Minimal-ingredient foods emphasize simplicity and purity, often containing only a few natural components to enhance flavor and nutritional value without additives. Multi-ingredient foods offer complex flavors and textures by combining various elements, catering to diverse tastes and culinary creativity. Choosing between minimal and multi-ingredient foods depends on dietary preferences, health goals, and cooking styles.
Table of Comparison
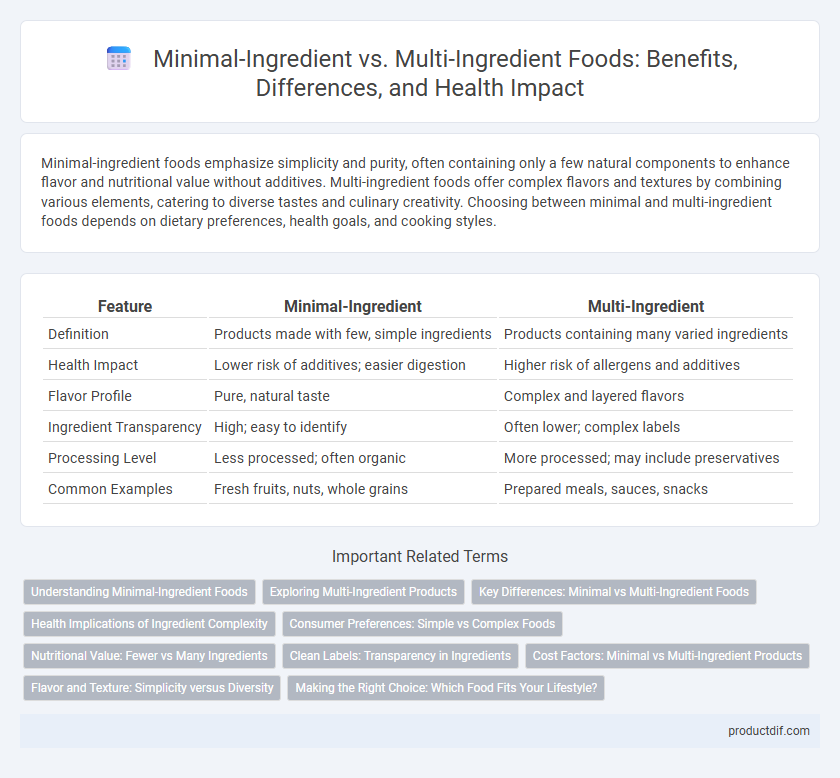
| Feature | Minimal-Ingredient | Multi-Ingredient |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Products made with few, simple ingredients | Products containing many varied ingredients |
| Health Impact | Lower risk of additives; easier digestion | Higher risk of allergens and additives |
| Flavor Profile | Pure, natural taste | Complex and layered flavors |
| Ingredient Transparency | High; easy to identify | Often lower; complex labels |
| Processing Level | Less processed; often organic | More processed; may include preservatives |
| Common Examples | Fresh fruits, nuts, whole grains | Prepared meals, sauces, snacks |
Understanding Minimal-Ingredient Foods
Minimal-ingredient foods prioritize simplicity by containing few, whole-food components, enhancing transparency and reducing exposure to additives or preservatives. These foods often appeal to health-conscious consumers seeking natural flavors and straightforward nutrition. Emphasizing minimal ingredients can improve digestibility and support cleaner eating habits by focusing on purity and quality.
Exploring Multi-Ingredient Products
Multi-ingredient food products offer complex flavor profiles and enhanced nutritional benefits by combining diverse natural components such as spices, herbs, fruits, and vegetables. These products cater to consumers seeking varied taste experiences and functional health properties in a single item, often incorporating antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals from multiple sources. Exploring multi-ingredient foods involves analyzing ingredient synergy, quality, and potential allergen impact to optimize product development and consumer satisfaction.
Key Differences: Minimal vs Multi-Ingredient Foods
Minimal-ingredient foods contain only a few, simple components, typically emphasizing whole, natural products with limited processing, which supports cleaner labeling and often appeals to health-conscious consumers. Multi-ingredient foods consist of a larger variety of components, including additives, preservatives, and flavorings, offering complex flavors and longer shelf life but potentially introducing allergens or synthetic substances. The key difference lies in ingredient transparency and nutritional simplicity versus culinary complexity and extended durability.
Health Implications of Ingredient Complexity
Minimal-ingredient foods typically contain fewer additives and preservatives, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and digestive issues compared to multi-ingredient products. Complex ingredient lists often include artificial additives, flavor enhancers, and high levels of sugar or sodium, which can contribute to chronic health conditions such as hypertension and obesity. Choosing simpler ingredient profiles supports better nutrient absorption and minimizes exposure to potentially harmful chemicals.
Consumer Preferences: Simple vs Complex Foods
Consumers increasingly favor minimal-ingredient foods for their perceived purity, transparency, and ease of digestion, driving demand for products with short, recognizable ingredient lists. Conversely, multi-ingredient foods appeal to those seeking complex flavor profiles, enhanced textures, and nutritional variety, often found in gourmet or ethnic cuisines. Market trends indicate a growing split, with health-conscious buyers prioritizing simplicity while adventurous eaters explore intricate culinary combinations.
Nutritional Value: Fewer vs Many Ingredients
Minimal-ingredient foods often deliver concentrated nutritional value by emphasizing whole, natural components with fewer additives, reducing the risk of unnecessary sugars, preservatives, and artificial flavors. Multi-ingredient foods may offer a broader spectrum of nutrients by combining diverse ingredients but can also introduce excess calories, sodium, and allergens. Evaluating the nutritional label is essential to balance the simplicity of minimal-ingredient products against the complexity and potential nutrient density of multi-ingredient options.
Clean Labels: Transparency in Ingredients
Clean labels prioritize transparency by listing simple, minimal ingredients that are easily recognizable and understood by consumers seeking natural food options. Minimal-ingredient products reduce additives, preservatives, and artificial components, aligning with growing consumer demand for purity and health-conscious choices. Multi-ingredient foods may offer complexity in flavor but often contain more synthetic substances, complicating transparency and potentially undermining clean label benefits.
Cost Factors: Minimal vs Multi-Ingredient Products
Minimal-ingredient products typically incur lower production costs due to reduced raw material expenses and simplified manufacturing processes, which can translate into more affordable retail prices. Multi-ingredient products often involve higher costs from sourcing diverse components, complex blending, and additional quality control measures, increasing overall expenses. Cost factors such as ingredient sourcing, processing complexity, and packaging also contribute significantly to the price difference between minimal and multi-ingredient food products.
Flavor and Texture: Simplicity versus Diversity
Minimal-ingredient recipes emphasize pure, natural flavors and straightforward textures, allowing each component to shine without overwhelming complexity. Multi-ingredient dishes offer diverse flavor profiles and intricate textures, creating layered culinary experiences that engage multiple senses. Balancing simplicity and diversity depends on the desired taste intensity and textural contrast in the final dish.
Making the Right Choice: Which Food Fits Your Lifestyle?
Choosing between minimal-ingredient and multi-ingredient foods depends on your lifestyle priorities, dietary restrictions, and health goals. Minimal-ingredient foods offer transparency and simplicity, ideal for those seeking whole, unprocessed options with fewer allergens and additives. Multi-ingredient foods provide complex flavors and enhanced nutrition, fitting active lifestyles that require convenience and variety in nutrient intake.
Minimal-Ingredient vs Multi-Ingredient Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com