Heirloom tomatoes are prized for their rich, varied flavors and unique colors, often grown from open-pollinated seeds that preserve genetic diversity. Hybrid tomatoes are bred for higher yields, disease resistance, and uniform appearance, making them ideal for commercial production. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid tomatoes depends on whether flavor complexity or crop reliability is the priority.
Table of Comparison
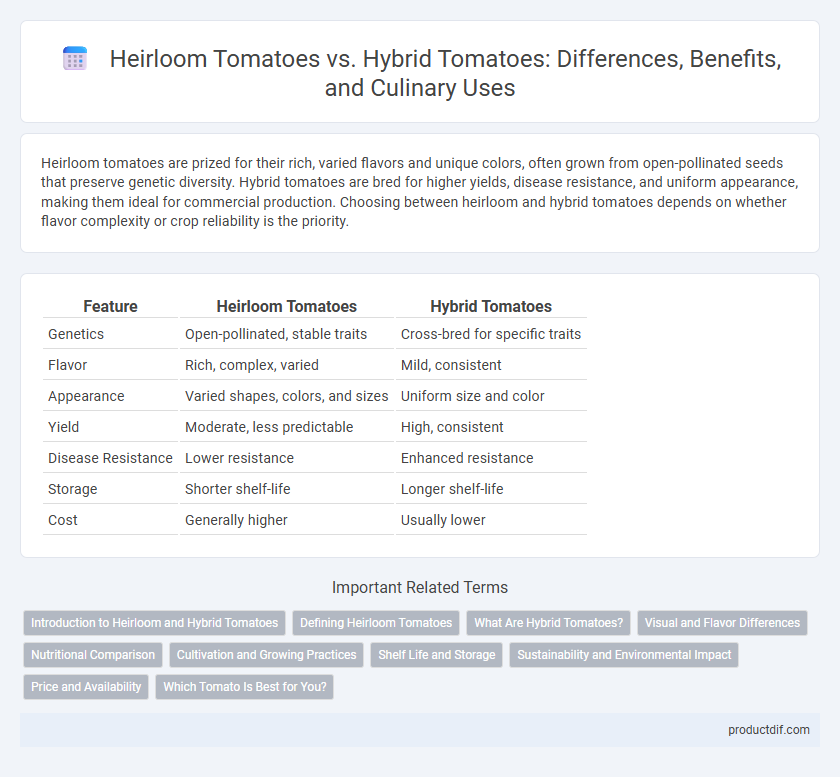
| Feature | Heirloom Tomatoes | Hybrid Tomatoes |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | Open-pollinated, stable traits | Cross-bred for specific traits |
| Flavor | Rich, complex, varied | Mild, consistent |
| Appearance | Varied shapes, colors, and sizes | Uniform size and color |
| Yield | Moderate, less predictable | High, consistent |
| Disease Resistance | Lower resistance | Enhanced resistance |
| Storage | Shorter shelf-life | Longer shelf-life |
| Cost | Generally higher | Usually lower |
Introduction to Heirloom and Hybrid Tomatoes
Heirloom tomatoes are open-pollinated varieties passed down through generations, prized for their rich flavors and diverse colors. Hybrid tomatoes result from crossbreeding two different tomato varieties to enhance traits like disease resistance, yield, and uniformity. Both types offer unique benefits, catering to different culinary and agricultural preferences.
Defining Heirloom Tomatoes
Heirloom tomatoes are open-pollinated varieties that have been passed down through generations, preserving unique flavors, colors, and shapes. These tomatoes are valued for their genetic diversity and rich taste profiles, often grown from seeds that are at least 50 years old. Unlike hybrid tomatoes, heirlooms are not crossbred for specific traits, resulting in natural variation and authentic flavors prized by chefs and home gardeners alike.
What Are Hybrid Tomatoes?
Hybrid tomatoes are cultivated by crossbreeding two different tomato varieties to produce plants with enhanced traits such as improved disease resistance, higher yields, and consistent flavor profiles. These tomatoes often exhibit uniform size, shape, and color, making them popular for commercial farming and large-scale production. Unlike heirloom tomatoes, hybrids prioritize durability and productivity over preserving genetic diversity and traditional characteristics.
Visual and Flavor Differences
Heirloom tomatoes showcase a diverse range of colors, shapes, and sizes with rich, complex flavors that often feature a balance of sweetness and acidity. Hybrid tomatoes generally have a uniform appearance, usually round and bright red, with a milder, less nuanced taste designed for durability and shelf life. The unique visual variety of heirlooms pairs with their intense, aromatic flavor profiles, setting them apart from the consistent but blander hybrids.
Nutritional Comparison
Heirloom tomatoes offer higher levels of antioxidants like lycopene and vitamin C compared to many hybrid varieties, enhancing their nutritional profile. Hybrid tomatoes are bred for durability and uniform appearance, often sacrificing some nutrient density for longer shelf life. Nutrient variations depend on specific cultivars, but heirlooms generally provide richer taste and superior micronutrient content.
Cultivation and Growing Practices
Heirloom tomatoes require careful seed saving and open-pollinated growing practices, thriving best in well-drained soil with consistent watering to maintain their unique flavors and genetics. Hybrid tomatoes are bred for disease resistance, higher yields, and uniformity, often cultivated using intensive farming techniques and controlled environments to maximize production. Both types benefit from proper sunlight exposure and regular pruning, but hybrids tolerate varied conditions better due to their engineered traits.
Shelf Life and Storage
Heirloom tomatoes typically have a shorter shelf life than hybrid tomatoes due to their delicate skin and higher moisture content, making them more susceptible to spoilage. Hybrid tomatoes are bred for durability and often last longer in storage, staying fresh for up to two weeks when kept in a cool, dry place. For optimal preservation, both types should be stored at room temperature away from direct sunlight, with refrigeration reserved only for fully ripe tomatoes to prevent texture degradation.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Heirloom tomatoes contribute to sustainability through genetic diversity, supporting resilient ecosystems and reducing dependency on commercial seed suppliers. Hybrid tomatoes, bred for higher yields and disease resistance, often require more chemical inputs and monoculture farming, impacting soil health and biodiversity. Choosing heirloom varieties promotes environmental sustainability by preserving unique genetics and encouraging organic farming practices.
Price and Availability
Heirloom tomatoes typically cost more due to their limited availability and labor-intensive cultivation, often found in farmers' markets or specialty stores. Hybrid tomatoes are widely available year-round in most supermarkets, benefiting from mass production and enhanced shelf life that lower prices. Consumers seeking affordable and easy-to-find tomatoes usually opt for hybrids, while those valuing unique flavors and varieties pay a premium for heirlooms.
Which Tomato Is Best for You?
Heirloom tomatoes offer rich, diverse flavors and unique colors ideal for fresh salads and gourmet dishes, while hybrid tomatoes provide higher yields, disease resistance, and longer shelf life suited for commercial farming and consistent cooking results. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid tomatoes depends on your preference for flavor complexity versus convenience and durability. Consider heirloom varieties for exceptional taste in home gardens and hybrids for reliable productivity and versatility in cooking.
Heirloom Tomatoes vs Hybrid Tomatoes Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com