Direct trade coffee emphasizes transparent relationships and higher quality beans by eliminating middlemen, ensuring farmers receive better compensation and consumers get fresher coffee. Fair trade coffee focuses on ethical labor practices and community development, guaranteeing minimum prices and premiums to support sustainable farming. Both approaches aim to improve farmers' livelihoods but differ in structure, with direct trade prioritizing quality and traceability while fair trade centers on social equity and certification standards.
Table of Comparison
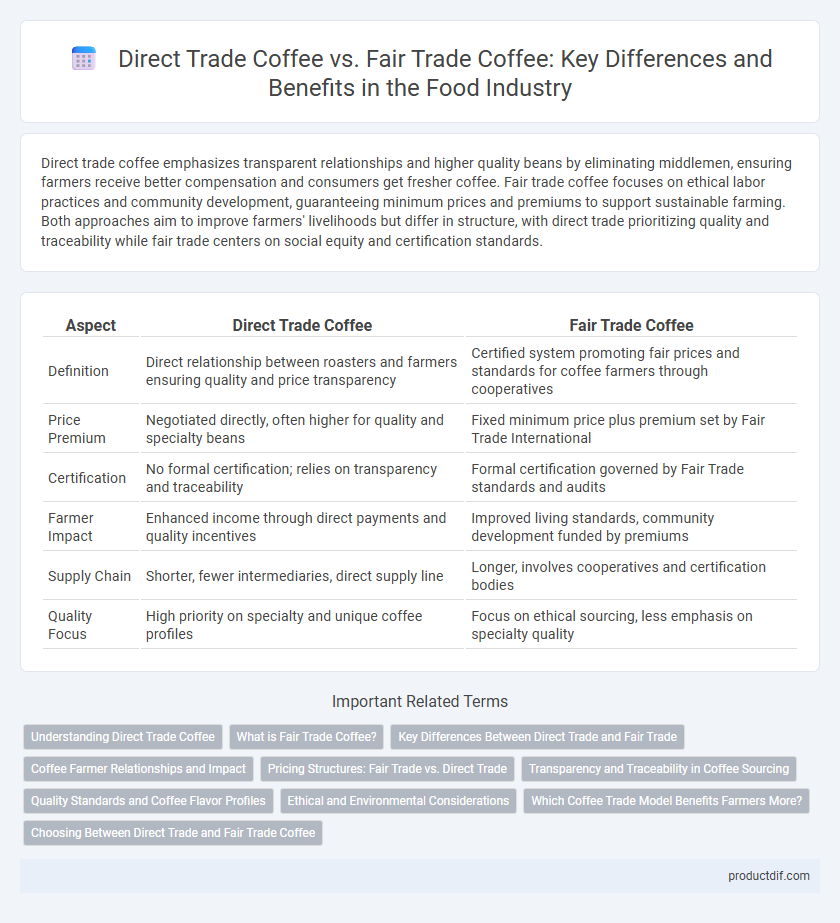
| Aspect | Direct Trade Coffee | Fair Trade Coffee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct relationship between roasters and farmers ensuring quality and price transparency | Certified system promoting fair prices and standards for coffee farmers through cooperatives |
| Price Premium | Negotiated directly, often higher for quality and specialty beans | Fixed minimum price plus premium set by Fair Trade International |
| Certification | No formal certification; relies on transparency and traceability | Formal certification governed by Fair Trade standards and audits |
| Farmer Impact | Enhanced income through direct payments and quality incentives | Improved living standards, community development funded by premiums |
| Supply Chain | Shorter, fewer intermediaries, direct supply line | Longer, involves cooperatives and certification bodies |
| Quality Focus | High priority on specialty and unique coffee profiles | Focus on ethical sourcing, less emphasis on specialty quality |
Understanding Direct Trade Coffee
Direct Trade Coffee emphasizes building transparent relationships between coffee roasters and farmers, ensuring higher quality beans and better prices for growers. This model bypasses intermediaries, allowing roasters to pay premiums based on bean quality and farmers to invest directly in sustainable practices. Fostering traceability and accountability, Direct Trade Coffee enhances coffee origin stories and promotes ethical sourcing.
What is Fair Trade Coffee?
Fair Trade coffee is sourced from growers who receive fair prices and premiums aimed at fostering sustainable farming practices and improving community welfare. This certification emphasizes ethical labor conditions, environmental standards, and transparency throughout the supply chain. By supporting Fair Trade coffee, consumers contribute to social equity and economic stability for small-scale farmers in developing countries.
Key Differences Between Direct Trade and Fair Trade
Direct Trade Coffee emphasizes transparent relationships and higher premiums paid directly to farmers, ensuring quality and ethical sourcing without third-party certification. Fair Trade Coffee relies on standardized certification systems that guarantee minimum prices and social premiums, supporting community development and environmental standards. The key differences lie in the level of farmer involvement, certification processes, and pricing mechanisms that impact sustainability and supply chain dynamics.
Coffee Farmer Relationships and Impact
Direct Trade Coffee fosters close, transparent relationships between roasters and coffee farmers, often resulting in higher premiums and tailored support that improves farm quality and sustainability. Fair Trade Coffee establishes a standardized certification ensuring minimum price guarantees and community development funds, but can sometimes limit direct interaction or flexibility for farmers. Both models aim to empower coffee growers, yet Direct Trade emphasizes personalized partnerships while Fair Trade focuses on collective standards and social impact.
Pricing Structures: Fair Trade vs. Direct Trade
Fair Trade coffee involves fixed minimum prices to protect farmers from volatile market fluctuations, ensuring a guaranteed income irrespective of global coffee price changes. Direct Trade coffee emphasizes negotiated prices between roasters and farmers, often resulting in premium payments tied to quality and relationship, which can exceed Fair Trade minimums. These pricing structures influence farmer incentives, with Fair Trade offering stability and Direct Trade potentially providing higher earnings through quality differentiation.
Transparency and Traceability in Coffee Sourcing
Direct Trade Coffee ensures higher transparency and traceability by establishing direct relationships with coffee farmers, allowing roasters to verify the exact origin, farming practices, and quality of the beans. Fair Trade Coffee offers traceability through certification and auditing processes, but intermediaries often limit direct communication between producers and buyers. Transparency in Direct Trade leads to better accountability and tailored support for farmers, enhancing sustainable practices and premium coffee quality.
Quality Standards and Coffee Flavor Profiles
Direct Trade Coffee emphasizes stringent quality standards by sourcing beans directly from farmers, ensuring meticulous selection and superior freshness that often results in vibrant, complex flavor profiles with bright acidity and nuanced fruit notes. Fair Trade Coffee prioritizes ethical sourcing and community development, with quality standards that are moderate but can vary widely, typically producing a more consistent yet less distinctive flavor profile characterized by balanced body and mild acidity. Both certifications impact coffee quality and flavor, but Direct Trade tends to deliver higher-grade beans and more pronounced, unique taste experiences due to closer farmer relationships and rigorous quality control.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
Direct Trade Coffee ensures ethical practices by establishing transparent, direct relationships with farmers, resulting in higher wages and improved working conditions, while reducing intermediaries that often exploit producers. Fair Trade Coffee emphasizes community development and environmental sustainability through certification standards requiring fair prices, organic farming, and eco-friendly practices to minimize deforestation and chemical use. Both methods promote ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship, but Direct Trade allows for more flexible agreements tailored to individual farmer needs, potentially enhancing social and ecological impacts.
Which Coffee Trade Model Benefits Farmers More?
Direct Trade Coffee offers farmers higher premiums by cutting out intermediaries and fostering close relationships with roasters, leading to better quality control and increased profits. Fair Trade Coffee provides a guaranteed minimum price and social premiums to support community development but often involves additional certification costs and less price flexibility. Overall, Direct Trade tends to benefit farmers more financially by promoting transparency and rewarding quality, though Fair Trade ensures baseline economic stability and social support.
Choosing Between Direct Trade and Fair Trade Coffee
Choosing between Direct Trade and Fair Trade coffee involves evaluating transparency and impact on farmers. Direct Trade emphasizes close relationships between roasters and farmers, often resulting in higher-quality beans and better compensation by eliminating intermediaries. Fair Trade focuses on certification standards that guarantee minimum prices and social welfare, ensuring ethical sourcing but sometimes lacking in direct farmer engagement and pricing flexibility.
Direct Trade Coffee vs Fair Trade Coffee Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com