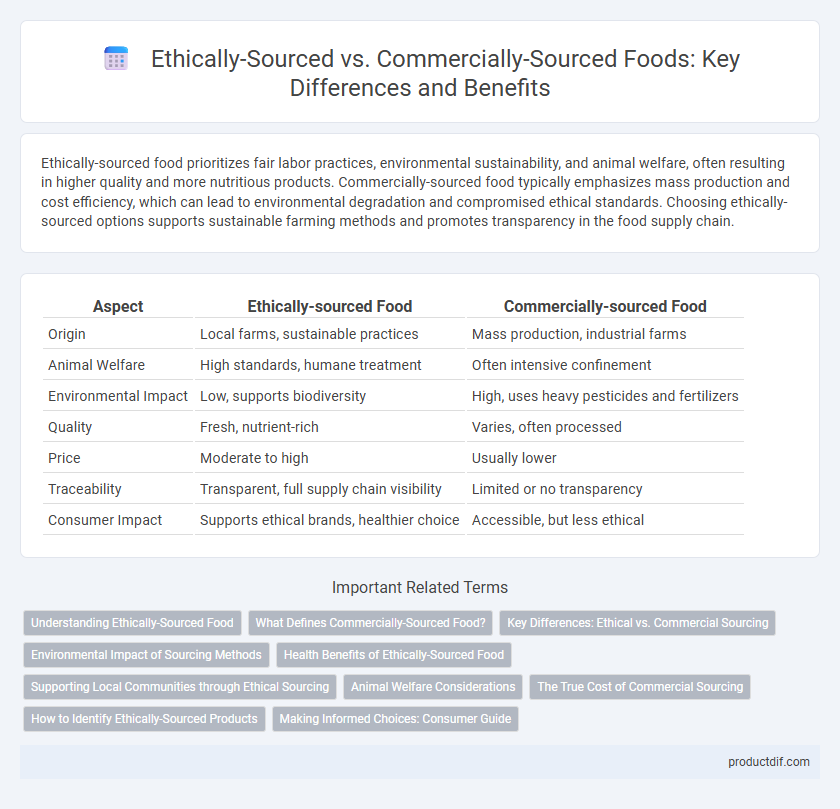
Ethically-sourced food prioritizes fair labor practices, environmental sustainability, and animal welfare, often resulting in higher quality and more nutritious products. Commercially-sourced food typically emphasizes mass production and cost efficiency, which can lead to environmental degradation and compromised ethical standards. Choosing ethically-sourced options supports sustainable farming methods and promotes transparency in the food supply chain.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ethically-sourced Food | Commercially-sourced Food |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Local farms, sustainable practices | Mass production, industrial farms |
| Animal Welfare | High standards, humane treatment | Often intensive confinement |
| Environmental Impact | Low, supports biodiversity | High, uses heavy pesticides and fertilizers |
| Quality | Fresh, nutrient-rich | Varies, often processed |
| Price | Moderate to high | Usually lower |
| Traceability | Transparent, full supply chain visibility | Limited or no transparency |
| Consumer Impact | Supports ethical brands, healthier choice | Accessible, but less ethical |
Understanding Ethically-Sourced Food
Ethically-sourced food prioritizes sustainable farming practices, fair labor conditions, and animal welfare, often verified through certifications such as Fair Trade, Organic, or Rainforest Alliance. Consumers choosing ethically-sourced products contribute to reducing environmental impact and supporting communities involved in food production. This approach contrasts with commercially-sourced food, which typically focuses on mass production and profitability, sometimes at the expense of ethical considerations.
What Defines Commercially-Sourced Food?
Commercially-sourced food primarily refers to products obtained through large-scale industrial farming and mass production methods aimed at maximizing yield and minimizing costs. These foods often involve conventional practices including the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to ensure consistent supply and affordability. The focus on efficiency and scale typically results in standardized products with wide distribution channels, contrasting with the sustainability and transparency emphasized in ethically-sourced food.
Key Differences: Ethical vs. Commercial Sourcing
Ethically-sourced food prioritizes animal welfare, fair labor practices, and environmental sustainability, often involving certifications like Fair Trade or Organic. Commercially-sourced food emphasizes mass production, cost efficiency, and high volume distribution, frequently relying on industrial farming and chemical inputs. Key differences lie in the impact on ecosystems, social responsibility, and transparency throughout the supply chain.
Environmental Impact of Sourcing Methods
Ethically-sourced food prioritizes sustainable farming practices that reduce carbon emissions and promote biodiversity, minimizing environmental degradation. Commercially-sourced food often relies on large-scale industrial agriculture, which contributes significantly to deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution. Choosing ethically-sourced products supports environmental conservation by enhancing ecosystem health and reducing the overall ecological footprint.
Health Benefits of Ethically-Sourced Food
Ethically-sourced food often contains fewer harmful chemicals and pesticides, promoting better overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. It typically comes from farms practicing sustainable agriculture, which enhances nutrient density and freshness. Consuming ethically-sourced food supports animal welfare and reduces exposure to antibiotics and hormones commonly found in commercially-sourced products.
Supporting Local Communities through Ethical Sourcing
Ethically-sourced food prioritizes fair wages and safe working conditions for local farmers, directly boosting community economies and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. Supporting local communities through ethical sourcing reduces exploitation common in commercially-sourced supply chains and encourages environmental stewardship. Consumers choosing ethically-sourced products contribute to preserving cultural heritage and fostering long-term economic resilience in rural areas.
Animal Welfare Considerations
Ethically-sourced food prioritizes animal welfare by ensuring humane living conditions, access to natural behaviors, and minimizing stress during farming and processing. Commercially-sourced products often focus on efficiency and cost-effectiveness, which can lead to overcrowded environments and practices that compromise animal well-being. Consumers increasingly prefer ethically-sourced goods to support sustainable and compassionate food systems that align with higher welfare standards.
The True Cost of Commercial Sourcing
Commercially-sourced food often involves large-scale industrial farming practices that can lead to environmental degradation, including soil depletion, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. These methods typically rely on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, increasing carbon emissions and contributing to climate change. Despite lower upfront costs, the hidden expenses related to public health, ecosystem damage, and resource depletion reveal the true cost of commercial sourcing far exceeds its market price.
How to Identify Ethically-Sourced Products
Look for certifications such as Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, or USDA Organic seals that indicate ethical sourcing practices. Traceability is key; ethically-sourced products often provide transparent supply chain information, highlighting worker welfare and environmental impact. Evaluate packaging labels and company websites for commitments to sustainable farming, fair labor conditions, and community support to ensure products align with ethical standards.
Making Informed Choices: Consumer Guide
Ethically-sourced food prioritizes fair labor practices, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability, ensuring consumers support responsible production. Commercially-sourced options often emphasize cost efficiency and wide availability but may lack transparency in sourcing and social impact. Making informed choices requires evaluating certifications, supply chain transparency, and company ethics to align purchases with personal values and long-term health benefits.
Ethically-sourced vs Commercially-sourced Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com