Infused oils offer enhanced flavors and aromas by incorporating herbs, spices, or fruits directly into the oil, making them ideal for drizzling over dishes or finishing recipes. Plain oils provide a neutral base with a consistent smoking point, suitable for cooking methods requiring high heat or subtle flavors. Choosing between infused and plain oils depends on the desired taste profile and cooking technique.
Table of Comparison
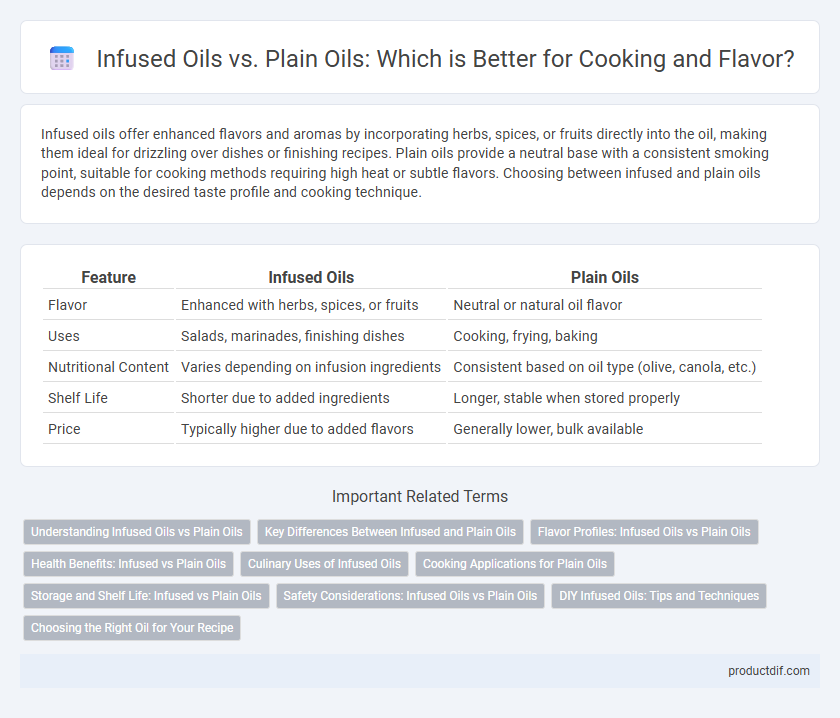
| Feature | Infused Oils | Plain Oils |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Enhanced with herbs, spices, or fruits | Neutral or natural oil flavor |
| Uses | Salads, marinades, finishing dishes | Cooking, frying, baking |
| Nutritional Content | Varies depending on infusion ingredients | Consistent based on oil type (olive, canola, etc.) |
| Shelf Life | Shorter due to added ingredients | Longer, stable when stored properly |
| Price | Typically higher due to added flavors | Generally lower, bulk available |
Understanding Infused Oils vs Plain Oils
Infused oils are created by steeping herbs, spices, or other flavorings in a base oil, which imparts additional aromas and tastes compared to plain oils. Plain oils, such as olive oil or canola oil, offer a neutral or naturally mild flavor profile and are typically used for cooking or as a base for infusions. Understanding the differences helps in selecting the right oil for culinary applications, balancing flavor intensity and nutritional benefits.
Key Differences Between Infused and Plain Oils
Infused oils contain added flavors derived from herbs, spices, or fruits, enhancing the taste and aroma of dishes, while plain oils have a neutral or natural flavor profile. The infusion process often involves steeping ingredients in oils like olive or sunflower, which imparts unique health benefits and culinary versatility not present in unflavored oils. Infused oils tend to have a shorter shelf life due to the inclusion of organic additives, whereas plain oils typically offer longer storage stability and higher smoke points for versatile cooking applications.
Flavor Profiles: Infused Oils vs Plain Oils
Infused oils offer complex flavor profiles derived from ingredients like herbs, spices, or fruits, enhancing dishes with aromatic and robust tastes. Plain oils, such as extra virgin olive oil or avocado oil, provide a neutral or mild flavor that allows the natural taste of food to shine without overpowering. The choice between infused and plain oils depends on the desired culinary effect, balancing intensity and subtlety in flavor.
Health Benefits: Infused vs Plain Oils
Infused oils contain added herbs, spices, or botanicals that enhance antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties compared to plain oils, which primarily provide essential fatty acids and vitamin E. The bioactive compounds in infused oils can support immune function and digestion, while plain oils deliver steady, unaltered nutrient profiles ideal for overall heart health. Choosing infused oils offers targeted health benefits through natural compounds absent in standard plain oils.
Culinary Uses of Infused Oils
Infused oils elevate culinary dishes by imparting concentrated flavors from herbs, spices, or fruits, enhancing salads, marinades, and finishing drizzles with vibrant taste profiles. Unlike plain oils, infused varieties provide a natural aroma and complexity that transform simple recipes into gourmet experiences. These oils are ideal for cold applications or brief heating, preserving delicate flavors that plain oils typically lack.
Cooking Applications for Plain Oils
Plain oils such as olive oil, canola oil, and vegetable oil offer neutral flavors and high smoke points, making them ideal for versatile cooking applications like frying, sauteing, and baking. These oils do not impart additional flavors, allowing the natural taste of the ingredients to shine through in dishes. Their stability under heat ensures even cooking and prevents unwanted flavor changes or burning during high-temperature cooking.
Storage and Shelf Life: Infused vs Plain Oils
Infused oils typically have a shorter shelf life than plain oils due to the presence of herbs, spices, or other flavoring agents that can introduce moisture and promote microbial growth. Plain oils, such as extra virgin olive oil or avocado oil, tend to have a longer storage stability when kept in a cool, dark place away from heat and light. Proper storage in airtight containers and refrigeration can extend the freshness of infused oils but may still require consumption within weeks to maintain optimal flavor and safety.
Safety Considerations: Infused Oils vs Plain Oils
Infused oils carry a higher risk of bacterial growth, particularly botulism, when fresh herbs or garlic are used without proper preservation methods, unlike plain oils that have a more stable shelf life due to the absence of added perishable ingredients. Safe preparation of infused oils requires techniques such as refrigeration, acidification, or commercial heat treatments to inhibit microbial hazards. Consumers should prioritize properly stored plain oils or commercially processed infused oils to minimize safety concerns related to foodborne pathogens.
DIY Infused Oils: Tips and Techniques
Creating DIY infused oils involves selecting high-quality base oils like olive or grapeseed and infusing them with herbs, spices, or citrus peels to enhance flavor profiles. Proper sterilization of containers and careful control of infusion time, typically ranging from a few days to several weeks, help prevent spoilage and ensure safe consumption. Using techniques such as cold infusion or gentle warming optimizes the extraction of essential oils and compounds, delivering robust, aromatic blends for culinary use.
Choosing the Right Oil for Your Recipe
Infused oils contain added flavors from herbs, spices, or fruits, enhancing dishes with distinctive aromas and tastes compared to plain oils. Selecting the right oil depends on the cooking method and flavor profile; for high-heat cooking, oils with high smoke points like avocado or refined olive oil are ideal, while infused oils suit drizzling or finishing dishes to add complexity. Understanding the oil's flavor intensity and smoke point ensures optimal results and balanced flavors in your recipe.
infused oils vs plain oils Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com