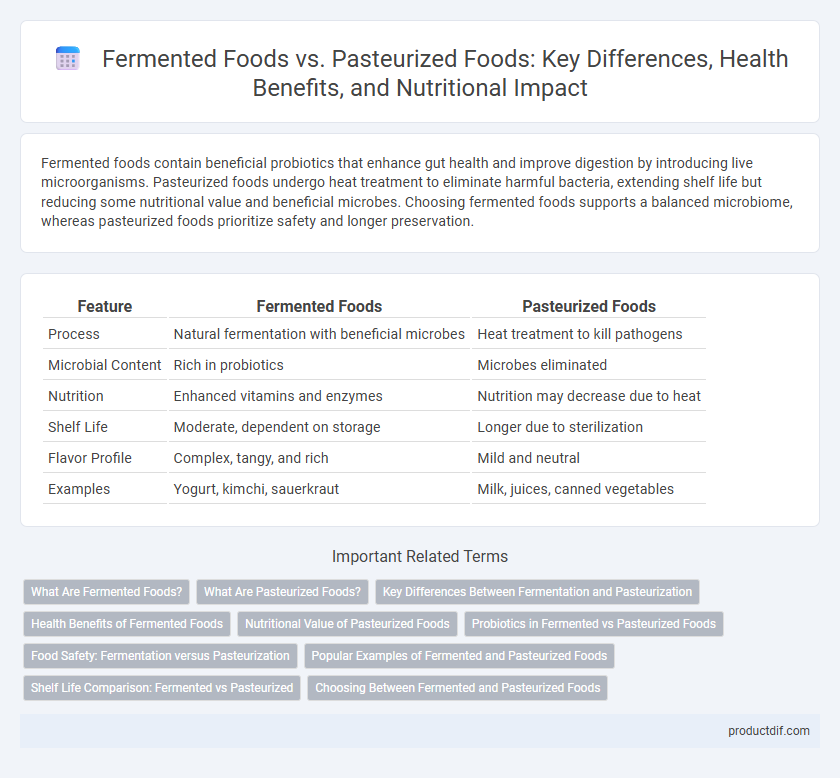
| Feature | Fermented Foods | Pasteurized Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Natural fermentation with beneficial microbes | Heat treatment to kill pathogens |
| Microbial Content | Rich in probiotics | Microbes eliminated |
| Nutrition | Enhanced vitamins and enzymes | Nutrition may decrease due to heat |
| Shelf Life | Moderate, dependent on storage | Longer due to sterilization |
| Flavor Profile | Complex, tangy, and rich | Mild and neutral |
| Examples | Yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut | Milk, juices, canned vegetables |
What Are Fermented Foods?
Fermented foods are products created through the natural process of fermentation, where beneficial bacteria and yeasts break down sugars and starches into acids, gases, or alcohol, enhancing flavor and preservation. Common examples include yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha, all rich in probiotics that support gut health. Unlike pasteurized foods, which undergo heat treatment to kill microbes, fermented foods maintain live beneficial cultures essential for digestive wellness and immune function.
What Are Pasteurized Foods?
Pasteurized foods undergo a heat treatment process designed to kill harmful bacteria and extend shelf life without significantly altering flavor or nutritional value. Common examples include milk, juice, and some dairy products, which are heated to specific temperatures for set periods to ensure safety. This method reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses but may also decrease certain beneficial microbes found in naturally fermented foods.
Key Differences Between Fermentation and Pasteurization
Fermented foods undergo a natural microbial process where beneficial bacteria convert sugars into acids or alcohol, enhancing flavor and promoting gut health, while pasteurized foods are heat-treated to kill harmful pathogens and extend shelf life without altering the food's basic composition. Fermentation preserves probiotics and enzymes critical for digestion, whereas pasteurization eliminates both harmful and beneficial microorganisms to ensure safety. The key difference lies in fermentation's role in improving nutritional value and digestibility versus pasteurization's focus on food safety and preservation.
Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut, contain beneficial probiotics that enhance gut health by promoting a balanced microbiome and improving digestion. These live microorganisms can boost immune function, reduce inflammation, and aid in nutrient absorption, contributing to overall well-being. In contrast, pasteurized foods undergo heat treatment that eliminates harmful bacteria but also destroys many beneficial microbes, reducing their potential health benefits.
Nutritional Value of Pasteurized Foods
Pasteurized foods retain essential nutrients such as vitamins A, C, and certain B vitamins, although the heat treatment may reduce some heat-sensitive compounds. This process effectively eliminates harmful bacteria, enhancing food safety while preserving the nutritional profile of dairy products, juices, and canned vegetables. Pasteurization maintains bioavailability of proteins and minerals, supporting overall dietary health despite slight nutrient losses.
Probiotics in Fermented vs Pasteurized Foods
Fermented foods contain live probiotics like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which enhance gut microbiota and improve digestion, immunity, and mental health. Pasteurized foods undergo heat treatment that eliminates most bacteria, including beneficial probiotics, reducing their potential to support gut health. Incorporating fermented foods such as yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut provides a natural source of active probiotics absent in pasteurized alternatives.
Food Safety: Fermentation versus Pasteurization
Fermented foods enhance food safety through natural microbial activity that inhibits pathogenic bacteria by producing acids and antimicrobial compounds. Pasteurization uses controlled heat to kill harmful microorganisms, offering immediate and reliable elimination of pathogens. While fermentation promotes probiotic benefits and flavor complexity, pasteurization ensures consistent safety by reducing microbial risks in a shorter time frame.
Popular Examples of Fermented and Pasteurized Foods
Kimchi, sauerkraut, and yogurt are popular examples of fermented foods rich in probiotics that support gut health. Pasteurized foods commonly include milk, fruit juices, and canned vegetables, where heat treatment ensures safety by eliminating harmful microorganisms. Fermented products enhance flavor and nutrition through natural microbial activity, whereas pasteurized foods prioritize preservation and pathogen reduction.
Shelf Life Comparison: Fermented vs Pasteurized
Fermented foods typically have an extended shelf life due to the natural production of lactic acid and beneficial microbes that inhibit spoilage organisms. Pasteurized foods rely on heat treatment to kill pathogens but often have a shorter shelf life since they lack live cultures that continuously protect against spoilage. Shelf stability in fermented products can range from weeks to months, whereas pasteurized foods usually remain safe for only days to weeks when refrigerated.
Choosing Between Fermented and Pasteurized Foods
Choosing between fermented and pasteurized foods depends on health benefits and flavor preferences. Fermented foods, rich in probiotics and enzymes, boost gut health and aid digestion, while pasteurized foods ensure safety by eliminating harmful pathogens through heat treatment but may lose some nutrients. Balancing the inclusion of both types supports immune function and provides diverse nutritional advantages in the diet.
Fermented Foods vs Pasteurized Foods Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com