A2 milk contains only the A2 beta-casein protein, which may be easier to digest and cause fewer gastrointestinal issues compared to conventional milk that contains both A1 and A2 proteins. Research suggests that individuals with lactose intolerance or milk sensitivity might experience less discomfort with A2 milk. Choosing A2 milk can be beneficial for those seeking a milk alternative that supports digestive health without compromising nutritional value.
Table of Comparison
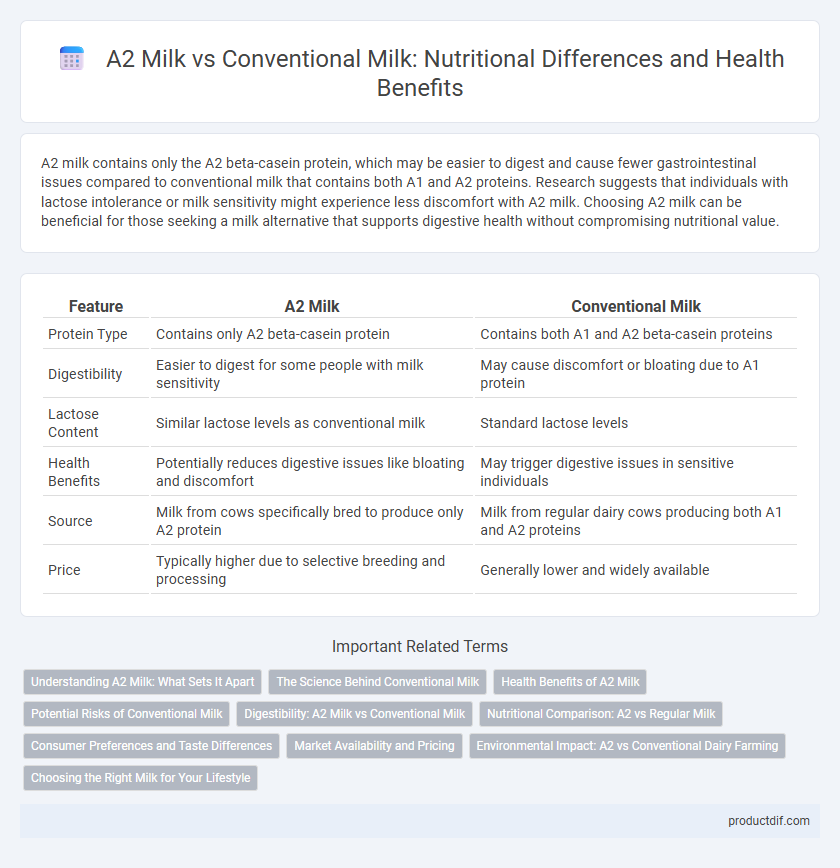
| Feature | A2 Milk | Conventional Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Type | Contains only A2 beta-casein protein | Contains both A1 and A2 beta-casein proteins |
| Digestibility | Easier to digest for some people with milk sensitivity | May cause discomfort or bloating due to A1 protein |
| Lactose Content | Similar lactose levels as conventional milk | Standard lactose levels |
| Health Benefits | Potentially reduces digestive issues like bloating and discomfort | May trigger digestive issues in sensitive individuals |
| Source | Milk from cows specifically bred to produce only A2 protein | Milk from regular dairy cows producing both A1 and A2 proteins |
| Price | Typically higher due to selective breeding and processing | Generally lower and widely available |
Understanding A2 Milk: What Sets It Apart
A2 milk contains only the A2 beta-casein protein, unlike conventional milk, which typically includes both A1 and A2 proteins. The difference in protein structure affects digestion, with A2 milk often associated with reduced gastrointestinal discomfort for individuals sensitive to A1 protein. Scientific studies suggest that A2 beta-casein may be easier to digest, making A2 milk a preferred choice for people with milk intolerance issues.
The Science Behind Conventional Milk
Conventional milk contains a complex mixture of proteins, fats, lactose, vitamins, and minerals, with casein and whey being the primary proteins influencing digestion and allergenic responses. Pasteurization and homogenization processes impact its nutritional profile and shelf life, but some bioactive components may be reduced during processing. The presence of A1 beta-casein protein in conventional milk is linked in scientific studies to digestive discomfort and inflammation in sensitive individuals, distinguishing it from A2 milk which contains only the A2 beta-casein variant.
Health Benefits of A2 Milk
A2 milk contains only the A2 beta-casein protein, which may reduce digestive discomfort and inflammation compared to conventional milk that contains both A1 and A2 proteins. Clinical studies suggest A2 milk can improve gut health by minimizing symptoms like bloating and abdominal pain in lactose intolerant individuals. Its easier digestibility and potential to lower the risk of heart disease and type 1 diabetes make A2 milk a healthier alternative to regular dairy products.
Potential Risks of Conventional Milk
Conventional milk often contains trace amounts of antibiotics and hormones used in dairy farming, which may pose health risks such as antibiotic resistance and hormonal imbalances. Its higher levels of A1 beta-casein protein have been linked to digestive discomfort and increased inflammation in sensitive individuals. Exposure to pesticides and contaminants from conventional farming practices further elevates the potential health hazards associated with regular consumption of conventional milk.
Digestibility: A2 Milk vs Conventional Milk
A2 milk contains only the A2 beta-casein protein, which breaks down more easily in the digestive tract compared to conventional milk that contains both A1 and A2 beta-casein proteins. The A1 protein in conventional milk can release beta-casomorphin-7 (BCM-7), a peptide linked to digestive discomfort in some individuals. Studies suggest that A2 milk may reduce symptoms like bloating and indigestion, making it a potentially better option for those with milk sensitivity.
Nutritional Comparison: A2 vs Regular Milk
A2 milk contains only the A2 beta-casein protein, which may be easier to digest for individuals sensitive to conventional milk that has both A1 and A2 proteins. Nutritionally, A2 milk provides similar amounts of protein, calcium, and vitamins D and B12 compared to regular milk, ensuring equivalent benefits for bone health and muscle repair. Some studies suggest A2 milk might reduce digestive discomfort without compromising essential nutrients found in conventional milk.
Consumer Preferences and Taste Differences
A2 milk contains only the A2 beta-casein protein, which some consumers prefer due to reported easier digestion and reduced discomfort compared to conventional milk containing both A1 and A2 proteins. Taste tests reveal subtle differences where A2 milk is often described as creamier and milder, influencing consumer preference toward perceived purity and digestive benefits. Market trends indicate a growing segment of health-conscious buyers prioritizing A2 milk for its potential suitability for sensitive stomachs and distinctive flavor profile.
Market Availability and Pricing
A2 milk is gaining market availability in health-focused stores and online platforms, often priced 20-40% higher than conventional milk due to its perceived health benefits and specialized production process. Conventional milk remains widely available in supermarkets, benefiting from established supply chains and economies of scale that keep its price lower and more accessible to the general consumer. The rising consumer demand for A2 milk is gradually expanding its retail presence but has not yet matched the distribution breadth of conventional milk.
Environmental Impact: A2 vs Conventional Dairy Farming
A2 milk production often involves smaller-scale, pasture-based dairy farms that prioritize sustainable practices, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions and improved soil health compared to conventional milk farming. Conventional dairy operations typically rely on intensive farming methods with higher carbon footprints due to greater feed, water usage, and methane emissions from large herds. Studies indicate that A2 dairies contribute to reduced environmental degradation by supporting biodiversity and minimizing resource consumption.
Choosing the Right Milk for Your Lifestyle
A2 milk contains only the A2 beta-casein protein, which may be easier to digest for individuals sensitive to conventional milk's A1 protein, making it a suitable choice for those with mild lactose intolerance or digestive discomfort. Conventional milk, rich in nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein, supports overall bone health and muscle function, ideal for individuals without milk protein sensitivities. Selecting the right milk depends on your digestive health, nutritional needs, and personal taste preferences to ensure optimal wellness.
A2 Milk vs Conventional Milk Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com