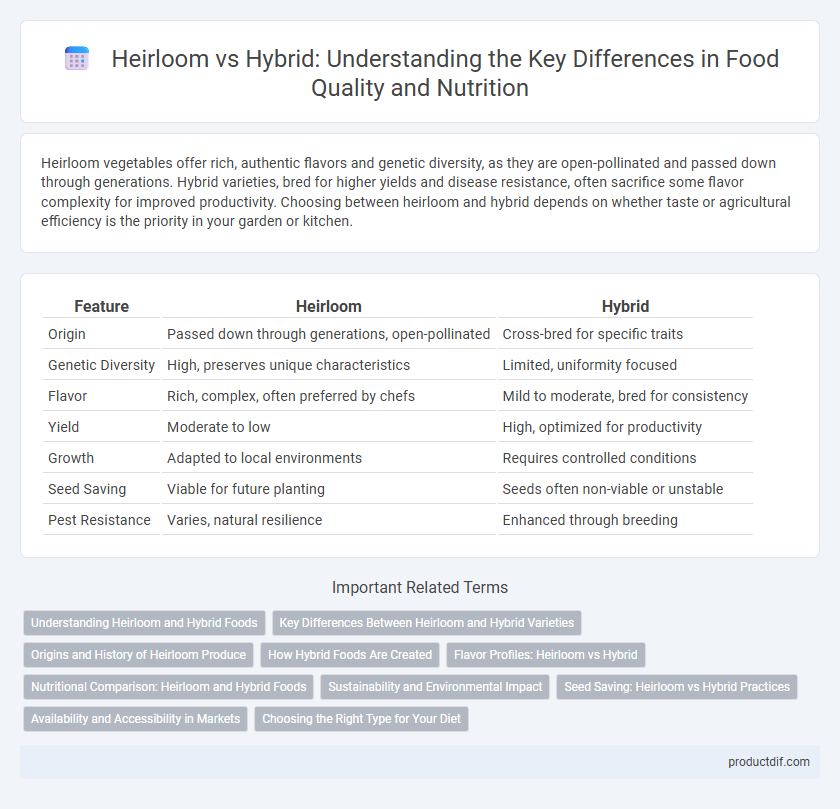
Heirloom vegetables offer rich, authentic flavors and genetic diversity, as they are open-pollinated and passed down through generations. Hybrid varieties, bred for higher yields and disease resistance, often sacrifice some flavor complexity for improved productivity. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid depends on whether taste or agricultural efficiency is the priority in your garden or kitchen.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heirloom | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Passed down through generations, open-pollinated | Cross-bred for specific traits |
| Genetic Diversity | High, preserves unique characteristics | Limited, uniformity focused |
| Flavor | Rich, complex, often preferred by chefs | Mild to moderate, bred for consistency |
| Yield | Moderate to low | High, optimized for productivity |
| Growth | Adapted to local environments | Requires controlled conditions |
| Seed Saving | Viable for future planting | Seeds often non-viable or unstable |
| Pest Resistance | Varies, natural resilience | Enhanced through breeding |
Understanding Heirloom and Hybrid Foods
Heirloom foods consist of open-pollinated plants that have been passed down through generations, prized for their rich flavors, genetic diversity, and historical significance. Hybrid foods result from crossbreeding different plant varieties to enhance traits like disease resistance, yield, and uniformity. Understanding the differences between heirloom and hybrid foods helps consumers make informed choices about flavor, nutrition, and sustainability in their diets.
Key Differences Between Heirloom and Hybrid Varieties
Heirloom varieties are open-pollinated plants that retain genetic traits passed through generations, offering unique flavors and diversity but often lower yield and disease resistance. Hybrid varieties result from crossbreeding two distinct parent plants to enhance traits like higher productivity, uniformity, and improved pest resistance. The key differences lie in genetic stability, flavor profiles, and agricultural performance, influencing gardeners' and farmers' choices for cultivation and consumption.
Origins and History of Heirloom Produce
Heirloom produce traces its origins to traditional varieties cultivated and preserved by farmers for generations, often passed down over 50 years or more, reflecting a rich agricultural heritage. Unlike hybrid varieties bred in the 20th century for uniformity and disease resistance, heirlooms offer unique flavors and genetic diversity, rooted in specific regional and cultural histories. These heirloom seeds were saved before the rise of industrial agriculture, preserving genetic traits that modern hybrids may lack.
How Hybrid Foods Are Created
Hybrid foods are created through the controlled cross-pollination of two distinct plant varieties to combine desirable traits such as disease resistance, higher yields, and uniformity. This process involves selecting parent plants with specific genetic characteristics and manually transferring pollen to achieve targeted improvements in crop quality. Unlike heirloom varieties, hybrids often exhibit improved vigor and adaptability due to the combination of diverse genetic material.
Flavor Profiles: Heirloom vs Hybrid
Heirloom tomatoes typically offer richer, more complex flavor profiles with a balance of sweetness, acidity, and earthiness due to their open-pollinated nature and genetic diversity. Hybrid tomatoes often prioritize yield, disease resistance, and shelf life, resulting in a milder, less nuanced taste. Consumers seeking robust and distinctive flavors usually prefer heirloom varieties over hybrids for culinary uses.
Nutritional Comparison: Heirloom and Hybrid Foods
Heirloom foods often contain higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals due to their genetic diversity and natural cultivation methods, enhancing their nutritional profile compared to many hybrid varieties. Hybrid foods are selectively bred for yield and pest resistance but can sometimes exhibit reduced nutrient density as a trade-off. Scientific studies indicate that while hybrids offer agricultural benefits, heirloom varieties may provide superior nutritional benefits for health-conscious consumers.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Heirloom seeds promote biodiversity by preserving unique plant varieties adapted to local climates, reducing the need for chemical inputs and supporting sustainable agriculture. Hybrid seeds often require synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which can lead to soil degradation and increased environmental pollution. Choosing heirloom varieties helps maintain genetic diversity and enhances ecosystem resilience, fostering long-term agricultural sustainability.
Seed Saving: Heirloom vs Hybrid Practices
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated varieties that produce plants true to type, making them ideal for seed saving and preserving genetic diversity in crops. Hybrid seeds result from crossing two distinct parent lines, often leading to superior yield and disease resistance but producing inconsistent offspring, which limits their viability for reliable seed saving. Gardeners committed to sustainable practices prefer heirloom seeds to maintain crop heritage and ensure consistent plant traits across seasons.
Availability and Accessibility in Markets
Heirloom varieties are often limited in availability, primarily found in farmers' markets and specialty stores, making them less accessible to the general public. Hybrid produce dominates supermarkets due to their higher yields, disease resistance, and longer shelf life, ensuring consistent supply and easier access. Consumer demand and regional agricultural practices further influence the market presence of heirloom versus hybrid varieties.
Choosing the Right Type for Your Diet
Heirloom varieties offer rich flavors and higher nutrient diversity, making them ideal for those seeking natural, traditional diets with minimal genetic modification. Hybrid plants provide higher yields and disease resistance, supporting efficient production and consistent quality for balanced nutrition. Selecting between heirloom and hybrid depends on prioritizing flavor and heritage versus productivity and resilience in your dietary needs.
heirloom vs hybrid Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com