Plant-based diets emphasize fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and legumes, offering high fiber and essential nutrients with lower saturated fat content. Animal-based foods provide complete proteins, rich in vitamin B12, iron, and calcium but often come with higher cholesterol and saturated fats. Balancing both sources can support diverse nutritional needs and promote overall health.
Table of Comparison
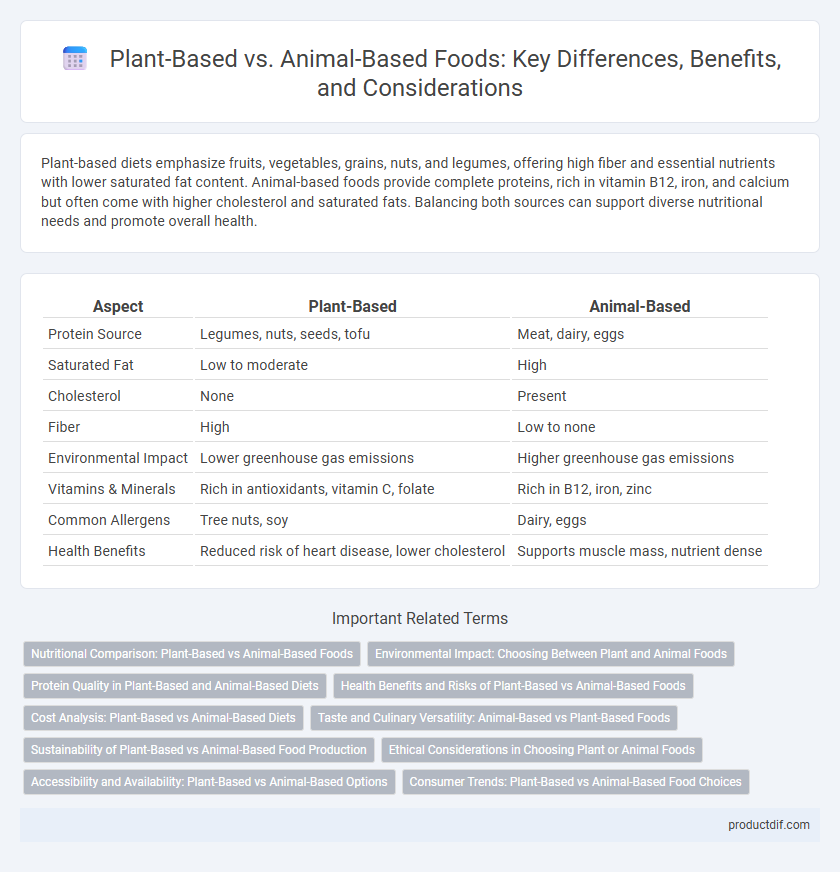
| Aspect | Plant-Based | Animal-Based |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Source | Legumes, nuts, seeds, tofu | Meat, dairy, eggs |
| Saturated Fat | Low to moderate | High |
| Cholesterol | None | Present |
| Fiber | High | Low to none |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions | Higher greenhouse gas emissions |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Rich in antioxidants, vitamin C, folate | Rich in B12, iron, zinc |
| Common Allergens | Tree nuts, soy | Dairy, eggs |
| Health Benefits | Reduced risk of heart disease, lower cholesterol | Supports muscle mass, nutrient dense |
Nutritional Comparison: Plant-Based vs Animal-Based Foods
Plant-based foods typically provide higher levels of dietary fiber, antioxidants, vitamins C and E, and phytochemicals that promote overall health and reduce chronic disease risks. Animal-based foods offer concentrated sources of complete proteins, vitamin B12, heme iron, and essential omega-3 fatty acids like DHA and EPA, which are crucial for brain function and muscle maintenance. A balanced diet incorporating both plant and animal sources can optimize nutrient intake and support diverse nutritional needs.
Environmental Impact: Choosing Between Plant and Animal Foods
Plant-based foods generally have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to animal-based foods, requiring less water, land, and greenhouse gas emissions. Livestock farming contributes to deforestation, methane emissions, and extensive resource use, intensifying climate change effects. Transitioning to a plant-based diet can reduce carbon footprints and promote more sustainable food systems globally.
Protein Quality in Plant-Based and Animal-Based Diets
Protein quality in plant-based diets varies due to incomplete amino acid profiles in many sources, often requiring combinations of legumes, grains, and nuts to achieve complete protein intake. Animal-based proteins typically provide all essential amino acids in adequate proportions, making them complete proteins with high bioavailability. Advances in food technology and protein blending now allow plant-based diets to meet or exceed traditional animal-based protein quality standards.
Health Benefits and Risks of Plant-Based vs Animal-Based Foods
Plant-based foods are rich in fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, which support heart health, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and certain cancers. Animal-based foods provide complete proteins and essential nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids but may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and certain cancers when consumed in excess. Balancing plant-based and animal-based foods can optimize nutrient intake while minimizing health risks associated with processed meats and saturated fats.
Cost Analysis: Plant-Based vs Animal-Based Diets
Plant-based diets generally incur lower costs due to the affordability of legumes, grains, and seasonal vegetables compared to animal-based products like meat, dairy, and eggs, which often require higher production expenses. Research indicates that substituting animal proteins with plant proteins can reduce grocery bills by up to 20-30% annually. Cost efficiency in plant-based diets is reinforced by bulk purchasing and reduced healthcare expenses associated with chronic diseases linked to high animal product consumption.
Taste and Culinary Versatility: Animal-Based vs Plant-Based Foods
Animal-based foods often provide rich umami flavors and a variety of textures that enhance savory dishes, while plant-based foods offer diverse flavors ranging from earthy to sweet, with the ability to absorb spices and seasonings. Culinary versatility in animal-based products includes uses in grilling, roasting, and broiling, delivering distinct char and caramelization, whereas plant-based alternatives excel in blending, marinating, and creating complex flavor profiles through herbs and natural umami sources like mushrooms and legumes. Both food types present unique taste experiences and preparation techniques that can be optimized depending on dietary preferences and culinary goals.
Sustainability of Plant-Based vs Animal-Based Food Production
Plant-based food production significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to animal-based systems, reducing carbon footprints by up to 70%. It also requires less land and water, with crops like legumes and grains using 50-80% fewer natural resources than livestock farming. Sustainable agriculture practices in plant-based diets contribute to biodiversity preservation and soil health, critical for long-term environmental balance.
Ethical Considerations in Choosing Plant or Animal Foods
Choosing plant-based foods significantly reduces animal suffering and supports more sustainable farming practices, addressing ethical concerns related to factory farming and animal cruelty. Animal-based foods often involve ethical dilemmas surrounding animal welfare, environmental degradation, and resource-intensive production methods. Emphasizing plant-based choices aligns with ethical priorities by promoting biodiversity, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and encouraging compassionate consumption.
Accessibility and Availability: Plant-Based vs Animal-Based Options
Plant-based foods have become increasingly accessible through growing availability in grocery stores, farmers' markets, and restaurants, often benefiting from expanding supply chains and consumer demand. Animal-based options remain widely available and deeply integrated into traditional food systems, with established distribution networks ensuring year-round access worldwide. Despite advancements in plant-based product variety, geographic and economic factors influence the overall accessibility and affordability of both food categories.
Consumer Trends: Plant-Based vs Animal-Based Food Choices
Consumer trends increasingly favor plant-based foods, driven by health, sustainability, and ethical considerations, leading to a surge in demand for alternatives such as plant-based meats and dairy substitutes. Market research indicates a significant growth rate in vegan and vegetarian product segments, with younger demographics showing the highest adoption rates. Despite this plant-based momentum, animal-based products remain dominant in many regions due to cultural preferences and perceived nutritional benefits.
Plant-Based vs Animal-Based Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com