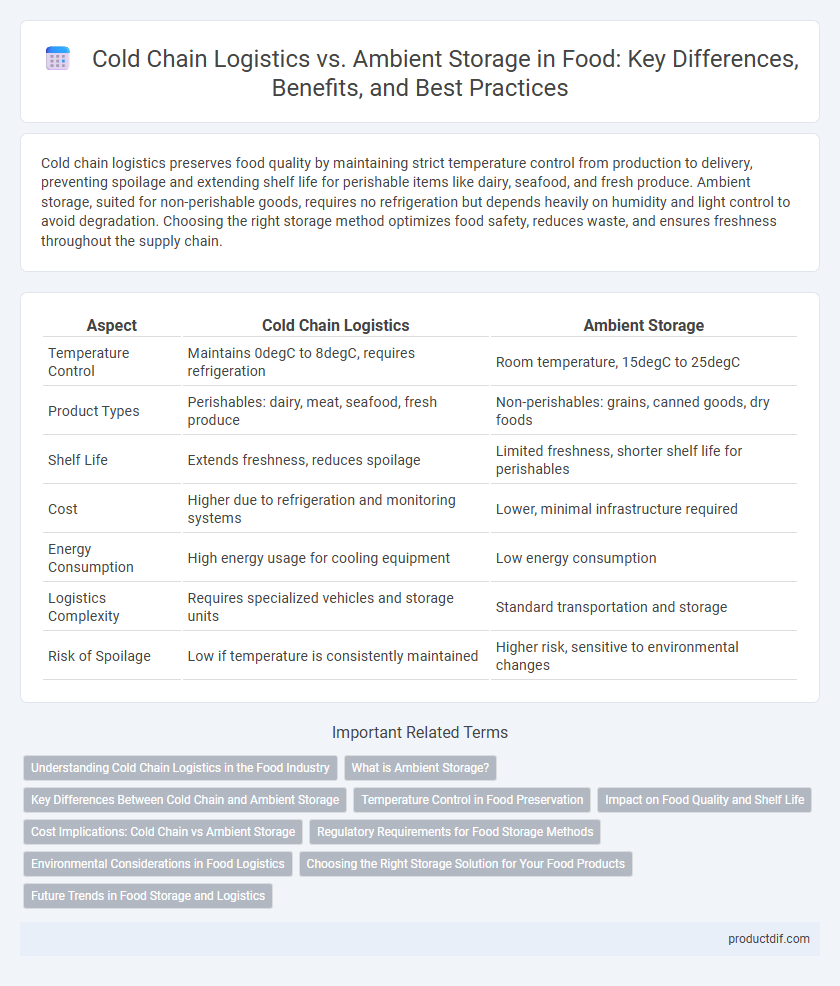
Cold chain logistics preserves food quality by maintaining strict temperature control from production to delivery, preventing spoilage and extending shelf life for perishable items like dairy, seafood, and fresh produce. Ambient storage, suited for non-perishable goods, requires no refrigeration but depends heavily on humidity and light control to avoid degradation. Choosing the right storage method optimizes food safety, reduces waste, and ensures freshness throughout the supply chain.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cold Chain Logistics | Ambient Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Maintains 0degC to 8degC, requires refrigeration | Room temperature, 15degC to 25degC |
| Product Types | Perishables: dairy, meat, seafood, fresh produce | Non-perishables: grains, canned goods, dry foods |
| Shelf Life | Extends freshness, reduces spoilage | Limited freshness, shorter shelf life for perishables |
| Cost | Higher due to refrigeration and monitoring systems | Lower, minimal infrastructure required |
| Energy Consumption | High energy usage for cooling equipment | Low energy consumption |
| Logistics Complexity | Requires specialized vehicles and storage units | Standard transportation and storage |
| Risk of Spoilage | Low if temperature is consistently maintained | Higher risk, sensitive to environmental changes |
Understanding Cold Chain Logistics in the Food Industry
Cold chain logistics in the food industry involves maintaining a temperature-controlled supply chain to preserve perishable items like dairy, meat, and seafood from farm to consumer, ensuring food safety and quality. This process includes refrigerated transportation, cold storage facilities, and temperature monitoring systems that prevent spoilage and bacterial growth. In contrast to ambient storage, cold chain logistics significantly extends shelf life and reduces food waste by maintaining stringent temperature regulations throughout the distribution network.
What is Ambient Storage?
Ambient storage refers to the method of storing food products at normal room temperature conditions, typically between 20degC and 25degC, without the need for refrigeration or freezing. This storage technique is ideal for shelf-stable foods such as canned goods, dry grains, and certain fruits and vegetables that do not require temperature control to maintain quality and safety. Ambient storage reduces energy costs and simplifies logistics compared to cold chain logistics, which involves strict temperature management throughout the supply chain.
Key Differences Between Cold Chain and Ambient Storage
Cold chain logistics involves temperature-controlled supply chains essential for preserving perishable foods, while ambient storage maintains products at room temperature suitable for non-perishable items. Key differences include temperature regulation, with cold chain requiring constant refrigeration between 0degC and 8degC, versus ambient storage typically ranging from 15degC to 25degC. Cold chain logistics ensures extended shelf life and safety for dairy, meat, and seafood, whereas ambient storage is adequate for cereals, canned goods, and dry products.
Temperature Control in Food Preservation
Cold chain logistics ensures strict temperature control from production to delivery, preserving food quality and extending shelf life by maintaining consistent refrigeration between 0degC and 4degC for perishable items. Ambient storage, typically at room temperature (20degC to 25degC), is suitable for non-perishable foods but risks microbial growth and nutrient degradation in sensitive products. Effective temperature management in cold chain logistics mitigates spoilage, enhances food safety, and reduces food waste compared to ambient storage environments.
Impact on Food Quality and Shelf Life
Cold chain logistics maintains food products at precise low temperatures, significantly slowing microbial growth and enzymatic reactions, which extends shelf life and preserves nutritional quality. In contrast, ambient storage exposes food to fluctuating temperatures that accelerate spoilage, nutrient degradation, and texture deterioration. Employing cold chain systems is critical for perishable items like dairy, seafood, and fresh produce to ensure safety and maximize freshness.
Cost Implications: Cold Chain vs Ambient Storage
Cold chain logistics involves refrigerated transportation and storage, which significantly increases operational costs due to energy consumption, specialized equipment, and monitoring systems. Ambient storage reduces expenses by maintaining products at room temperature but risks higher spoilage rates and shorter shelf life, potentially impacting overall profitability. Businesses must balance the upfront and ongoing costs of cold chain logistics against the potential losses from ambient storage to optimize supply chain efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Regulatory Requirements for Food Storage Methods
Cold Chain Logistics must comply with strict temperature control regulations such as FDA 21 CFR Part 11 and the EU's HACCP guidelines to ensure perishable foods remain safe from microbial growth. Ambient Storage, governed by standards like the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) and ISO 22000, emphasizes controlled humidity and contamination prevention but does not require constant refrigeration. Regulatory requirements for both methods mandate traceability, record-keeping, and risk assessment to maintain food quality and consumer safety throughout storage and distribution.
Environmental Considerations in Food Logistics
Cold chain logistics requires significant energy consumption due to refrigeration units operating continuously, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions compared to ambient storage, which relies on natural temperature conditions with minimal energy use. Ambient storage reduces carbon footprint by eliminating the need for powered cooling systems, but may increase food spoilage risk for perishable goods, leading to potential waste and environmental impact. Optimizing cold chain efficiency with renewable energy sources and advanced insulation technologies can mitigate environmental concerns while ensuring food safety in perishable product transportation.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution for Your Food Products
Selecting the appropriate storage solution depends on the specific temperature requirements and shelf life of food products. Cold chain logistics ensures optimal preservation for perishable items like dairy, seafood, and fresh produce by maintaining consistent refrigeration from production to delivery. Ambient storage suits non-perishable goods such as canned foods and grains, reducing energy costs while providing adequate protection.
Future Trends in Food Storage and Logistics
Cold chain logistics will increasingly integrate advanced IoT sensors and AI-driven temperature monitoring systems to ensure the freshness and safety of perishable food products during transportation. Ambient storage methods are evolving with innovations in modified atmosphere packaging and natural preservatives to extend shelf life without refrigeration. Sustainable practices such as energy-efficient refrigeration technologies and blockchain for transparent supply chain tracking are shaping the future of food storage and logistics.
Cold Chain Logistics vs Ambient Storage Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com