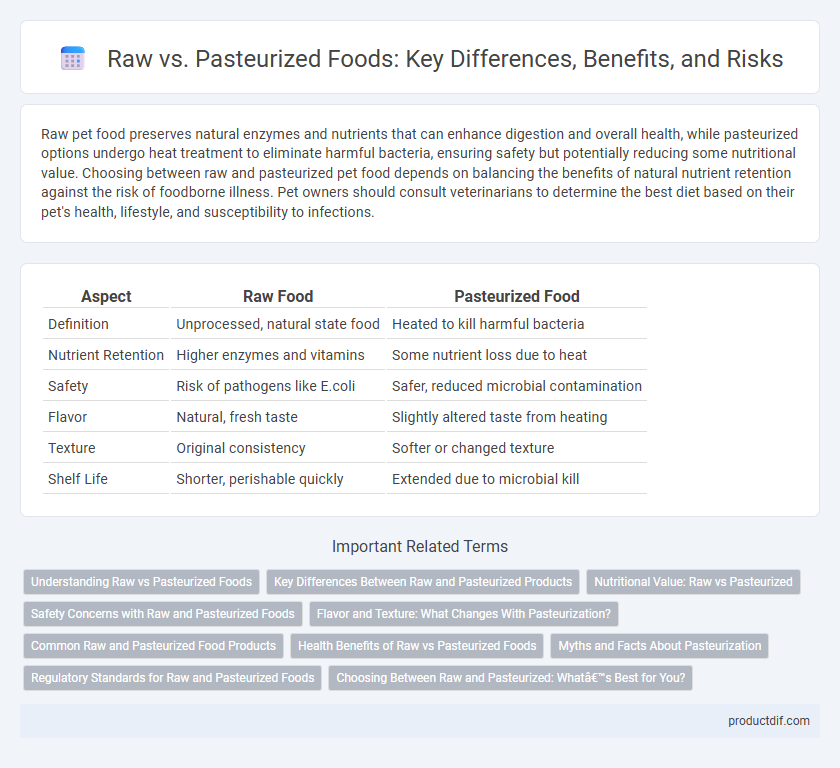
Raw pet food preserves natural enzymes and nutrients that can enhance digestion and overall health, while pasteurized options undergo heat treatment to eliminate harmful bacteria, ensuring safety but potentially reducing some nutritional value. Choosing between raw and pasteurized pet food depends on balancing the benefits of natural nutrient retention against the risk of foodborne illness. Pet owners should consult veterinarians to determine the best diet based on their pet's health, lifestyle, and susceptibility to infections.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Raw Food | Pasteurized Food |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unprocessed, natural state food | Heated to kill harmful bacteria |
| Nutrient Retention | Higher enzymes and vitamins | Some nutrient loss due to heat |
| Safety | Risk of pathogens like E.coli | Safer, reduced microbial contamination |
| Flavor | Natural, fresh taste | Slightly altered taste from heating |
| Texture | Original consistency | Softer or changed texture |
| Shelf Life | Shorter, perishable quickly | Extended due to microbial kill |
Understanding Raw vs Pasteurized Foods
Raw foods retain their natural enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, offering a nutrient-rich profile that may degrade during heat processing. Pasteurized foods undergo heating to eliminate harmful bacteria, enhancing safety but potentially reducing certain heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C. Understanding the balance between nutritional benefits and food safety is essential when choosing between raw and pasteurized options.
Key Differences Between Raw and Pasteurized Products
Raw products retain natural enzymes, probiotics, and nutrients that are often diminished or destroyed during pasteurization, which uses heat to kill harmful bacteria. Pasteurized foods offer enhanced safety by reducing pathogens but may experience changes in flavor, texture, and nutrient content due to thermal processing. Consumers prioritize raw options for their perceived health benefits and unaltered composition, while pasteurized choices are favored for extended shelf life and food safety assurances.
Nutritional Value: Raw vs Pasteurized
Raw foods often retain higher levels of vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants compared to their pasteurized counterparts, preserving essential nutrients like vitamin C and B-complex vitamins. Pasteurization, while effective in eliminating harmful bacteria, can degrade heat-sensitive nutrients and reduce overall antioxidant capacity. Consumers seeking maximum nutritional benefits may prefer raw options, particularly for fruits, vegetables, and dairy products rich in live enzymes and phytochemicals.
Safety Concerns with Raw and Pasteurized Foods
Raw foods, such as unpasteurized milk and juices, pose safety concerns due to the potential presence of harmful bacteria like E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria, increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses. Pasteurization effectively reduces these risks by heating products to a specific temperature that kills pathogens while preserving nutritional quality. Consumers, especially pregnant women, young children, and immunocompromised individuals, are advised to choose pasteurized options to ensure food safety.
Flavor and Texture: What Changes With Pasteurization?
Raw foods often retain a more robust and complex flavor profile due to the preservation of natural enzymes and microflora, which can be diminished during pasteurization. Pasteurization typically alters texture by softening ingredients and reducing crispness, as heat exposure affects cell structure and moisture content. These changes can lead to a milder taste and softer mouthfeel, which may appeal to some consumers while others prefer the more intense flavors and varied textures of raw foods.
Common Raw and Pasteurized Food Products
Common raw food products include fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and unpasteurized dairy such as raw milk and soft cheeses. Pasteurized food products primarily consist of milk, cheese, fruit juices, and eggs that have undergone heat treatment to eliminate harmful bacteria. Selecting between raw and pasteurized foods depends on preferences for nutritional content, safety standards, and potential health risks associated with microbial contamination.
Health Benefits of Raw vs Pasteurized Foods
Raw foods retain natural enzymes and higher vitamin content, which may enhance digestion and nutrient absorption compared to pasteurized foods. Pasteurization increases food safety by eliminating harmful pathogens but can reduce heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C and certain antioxidants. Consuming a balanced diet incorporating both raw and pasteurized foods maximizes nutritional benefits while minimizing risks of foodborne illness.
Myths and Facts About Pasteurization
Pasteurization effectively eliminates harmful bacteria in milk, disproving myths that it diminishes all nutritional value; in reality, it preserves most vitamins and minerals while ensuring safety. Contrary to beliefs that raw foods retain superior enzymes, pasteurization targets pathogens without significantly affecting enzyme activity essential for digestion. Scientific studies consistently support pasteurization's role in reducing foodborne illnesses, debunking misconceptions that raw consumption is inherently healthier or safer.
Regulatory Standards for Raw and Pasteurized Foods
Regulatory standards for raw and pasteurized foods vary significantly to ensure consumer safety and quality. Raw foods, such as unpasteurized milk and juices, are subject to stricter microbial testing and labeling requirements to mitigate risks of pathogens like Listeria and Salmonella. Pasteurized foods undergo standardized heat treatment processes defined by agencies like the FDA and USDA, ensuring elimination of harmful bacteria while maintaining nutritional value and extending shelf life.
Choosing Between Raw and Pasteurized: What’s Best for You?
Choosing between raw and pasteurized foods depends largely on your health needs and taste preferences. Raw foods retain natural enzymes and nutrients often reduced by pasteurization, benefiting those seeking maximum nutritional value. Pasteurized products offer enhanced safety by eliminating harmful bacteria, ideal for vulnerable groups like pregnant women or immunocompromised individuals.
Raw vs Pasteurized Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com