Artisanal production emphasizes handcrafted techniques, quality ingredients, and unique flavors, resulting in products with distinct character and higher perceived value. Mass production relies on standardized processes and large-scale efficiency to deliver consistent products at lower costs, often sacrificing individuality and complexity. Choosing between artisanal and mass-produced foods depends on consumer priorities such as authenticity, quality, and affordability.
Table of Comparison
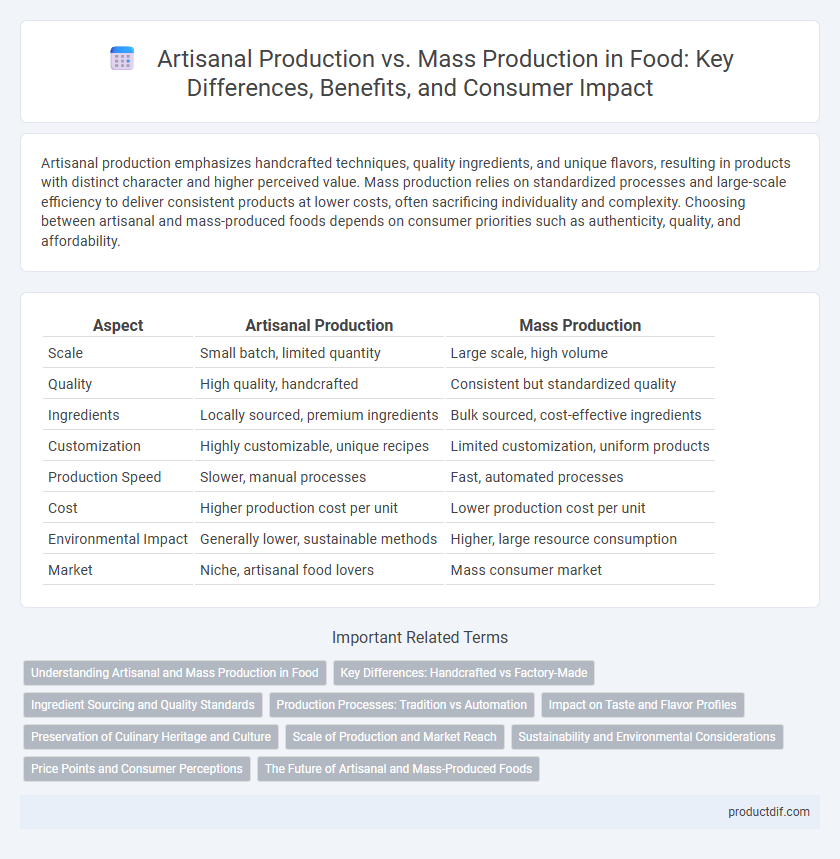
| Aspect | Artisanal Production | Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Small batch, limited quantity | Large scale, high volume |
| Quality | High quality, handcrafted | Consistent but standardized quality |
| Ingredients | Locally sourced, premium ingredients | Bulk sourced, cost-effective ingredients |
| Customization | Highly customizable, unique recipes | Limited customization, uniform products |
| Production Speed | Slower, manual processes | Fast, automated processes |
| Cost | Higher production cost per unit | Lower production cost per unit |
| Environmental Impact | Generally lower, sustainable methods | Higher, large resource consumption |
| Market | Niche, artisanal food lovers | Mass consumer market |
Understanding Artisanal and Mass Production in Food
Artisanal food production emphasizes handcrafted techniques, small batch sizes, and high-quality, often locally sourced ingredients, resulting in unique flavors and textures. Mass production involves large-scale manufacturing processes utilizing standardized recipes, automation, and cost-efficient methods to ensure consistent products and widespread distribution. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers appreciate the trade-offs between authenticity, craftsmanship, and accessibility in the food industry.
Key Differences: Handcrafted vs Factory-Made
Artisanal food production emphasizes handcrafted techniques, relying on skilled artisans who use traditional methods to create unique, high-quality products with distinct flavors and textures. In contrast, mass production employs automated factory processes designed for large-scale output, prioritizing uniformity, consistency, and efficiency over individual craftsmanship. This key difference affects product variety, ingredient sourcing, and the overall consumer experience in the food industry.
Ingredient Sourcing and Quality Standards
Artisanal production prioritizes sourcing high-quality, often locally-sourced ingredients with strict adherence to traditional methods, ensuring distinctive flavors and superior freshness. Mass production relies on large-scale ingredient procurement, often from global suppliers, emphasizing cost-efficiency but potentially compromising consistency and ingredient quality. Quality standards in artisanal food emphasize small-batch control and authenticity, whereas mass production focuses on uniformity and meeting regulatory benchmarks for large quantities.
Production Processes: Tradition vs Automation
Artisanal production relies on traditional handcrafted methods, emphasizing skill, precision, and small-batch quality control to preserve flavor and texture. Mass production utilizes automated machinery and standardized processes to achieve high volume, consistency, and cost efficiency. The contrast between the precision of human craftsmanship and the speed of mechanized workflows defines the core difference in food manufacturing practices.
Impact on Taste and Flavor Profiles
Artisanal production preserves complex, nuanced flavor profiles by using traditional methods and high-quality, locally sourced ingredients, resulting in richer and more distinctive taste experiences. Mass production often relies on standardized processes and additives to ensure consistency, which can dilute flavors and reduce the depth typically found in handcrafted foods. Flavor intensity and variety are generally superior in artisanal goods due to slower fermentation, minimal processing, and careful ingredient selection.
Preservation of Culinary Heritage and Culture
Artisanal food production plays a crucial role in preserving culinary heritage by maintaining traditional recipes, techniques, and local ingredients that reflect cultural identity. Unlike mass production, which often prioritizes efficiency and uniformity, artisanal methods sustain regional flavors and craftsmanship passed down through generations. This dedication to authenticity supports the survival of diverse food cultures and promotes a deeper appreciation of gastronomic history.
Scale of Production and Market Reach
Artisanal food production emphasizes small-scale, handcrafted processes with limited batch sizes, resulting in unique flavors and high-quality ingredients. Mass production employs automated techniques and large-scale facilities to produce standardized products at high volume, optimizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The market reach for artisanal foods tends to be niche and localized, while mass-produced foods cater to expansive, often global distribution networks.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Artisanal food production minimizes environmental impact by utilizing local ingredients and traditional methods that reduce waste and energy consumption. Mass production often relies on large-scale industrial processes that contribute to higher carbon emissions, resource depletion, and packaging waste. Sustainable food systems benefit from artisanal practices by promoting biodiversity, supporting small-scale farmers, and fostering eco-friendly consumption patterns.
Price Points and Consumer Perceptions
Artisanal food production often commands higher price points due to its emphasis on quality ingredients, handcrafted techniques, and limited batch sizes, attracting consumers who value authenticity and uniqueness. In contrast, mass-produced foods benefit from economies of scale, offering lower prices but sometimes perceived as less flavorful or nutritious. Consumer perceptions heavily favor artisanal products for their premium experience, though affordability keeps mass production dominant in everyday purchasing decisions.
The Future of Artisanal and Mass-Produced Foods
Artisanal food production emphasizes quality, unique flavors, and sustainable practices, appealing to consumers seeking authenticity and health-conscious options. Mass-produced foods leverage technology and scale to meet global demand with consistent prices and accessibility, driving innovation in food preservation and packaging. The future of food lies in integrating artisanal craftsmanship with advanced mass production techniques to balance tradition, efficiency, and environmental impact.
Artisanal Production vs Mass Production Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com