Artisanal food processing preserves traditional methods that prioritize quality, unique flavors, and natural ingredients, resulting in distinctive products with rich textures and authentic taste profiles. Industrial processing emphasizes efficiency, large-scale production, and consistency, often utilizing additives and preservatives to extend shelf life and reduce costs. Consumers seeking natural, handcrafted foods often prefer artisanal options, while those valuing convenience and affordability tend to choose industrially processed products.
Table of Comparison
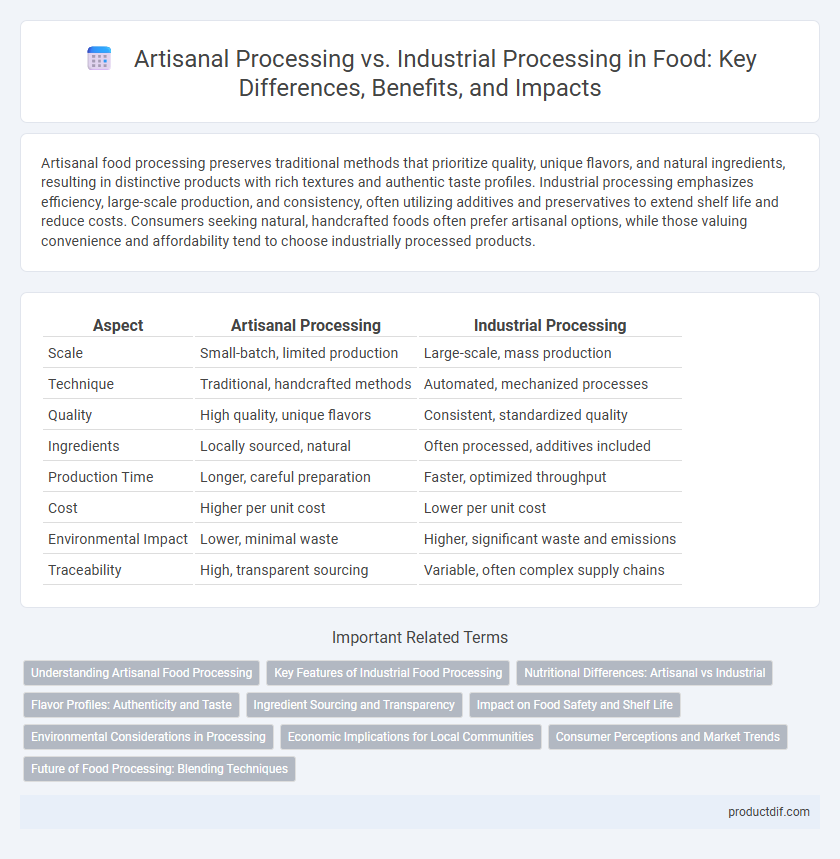
| Aspect | Artisanal Processing | Industrial Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Small-batch, limited production | Large-scale, mass production |
| Technique | Traditional, handcrafted methods | Automated, mechanized processes |
| Quality | High quality, unique flavors | Consistent, standardized quality |
| Ingredients | Locally sourced, natural | Often processed, additives included |
| Production Time | Longer, careful preparation | Faster, optimized throughput |
| Cost | Higher per unit cost | Lower per unit cost |
| Environmental Impact | Lower, minimal waste | Higher, significant waste and emissions |
| Traceability | High, transparent sourcing | Variable, often complex supply chains |
Understanding Artisanal Food Processing
Artisanal food processing emphasizes traditional methods, small-scale production, and the use of high-quality, locally sourced ingredients, preserving unique flavors and cultural heritage. Unlike industrial processing, which prioritizes uniformity, mass production, and extended shelf life through mechanization and additives, artisanal techniques rely on manual craftsmanship and natural processes. This approach often results in superior taste, nutritional value, and authenticity, appealing to consumers seeking transparency and sustainability in their food choices.
Key Features of Industrial Food Processing
Industrial food processing involves large-scale production techniques designed for mass distribution, emphasizing uniformity, efficiency, and extended shelf life. Key features include the use of automated machinery, standardized recipes, and preservatives to maintain product consistency and safety. This method prioritizes high volume output and cost-effectiveness over the unique flavors and textures often found in artisanal foods.
Nutritional Differences: Artisanal vs Industrial
Artisanal food processing typically retains higher levels of natural nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants due to minimal heat exposure and the use of traditional methods. Industrial processing often involves high-temperature treatments and extensive refining, which can degrade sensitive nutrients and reduce fiber content. As a result, artisanal products frequently offer superior nutritional profiles, with enhanced bioavailability and fewer additives.
Flavor Profiles: Authenticity and Taste
Artisanal processing preserves unique flavor profiles by utilizing traditional methods that emphasize ingredient quality and slow fermentation, resulting in complex, authentic tastes. Industrial processing often standardizes production for consistency, which can lead to muted or uniform flavors lacking depth and regional character. Consumers seeking authentic taste experiences frequently prefer artisanal foods for their rich, nuanced flavor profiles that reflect cultural heritage.
Ingredient Sourcing and Transparency
Artisanal processing emphasizes sourcing ingredients from local, sustainable farms, ensuring high transparency in traceability and quality. Industrial processing relies on large-scale suppliers, often prioritizing cost-efficiency over detailed ingredient disclosure. Consumers seeking authentic, high-quality products typically prefer artisanal methods due to their clearer ingredient origins and ethical sourcing practices.
Impact on Food Safety and Shelf Life
Artisanal processing often relies on traditional methods with limited mechanization, which can increase variability in microbial control and potentially elevate food safety risks compared to industrial processing. Industrial processing employs standardized protocols, advanced technologies, and rigorous quality control measures that enhance pathogen elimination and extend shelf life through preservatives and controlled packaging. Consequently, industrial methods generally offer improved food safety assurance and longer shelf stability, while artisanal products may prioritize flavor and authenticity over uniform safety outcomes.
Environmental Considerations in Processing
Artisanal food processing typically generates lower carbon emissions due to small-scale, manual techniques that consume less energy and produce minimal waste. Industrial processing, while efficient for mass production, often relies on high energy inputs and extensive packaging, contributing significantly to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Choosing artisanal methods supports sustainable practices by prioritizing local sourcing and reducing the ecological footprint in the food supply chain.
Economic Implications for Local Communities
Artisanal food processing supports local economies by creating jobs and preserving traditional skills, often leading to higher product value and market differentiation. Industrial processing typically benefits from economies of scale, increasing production efficiency but potentially displacing small-scale producers and limiting local economic growth. The economic implications for local communities hinge on balancing these approaches to sustain livelihoods and promote regional development.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Consumer perceptions strongly favor artisanal processing for its emphasis on quality, authenticity, and traditional methods, often associated with healthier and more natural products. Market trends reveal a growing demand for artisanal foods, driven by increasing awareness of ingredient sourcing and small-batch production. In contrast, industrial processing is perceived as efficient but linked to concerns about additives and mass production, influencing niche markets toward artisanal alternatives.
Future of Food Processing: Blending Techniques
Artisanal processing prioritizes traditional methods and local ingredients, producing unique flavors and textures that emphasize quality and sustainability. Industrial processing employs advanced technologies and large-scale operations to ensure consistency, efficiency, and mass production, often integrating automation and data analytics. The future of food processing lies in blending these techniques, combining artisanal craftsmanship with industrial innovation to create customizable, high-quality products that meet diverse consumer demands and reduce environmental impact.
Artisanal processing vs Industrial processing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com