Ethnic cuisine offers authentic flavors and traditional recipes rooted in specific cultures, preserving culinary heritage and regional ingredients. Fusion cuisine blends elements from multiple culinary traditions, creating innovative dishes that appeal to diverse palates and encourage creativity in the kitchen. Both approaches enrich the food landscape by celebrating cultural identity and pushing the boundaries of flavor combinations.
Table of Comparison
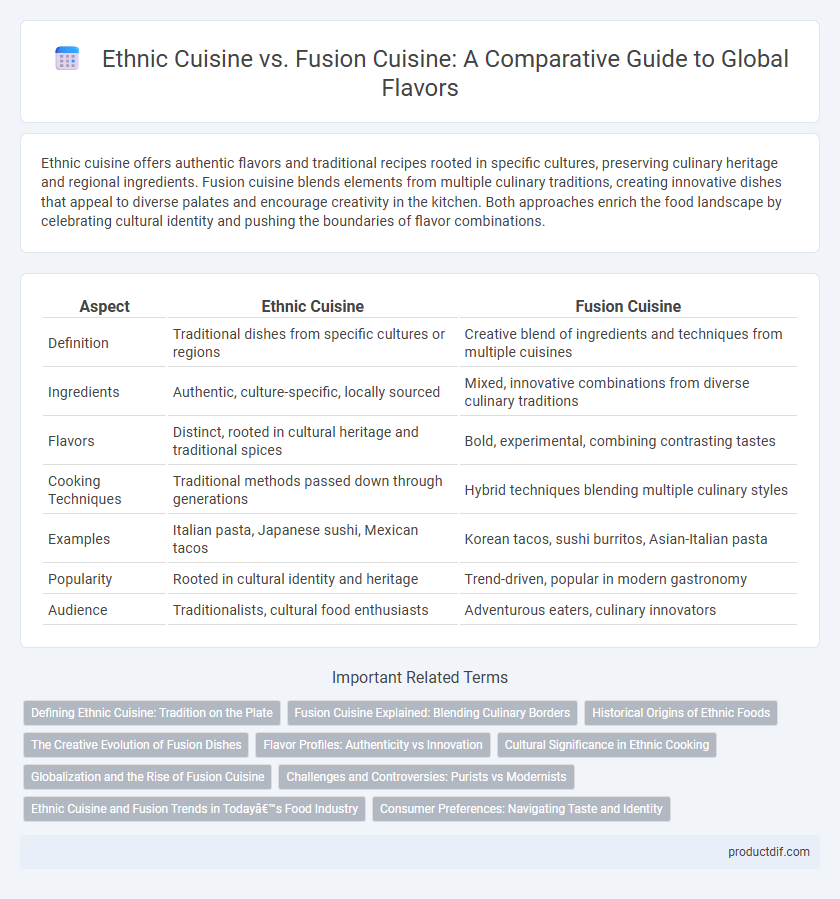
| Aspect | Ethnic Cuisine | Fusion Cuisine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional dishes from specific cultures or regions | Creative blend of ingredients and techniques from multiple cuisines |
| Ingredients | Authentic, culture-specific, locally sourced | Mixed, innovative combinations from diverse culinary traditions |
| Flavors | Distinct, rooted in cultural heritage and traditional spices | Bold, experimental, combining contrasting tastes |
| Cooking Techniques | Traditional methods passed down through generations | Hybrid techniques blending multiple culinary styles |
| Examples | Italian pasta, Japanese sushi, Mexican tacos | Korean tacos, sushi burritos, Asian-Italian pasta |
| Popularity | Rooted in cultural identity and heritage | Trend-driven, popular in modern gastronomy |
| Audience | Traditionalists, cultural food enthusiasts | Adventurous eaters, culinary innovators |
Defining Ethnic Cuisine: Tradition on the Plate
Ethnic cuisine represents traditional foods that are deeply rooted in the culture, history, and geography of a specific region or community, showcasing authentic flavors and cooking methods passed down through generations. These dishes emphasize heritage ingredients and culinary practices unique to their origins, offering a genuine taste experience that reflects cultural identity. Unlike fusion cuisine, ethnic cuisine prioritizes preserving traditional recipes and the cultural stories embedded in each meal.
Fusion Cuisine Explained: Blending Culinary Borders
Fusion cuisine blends diverse culinary traditions by combining ingredients, techniques, and flavors from different cultures to create innovative dishes. This approach transcends ethnic cuisine's emphasis on preserving traditional recipes, offering a dynamic dining experience characterized by originality and experimentation. By harmonizing elements from Asian, European, Latin American, and other food cultures, fusion cuisine redefines global gastronomy and broadens palates worldwide.
Historical Origins of Ethnic Foods
Ethnic cuisine originates from specific cultural and geographic traditions, often rooted in centuries of regional agricultural practices, religious customs, and historical events that shaped food preparation and ingredient use. Traditional dishes like Italian pasta, Indian curry, or Mexican mole reflect the historical context of their native regions, preserving unique flavors and cooking techniques passed down through generations. Fusion cuisine, by contrast, blends elements from multiple ethnic backgrounds, creating innovative dishes that evolve beyond original cultural boundaries.
The Creative Evolution of Fusion Dishes
Fusion cuisine represents the creative evolution of ethnic dishes by blending traditional flavors and cooking techniques from diverse cultures, resulting in innovative culinary experiences. Chefs experiment with cross-cultural ingredients such as Asian spices combined with Mediterranean herbs, crafting unique flavor profiles that challenge conventional food boundaries. This dynamic approach not only celebrates cultural diversity but also pushes the limits of gastronomy, attracting adventurous diners seeking novel tastes.
Flavor Profiles: Authenticity vs Innovation
Ethnic cuisine emphasizes authentic flavor profiles rooted in traditional spices, herbs, and cooking methods that reflect cultural heritage and regional ingredients. Fusion cuisine innovates by blending diverse culinary techniques and ingredients from multiple ethnic backgrounds, creating bold, unexpected flavor combinations that challenge conventional taste boundaries. Both approaches offer unique gustatory experiences, with ethnic cuisine preserving time-honored authenticity and fusion cuisine driving creative, dynamic flavor exploration.
Cultural Significance in Ethnic Cooking
Ethnic cuisine preserves traditional cooking methods and recipes that embody the history, values, and identity of specific cultural groups, serving as a culinary archive passed down through generations. The ingredients, techniques, and flavors are deeply rooted in regional resources and social customs, reinforcing cultural continuity and community bonds. In contrast, fusion cuisine merges elements from multiple ethnic backgrounds, creating innovative dishes that reflect globalization and cultural exchange rather than singular, historical narratives.
Globalization and the Rise of Fusion Cuisine
Globalization has accelerated the blending of diverse culinary traditions, giving rise to fusion cuisine, which creatively combines elements from multiple ethnic cuisines. This trend reflects increasingly interconnected food cultures as chefs experiment with flavors, techniques, and ingredients from around the world. Fusion cuisine appeals to adventurous diners seeking novel taste experiences that transcend traditional ethnic boundaries.
Challenges and Controversies: Purists vs Modernists
Ethnic cuisine often faces challenges from purists who argue that traditional recipes should be preserved without alteration, emphasizing cultural authenticity and heritage. Fusion cuisine, favored by modernists, blends elements from multiple culinary traditions, sparking controversy over cultural appropriation and the dilution of original flavors. This tension highlights ongoing debates about respect for food origins versus innovation in gastronomy.
Ethnic Cuisine and Fusion Trends in Today’s Food Industry
Ethnic cuisine preserves traditional culinary practices and authentic flavors rooted in specific cultures, offering consumers an immersive gastronomic experience that highlights diverse ingredients and cooking techniques. Fusion cuisine blends elements from multiple ethnic culinary traditions, creating innovative dishes that appeal to adventurous palates and promote cross-cultural food exploration. Trends in today's food industry show a growing appreciation for ethnic cuisine's authenticity alongside the creative expansion driven by fusion, with chefs and restaurants leveraging both to meet evolving consumer demands for originality and cultural connection.
Consumer Preferences: Navigating Taste and Identity
Consumer preferences in ethnic cuisine emphasize authenticity, cultural heritage, and traditional flavor profiles that connect diners to specific regions and histories. Fusion cuisine appeals to adventurous eaters seeking innovative combinations and novel taste experiences that blend multiple culinary traditions. Balancing taste and identity, consumers often choose ethnic cuisine for genuine cultural immersion, while fusion cuisine attracts those valuing creativity and modernization in food.
Ethnic cuisine vs Fusion cuisine Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com