Single-origin products emphasize traceability and unique flavor profiles by sourcing ingredients from a specific region, enhancing quality and authenticity. Multi-origin products blend ingredients from various locations to create balanced flavors and consistent supply, often offering more affordability. Choosing between them depends on personal preference for distinct taste nuances or reliable product availability.
Table of Comparison
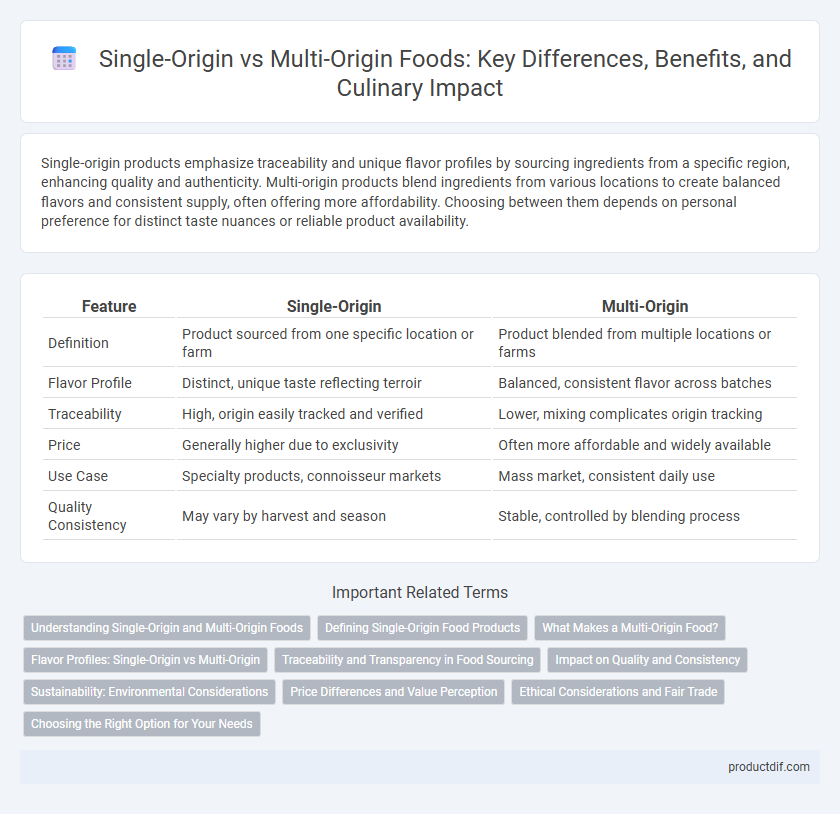
| Feature | Single-Origin | Multi-Origin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Product sourced from one specific location or farm | Product blended from multiple locations or farms |
| Flavor Profile | Distinct, unique taste reflecting terroir | Balanced, consistent flavor across batches |
| Traceability | High, origin easily tracked and verified | Lower, mixing complicates origin tracking |
| Price | Generally higher due to exclusivity | Often more affordable and widely available |
| Use Case | Specialty products, connoisseur markets | Mass market, consistent daily use |
| Quality Consistency | May vary by harvest and season | Stable, controlled by blending process |
Understanding Single-Origin and Multi-Origin Foods
Single-origin foods come from a specific geographic location, ensuring unique flavor profiles and traceability, often associated with higher quality and sustainability. Multi-origin foods blend ingredients sourced from various regions, offering consistency in taste and increased availability but sometimes lacking distinct regional characteristics. Understanding the differences helps consumers make informed choices based on flavor preferences, ethical considerations, and product reliability.
Defining Single-Origin Food Products
Single-origin food products are sourced exclusively from a specific geographic location, ensuring unique flavor profiles influenced by local soil, climate, and farming practices. These products offer traceability and authenticity, often linked to higher quality and sustainability standards. In contrast, multi-origin foods combine ingredients from various regions, which can dilute distinct characteristics but provide consistency and cost efficiency.
What Makes a Multi-Origin Food?
Multi-origin food is characterized by ingredients sourced from multiple geographic regions, combining diverse flavors, qualities, and agricultural practices. This blending enhances complexity and balance in taste profiles, often aiming for consistency across seasons or batches. Multi-origin sourcing allows producers to optimize quality, price, and availability by selecting the best inputs from various origins.
Flavor Profiles: Single-Origin vs Multi-Origin
Single-origin coffee beans offer distinct and consistent flavor profiles that highlight the unique characteristics of a specific region or farm, often featuring nuanced notes such as floral, fruity, or chocolate undertones. Multi-origin blends combine beans from various locations, creating complex and balanced flavor profiles that can enhance body, acidity, and aroma through careful blending. The choice between single-origin and multi-origin influences the taste experience by either emphasizing purity and specificity or achieving harmony and complexity in flavor.
Traceability and Transparency in Food Sourcing
Single-origin food products offer superior traceability by linking ingredients directly to a specific farm or region, ensuring clear transparency about farming practices and environmental impact. Multi-origin sourcing combines ingredients from multiple locations, which can complicate tracking and reduce visibility into the supply chain's sustainability standards. Enhanced transparency in single-origin sourcing supports consumer trust and better food safety management through detailed provenance data.
Impact on Quality and Consistency
Single-origin foods, sourced from a specific region or farm, offer distinct flavor profiles and higher quality due to controlled growing conditions. Multi-origin products blend ingredients from various locations, ensuring consistency in flavor and supply but often sacrificing unique characteristics. This difference significantly impacts consumer experience, with single-origin favored for premium quality and multi-origin valued for reliability.
Sustainability: Environmental Considerations
Single-origin food products often support sustainability by promoting biodiversity and reducing carbon footprints through localized farming practices. Multi-origin sourcing can lead to increased environmental impact due to transportation emissions and inconsistent agricultural standards across regions. Sustainable choices favor single-origin items that enhance traceability and encourage environmentally responsible farming methods.
Price Differences and Value Perception
Single-origin foods often command higher prices due to their traceability and perceived purity, appealing to consumers seeking authenticity and premium quality. Multi-origin products typically offer more competitive pricing, benefiting from blended sourcing that reduces costs without sacrificing overall flavor consistency. Value perception shifts as buyers weigh the exclusivity and transparency of single-origin options against the affordability and accessibility of multi-origin alternatives.
Ethical Considerations and Fair Trade
Single-origin coffee sources beans from one specific region, often allowing for better tracking of ethical practices and fair trade certifications that ensure farmers receive fair wages and work under safe conditions. Multi-origin blends can present challenges in verifying ethical standards due to the complexity of sourcing from multiple regions, potentially obscuring transparency and fair compensation. Supporting single-origin products often promotes sustainable farming practices and amplifies the economic benefits for small-scale farmers within a defined community.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Needs
Single-origin foods offer distinct flavors and traceability, ideal for consumers seeking unique taste profiles and ethical sourcing transparency. Multi-origin products provide consistency and affordability, making them suitable for everyday use and large-scale production. Assessing your priorities in flavor complexity, budget, and supply reliability helps determine the best choice between single-origin and multi-origin options.
Single-Origin vs Multi-Origin Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com