Artisan food emphasizes handcrafted techniques, unique flavors, and high-quality, locally sourced ingredients, appealing to consumers seeking authenticity and culinary craftsmanship. Mass-produced food prioritizes efficiency, consistency, and scalability, often using standardized recipes and industrial processes to meet large-scale demand. The growing consumer interest in health and sustainability continues to drive a preference for artisan products over mass-produced alternatives.
Table of Comparison
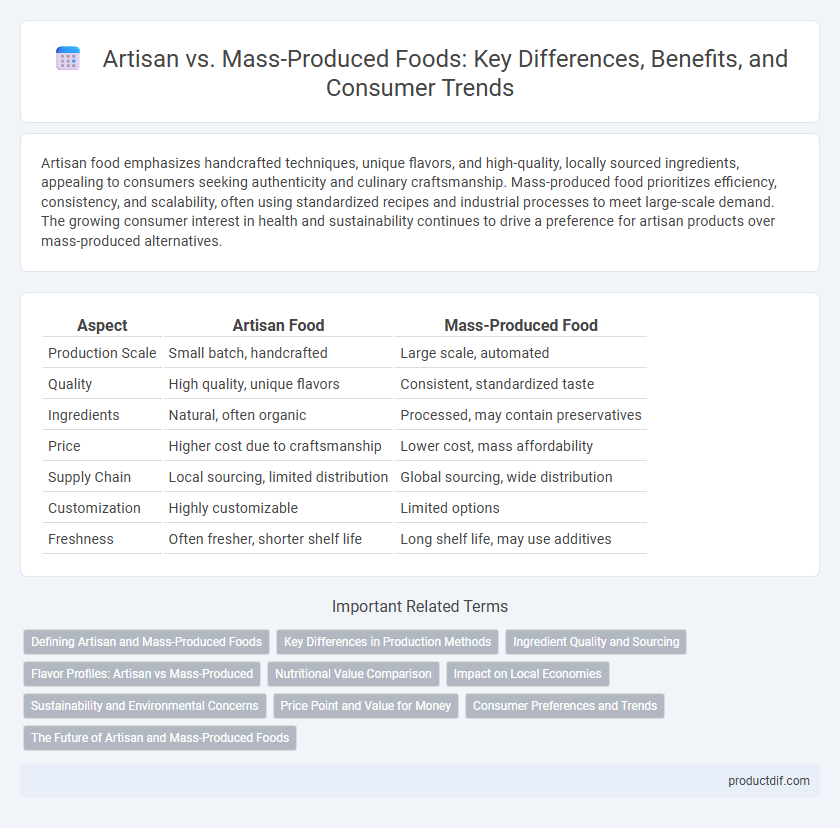
| Aspect | Artisan Food | Mass-Produced Food |
|---|---|---|
| Production Scale | Small batch, handcrafted | Large scale, automated |
| Quality | High quality, unique flavors | Consistent, standardized taste |
| Ingredients | Natural, often organic | Processed, may contain preservatives |
| Price | Higher cost due to craftsmanship | Lower cost, mass affordability |
| Supply Chain | Local sourcing, limited distribution | Global sourcing, wide distribution |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited options |
| Freshness | Often fresher, shorter shelf life | Long shelf life, may use additives |
Defining Artisan and Mass-Produced Foods
Artisan foods are handcrafted products made in small batches using traditional methods and high-quality, often locally sourced ingredients, emphasizing taste, authenticity, and craftsmanship. Mass-produced foods are manufactured on a large scale with automated processes, focusing on consistency, affordability, and extended shelf life through the use of preservatives and standardized ingredients. The distinction lies in the production scale, ingredient quality, and the attention to detail in flavor and texture.
Key Differences in Production Methods
Artisan food production involves small-scale, handcrafted techniques emphasizing quality, traditional methods, and unique flavors, often using locally sourced ingredients. Mass-produced food relies on large-scale industrial processes with automation and standardized recipes to ensure consistency, efficiency, and lower costs. The key differences lie in craftsmanship, ingredient sourcing, and production volume, impacting flavor complexity and product uniqueness.
Ingredient Quality and Sourcing
Artisan foods prioritize high-quality, locally sourced ingredients, often organic and sustainably harvested, ensuring superior freshness and flavor. Mass-produced products frequently rely on cost-effective, standardized ingredients that may include preservatives and additives to extend shelf life and reduce expenses. Ingredient sourcing in artisan food emphasizes traceability and ethical practices, contrasting with large-scale manufacturing's focus on efficiency and volume.
Flavor Profiles: Artisan vs Mass-Produced
Artisan foods often deliver complex, nuanced flavor profiles due to traditional techniques and high-quality, locally sourced ingredients, creating unique sensory experiences. Mass-produced foods tend to prioritize consistency and shelf-stability, resulting in more uniform but less intricate tastes. The fermentation, aging, and handcrafting processes in artisan production enhance depth and richness, whereas industrial methods often rely on additives to mimic flavor intensity.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Artisan foods typically retain higher nutritional value due to minimal processing, preserving essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants found in fresh ingredients. Mass-produced foods often contain preservatives, additives, and lower nutrient density resulting from extensive processing and prolonged storage. Consumers seeking nutrient-rich diets may benefit more from artisan options crafted with traditional methods and natural components.
Impact on Local Economies
Artisan food products stimulate local economies by supporting small-scale farmers, craftsmen, and businesses, leading to job creation and community sustainability. Mass-produced foods often rely on large supply chains, which can result in profits flowing out of local areas and reduced economic diversification. Investing in artisan food encourages the preservation of local culture and traditions, reinforcing economic resilience at the community level.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Artisan food production typically emphasizes sustainable practices by using local, organic ingredients and minimizing waste, reducing carbon footprints compared to mass-produced food. Mass-produced food often relies on large-scale industrial processes that contribute significantly to resource depletion, greenhouse gas emissions, and packaging waste. Prioritizing artisanal methods supports biodiversity and environmentally friendly farming techniques, promoting long-term ecological balance.
Price Point and Value for Money
Artisan foods typically command higher price points due to handcrafted processes, premium ingredients, and limited production runs, offering superior taste and quality that justify the cost. Mass-produced foods benefit from economies of scale, resulting in lower prices but often compromise on freshness, uniqueness, and ingredient integrity. Consumers seeking value for money weigh the balance between affordable pricing and the elevated sensory and nutritional experience offered by artisan products.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumers increasingly favor artisan foods for their distinct flavors, quality ingredients, and handcrafted techniques, reflecting a growing desire for authenticity and unique culinary experiences. Mass-produced products, while offering convenience and lower prices, often lack the artisanal appeal that appeals to niche markets prioritizing sustainability and local sourcing. Current trends show a rising demand for transparent labeling and ethical production methods, with many consumers willing to pay a premium for artisan brands that emphasize craftsmanship and tradition.
The Future of Artisan and Mass-Produced Foods
Artisan foods emphasize craftsmanship, unique flavors, and local ingredients, catering to growing consumer demand for authenticity and sustainability. Mass-produced foods focus on efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and widespread availability, driven by advanced automation and global supply chains. The future of food lies in blending artisanal qualities with scalable production technologies to meet diverse consumer preferences and environmental goals.
Artisan vs Mass-produced Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com