Upcycled ingredients reduce food waste by repurposing byproducts and surplus materials, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional ingredients. These ingredients often retain high nutritional value while promoting environmental responsibility in the food industry. Choosing upcycled ingredients supports circular economy practices without compromising taste or quality in recipes.
Table of Comparison
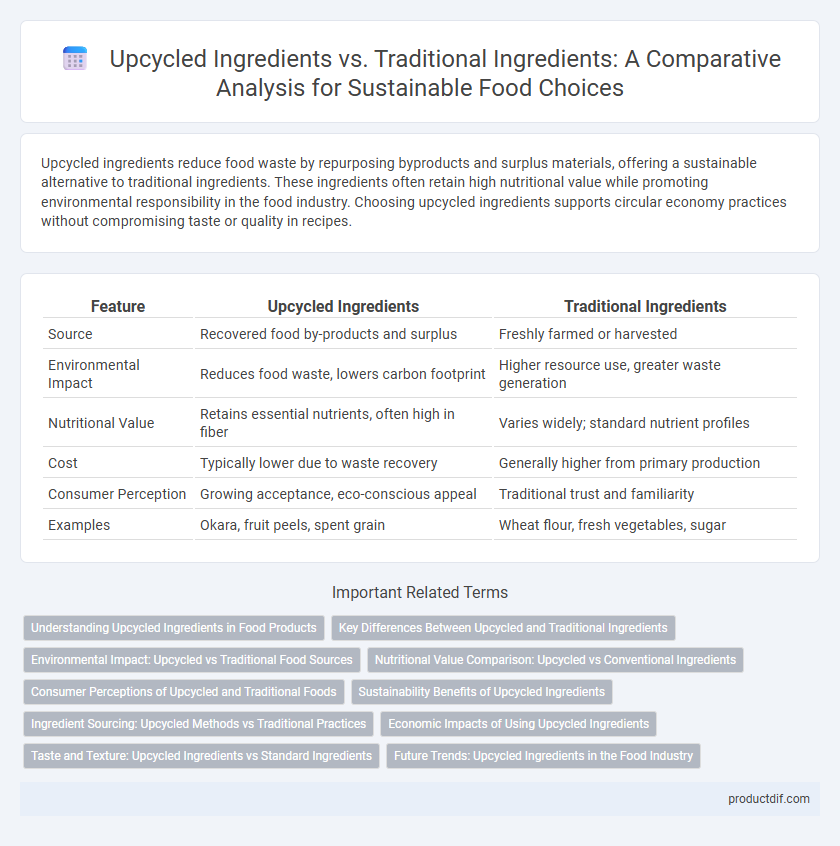
| Feature | Upcycled Ingredients | Traditional Ingredients |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered food by-products and surplus | Freshly farmed or harvested |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces food waste, lowers carbon footprint | Higher resource use, greater waste generation |
| Nutritional Value | Retains essential nutrients, often high in fiber | Varies widely; standard nutrient profiles |
| Cost | Typically lower due to waste recovery | Generally higher from primary production |
| Consumer Perception | Growing acceptance, eco-conscious appeal | Traditional trust and familiarity |
| Examples | Okara, fruit peels, spent grain | Wheat flour, fresh vegetables, sugar |
Understanding Upcycled Ingredients in Food Products
Upcycled ingredients in food products are derived from surplus or by-products that would otherwise be discarded, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional ingredients. These ingredients retain nutritional value and contribute to reducing food waste, promoting environmental conservation. Utilizing upcycled components supports circular economy practices while maintaining product quality and taste.
Key Differences Between Upcycled and Traditional Ingredients
Upcycled ingredients are sourced from food byproducts or surplus that would otherwise go to waste, emphasizing sustainability and resource efficiency, whereas traditional ingredients are typically harvested or manufactured specifically for direct consumption. Nutritional profiles of upcycled ingredients often remain comparable to traditional ones but can offer unique benefits like enhanced fiber or antioxidant content due to their original food source. The environmental impact of upcycled ingredients is significantly lower, reducing food waste and greenhouse gas emissions compared to the conventional production and processing of traditional ingredients.
Environmental Impact: Upcycled vs Traditional Food Sources
Upcycled ingredients significantly reduce food waste by repurposing by-products and surplus food, lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional agricultural sources. Traditional food production often requires higher water usage, land exploitation, and energy consumption, contributing to deforestation and habitat loss. Utilizing upcycled ingredients supports circular economy principles, minimizing environmental footprint while promoting sustainable food systems.
Nutritional Value Comparison: Upcycled vs Conventional Ingredients
Upcycled ingredients often retain high nutritional value by utilizing parts of food that are traditionally discarded, such as fruit peels, seeds, and pulp, which are rich in fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Conventional ingredients may undergo more extensive processing, sometimes leading to nutrient depletion, whereas upcycled ingredients emphasize maximizing natural nutrient retention. Studies indicate that upcycled foods can provide a comparable or even enhanced nutrient profile, promoting sustainability without compromising dietary quality.
Consumer Perceptions of Upcycled and Traditional Foods
Consumers increasingly perceive upcycled ingredients as environmentally responsible and innovative, associating them with sustainability and waste reduction. Traditional ingredients often convey familiarity and trust rooted in cultural and culinary heritage, appealing to those valuing taste consistency and authenticity. Market research highlights a growing preference for upcycled foods among eco-conscious demographics, though taste, safety, and quality concerns remain critical factors influencing broader acceptance.
Sustainability Benefits of Upcycled Ingredients
Upcycled ingredients significantly reduce food waste by repurposing surplus or imperfect produce that would otherwise be discarded, thereby conserving natural resources like water, energy, and land. The incorporation of upcycled ingredients lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional ingredients due to minimized agricultural and processing inputs. Sustainable food systems benefit from upcycled ingredients as they promote circular economy principles, enhance supply chain efficiency, and support biodiversity preservation.
Ingredient Sourcing: Upcycled Methods vs Traditional Practices
Upcycled ingredients are sourced from by-products and surplus food that would otherwise be discarded, minimizing waste and promoting sustainability. Traditional ingredient sourcing often relies on primary agricultural outputs, which can demand significant land, water, and energy resources. Employing upcycled methods enhances resource efficiency and reduces the environmental impact compared to conventional ingredient procurement.
Economic Impacts of Using Upcycled Ingredients
Upcycled ingredients reduce food waste by transforming by-products into valuable resources, lowering raw material costs and enhancing profit margins for food manufacturers. Economic benefits include decreased disposal expenses and access to new markets focused on sustainability-driven consumer demand. The shift toward upcycled ingredients also stimulates innovation and job creation in supply chain sectors dedicated to circular economy practices.
Taste and Texture: Upcycled Ingredients vs Standard Ingredients
Upcycled ingredients often retain unique flavor profiles and textures due to their reduced processing, offering a richer and more complex taste compared to standard ingredients. Traditional ingredients typically provide consistent and familiar taste and texture, but may lack the depth found in upcycled alternatives. The incorporation of upcycled ingredients can enhance the sensory experience by introducing novel textures and intensified flavors that appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Future Trends: Upcycled Ingredients in the Food Industry
Upcycled ingredients are rapidly gaining traction in the food industry due to increasing consumer demand for sustainability and waste reduction. Future trends indicate a significant rise in the use of byproducts from food processing, such as fruit peels, spent grains, and vegetable pulp, to create nutrient-rich, eco-friendly products. Innovations in food technology are enhancing the sensory qualities and safety of upcycled ingredients, positioning them as viable alternatives to traditional ingredients in mainstream food production.
Upcycled Ingredients vs Traditional Ingredients Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com