Organic certification ensures food is produced without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms, emphasizing environmental sustainability and soil health. Non-GMO certification specifically guarantees that products do not contain genetically modified organisms but does not address other agricultural practices. Choosing organic certification provides broader assurances about farming methods, while non-GMO certification focuses solely on genetic modification concerns.
Table of Comparison
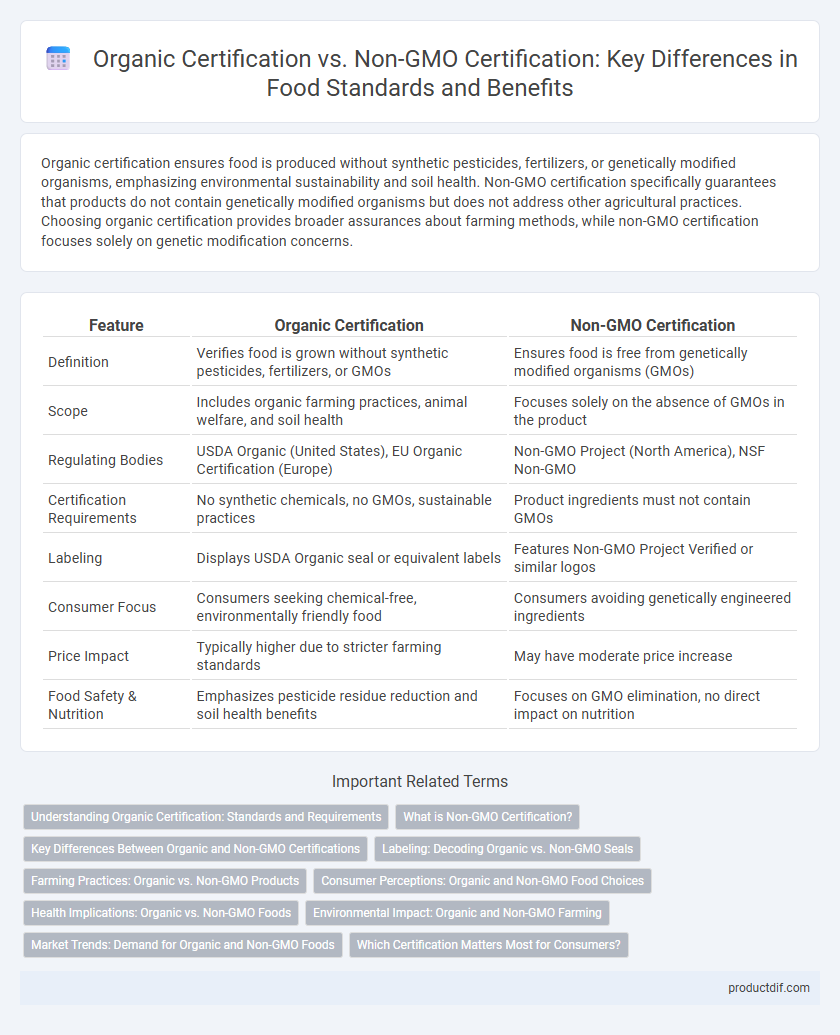
| Feature | Organic Certification | Non-GMO Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verifies food is grown without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or GMOs | Ensures food is free from genetically modified organisms (GMOs) |
| Scope | Includes organic farming practices, animal welfare, and soil health | Focuses solely on the absence of GMOs in the product |
| Regulating Bodies | USDA Organic (United States), EU Organic Certification (Europe) | Non-GMO Project (North America), NSF Non-GMO |
| Certification Requirements | No synthetic chemicals, no GMOs, sustainable practices | Product ingredients must not contain GMOs |
| Labeling | Displays USDA Organic seal or equivalent labels | Features Non-GMO Project Verified or similar logos |
| Consumer Focus | Consumers seeking chemical-free, environmentally friendly food | Consumers avoiding genetically engineered ingredients |
| Price Impact | Typically higher due to stricter farming standards | May have moderate price increase |
| Food Safety & Nutrition | Emphasizes pesticide residue reduction and soil health benefits | Focuses on GMO elimination, no direct impact on nutrition |
Understanding Organic Certification: Standards and Requirements
Organic certification requires adherence to strict agricultural practices that prohibit synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and irradiation, ensuring products are produced in environmentally sustainable ways. This certification involves comprehensive inspections, soil and water testing, and detailed record-keeping to verify compliance with the USDA Organic standards or equivalent regulatory bodies worldwide. In contrast, non-GMO certification focuses exclusively on verifying that the product contains no genetically modified ingredients but does not regulate other aspects like pesticide use or sustainability practices.
What is Non-GMO Certification?
Non-GMO Certification verifies that food products are produced without genetically modified organisms, ensuring adherence to strict testing and traceability standards. This certification is crucial for consumers seeking transparency about genetic engineering in their food, often managed by organizations like the Non-GMO Project. Unlike Organic Certification, which covers broader agricultural practices including pesticide use and soil health, Non-GMO Certification exclusively focuses on the absence of genetically engineered ingredients.
Key Differences Between Organic and Non-GMO Certifications
Organic certification requires that products meet strict standards including the absence of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms, while non-GMO certification exclusively verifies that products do not contain genetically modified ingredients. Organic standards encompass broader environmental and animal welfare criteria, whereas non-GMO certification focuses solely on genetic modification status. Consumers seeking comprehensive assurances about ecological impact and farming practices typically prefer organic-certified foods, whereas those concerned only with GMO-free products opt for non-GMO labels.
Labeling: Decoding Organic vs. Non-GMO Seals
Organic certification ensures that food is produced without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms, reflecting comprehensive farming practices regulated by USDA standards. Non-GMO certification specifically verifies that products contain no genetically modified ingredients, focusing solely on genetic integrity without addressing pesticide or fertilizer use. Understanding these labels helps consumers make informed choices based on priorities like chemical avoidance or GMO exclusion.
Farming Practices: Organic vs. Non-GMO Products
Organic certification requires farming practices that avoid synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms, prioritizing soil health and biodiversity through crop rotation and natural pest control. Non-GMO certification solely ensures that seeds and ingredients are not genetically modified but does not restrict the use of synthetic chemicals or conventional farming methods. Consequently, organic farming promotes ecological balance, while non-GMO certification focuses narrowly on genetic integrity without broader environmental standards.
Consumer Perceptions: Organic and Non-GMO Food Choices
Consumers often perceive organic certification as a marker of higher environmental and health standards, emphasizing pesticide-free and sustainably farmed products. Non-GMO certification specifically addresses genetic modification concerns, appealing to those wary of genetically engineered ingredients but not necessarily focused on broader farming practices. Preference trends indicate that organic labels tend to inspire greater trust and willingness to pay premium prices due to their comprehensive nature.
Health Implications: Organic vs. Non-GMO Foods
Organic certification ensures foods are grown without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms, often resulting in higher antioxidant levels and fewer pesticide residues, which may benefit long-term health. Non-GMO certification focuses solely on the absence of genetically modified ingredients but does not regulate pesticide use or farming practices, potentially allowing higher chemical residues. Consumers seeking comprehensive health benefits often prefer organic foods for their reduced exposure to synthetic chemicals and enhanced nutrient profiles.
Environmental Impact: Organic and Non-GMO Farming
Organic farming emphasizes biodiversity, soil health, and reduced chemical inputs, leading to lower environmental pollution and enhanced ecosystem services. Non-GMO certification primarily focuses on genetically modified organism exclusion without specific mandates on pesticide use or soil management, resulting in varied environmental outcomes. Studies show organic farms generally support greater biodiversity and improved soil quality compared to non-GMO farms lacking organic practices.
Market Trends: Demand for Organic and Non-GMO Foods
Rising consumer awareness about health and environmental impact drives significant growth in both organic and Non-GMO food markets. Organic certification ensures products meet strict standards for chemical use and sustainability, attracting eco-conscious buyers willing to pay premium prices. Non-GMO certification appeals to health-focused consumers seeking genetically unmodified foods, fueling retailer expansion and diversified product offerings.
Which Certification Matters Most for Consumers?
Organic certification ensures food is produced without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and GMOs, emphasizing environmental sustainability and overall health. Non-GMO certification specifically confirms the absence of genetically modified organisms, appealing to consumers concerned about genetic engineering rather than broader agricultural practices. For consumers prioritizing comprehensive natural farming methods and chemical-free products, organic certification matters more, while those solely avoiding GMOs may focus on non-GMO certification.
Organic Certification vs Non-GMO Certification Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com