Biodynamic wine is crafted using holistic farming principles that integrate lunar cycles, compost preparations, and biodiversity to enhance soil health and vine vitality. Organic wine strictly prohibits synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, prioritizing natural cultivation methods without necessarily following the spiritual or cosmic practices found in biodynamics. Both methods promote sustainable agriculture, but biodynamic wine emphasizes a deeper ecological harmony and vitality in the vineyard.
Table of Comparison
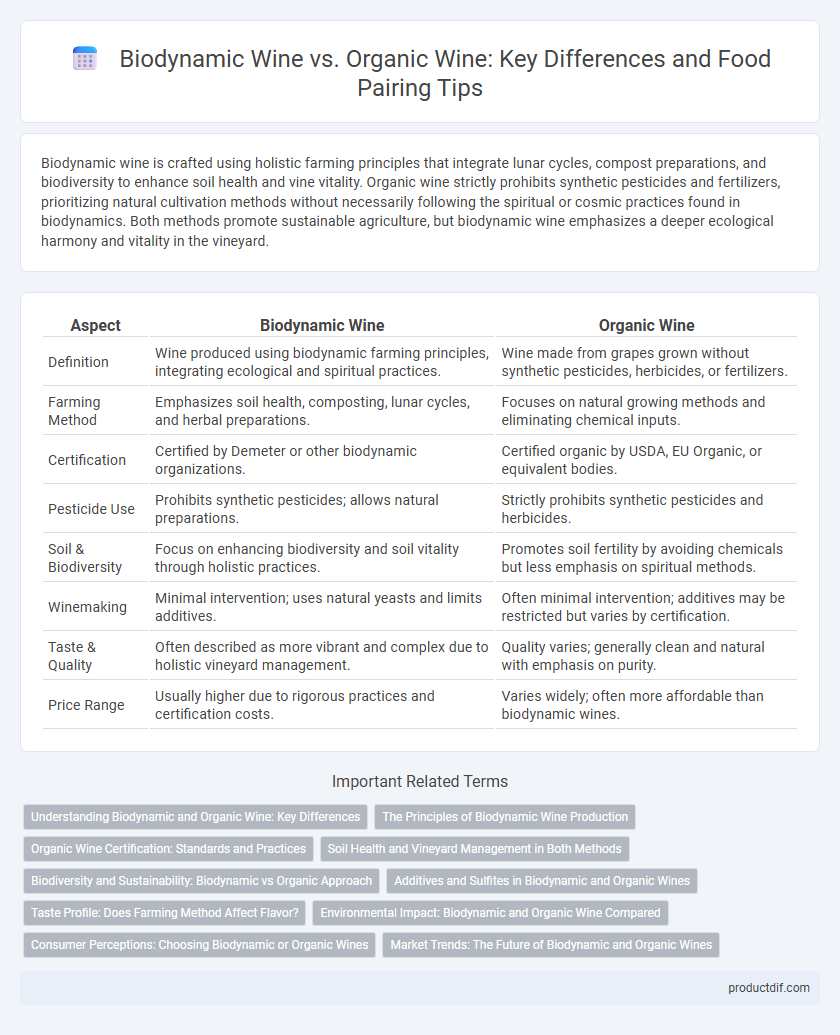
| Aspect | Biodynamic Wine | Organic Wine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wine produced using biodynamic farming principles, integrating ecological and spiritual practices. | Wine made from grapes grown without synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers. |
| Farming Method | Emphasizes soil health, composting, lunar cycles, and herbal preparations. | Focuses on natural growing methods and eliminating chemical inputs. |
| Certification | Certified by Demeter or other biodynamic organizations. | Certified organic by USDA, EU Organic, or equivalent bodies. |
| Pesticide Use | Prohibits synthetic pesticides; allows natural preparations. | Strictly prohibits synthetic pesticides and herbicides. |
| Soil & Biodiversity | Focus on enhancing biodiversity and soil vitality through holistic practices. | Promotes soil fertility by avoiding chemicals but less emphasis on spiritual methods. |
| Winemaking | Minimal intervention; uses natural yeasts and limits additives. | Often minimal intervention; additives may be restricted but varies by certification. |
| Taste & Quality | Often described as more vibrant and complex due to holistic vineyard management. | Quality varies; generally clean and natural with emphasis on purity. |
| Price Range | Usually higher due to rigorous practices and certification costs. | Varies widely; often more affordable than biodynamic wines. |
Understanding Biodynamic and Organic Wine: Key Differences
Biodynamic wine incorporates organic farming principles with added holistic practices such as lunar calendar planting and compost preparations to enhance vineyard vitality. Organic wine strictly prohibits synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, focusing on natural cultivation processes without biodynamic rituals. Both emphasize sustainability, but biodynamic wine integrates spiritual and ecological approaches for a unique terroir expression.
The Principles of Biodynamic Wine Production
Biodynamic wine production follows principles established by Rudolf Steiner, emphasizing holistic farm management, lunar cycles, and cosmic rhythms to enhance vine vitality and soil health. This approach uses specific preparations like fermented herbal sprays to promote biodiversity and natural disease resistance, distinguishing it from organic methods that primarily avoid synthetic chemicals. The integration of spiritual and ecological practices in biodynamics aims to create a self-sustaining ecosystem, resulting in wines that express their terroir with heightened complexity and balance.
Organic Wine Certification: Standards and Practices
Organic wine certification requires grapes to be grown without synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers, ensuring environmentally sustainable practices. Certification standards mandate strict adherence to organic farming methods, including soil health preservation and biodiversity promotion. In winemaking, approved organic techniques prohibit artificial additives and emphasize natural fermentation processes to maintain product integrity.
Soil Health and Vineyard Management in Both Methods
Biodynamic wine emphasizes a holistic approach to soil health by integrating lunar cycles and compost preparations that enhance microbial activity and soil vitality, promoting a self-sustaining ecosystem. Organic wine prioritizes natural soil enrichment using certified organic fertilizers and prohibits synthetic chemicals, maintaining soil fertility through crop rotation and cover cropping. Both methods aim to improve vineyard management by fostering biodiversity and soil structure but differ in their reliance on spiritual and ecological rhythms versus strict organic certification standards.
Biodiversity and Sustainability: Biodynamic vs Organic Approach
Biodynamic wine farming enhances biodiversity by integrating holistic practices that promote soil health, composting, and natural pest control, resulting in a self-sustaining ecosystem. Organic wine focuses on avoiding synthetic chemicals and pesticides, emphasizing sustainable agriculture but with less emphasis on ecological interrelationships compared to biodynamics. Both methods support sustainability, yet biodynamic viticulture uniquely fosters biodiversity through ritualistic practices and farm-wide natural harmony.
Additives and Sulfites in Biodynamic and Organic Wines
Biodynamic wines strictly limit additives and often exclude synthetic chemicals, emphasizing natural processes and fermentation, while organic wines prohibit synthetic pesticides and herbicides but may allow certain natural additives. Sulfite levels in biodynamic wines tend to be lower or completely absent due to minimal intervention techniques, whereas organic wines can contain sulfites but typically at reduced concentrations compared to conventional wines. Both biodynamic and organic certifications promote cleaner labels, but biodynamic standards are generally more rigorous regarding additive restrictions and sulfite usage.
Taste Profile: Does Farming Method Affect Flavor?
Biodynamic wines often exhibit complex, vibrant flavors with earthy and herbal undertones due to the use of natural composts and lunar cycle planting, enhancing soil vitality. Organic wines prioritize purity and freshness, reflecting the grape's innate characteristics by avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. The farming method impacts the taste profile by influencing grape quality, terroir expression, and microbial activity during fermentation.
Environmental Impact: Biodynamic and Organic Wine Compared
Biodynamic wine farming employs holistic practices that enhance soil health and biodiversity through compost preparations and lunar calendar planting, resulting in improved ecosystem resilience. Organic wine emphasizes the elimination of synthetic chemicals, reducing soil and water contamination while promoting natural pest control and nutrient cycles. Both methods significantly reduce environmental impact compared to conventional viticulture, but biodynamic farming offers a more integrative approach to ecosystem balance and sustainability.
Consumer Perceptions: Choosing Biodynamic or Organic Wines
Consumers choosing biodynamic wines often associate them with superior terroir expression and holistic vineyard practices, reflecting a deep connection to nature and soil vitality. Organic wines attract buyers prioritizing chemical-free cultivation and sustainable farming, emphasizing health-consciousness and environmental responsibility. Perceptions lean toward biodynamic wines as artisanal and spiritually driven, while organic wines are viewed as safe, reliable, and eco-friendly options.
Market Trends: The Future of Biodynamic and Organic Wines
Growing consumer demand for sustainable agriculture drives the expansion of both biodynamic and organic wine markets, with biodynamic wines gaining niche appeal due to their holistic farming practices and unique terroir expression. Market analysis indicates a steady increase in retail sales, especially among millennial and Gen Z consumers prioritizing environmental impact and authenticity. Investment in biodynamic certification and organic vineyards is projected to rise, positioning these wine categories as key players in the evolving sustainable wine industry.
Biodynamic wine vs Organic wine Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com