Free-range poultry benefits from natural foraging, leading to better flavor and higher nutritional value compared to confined birds raised in limited space with restricted movement. Confined animals often experience stress and receive more antibiotics, which can impact meat quality and consumer health. Choosing free-range options supports animal welfare and promotes sustainable farming practices.
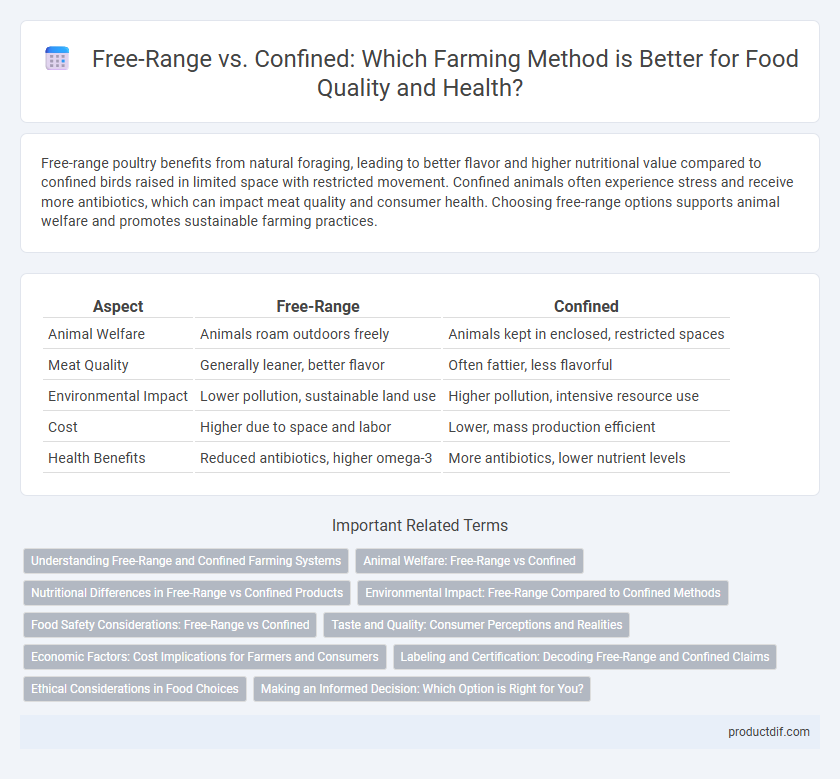
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Free-Range | Confined |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Welfare | Animals roam outdoors freely | Animals kept in enclosed, restricted spaces |
| Meat Quality | Generally leaner, better flavor | Often fattier, less flavorful |
| Environmental Impact | Lower pollution, sustainable land use | Higher pollution, intensive resource use |
| Cost | Higher due to space and labor | Lower, mass production efficient |
| Health Benefits | Reduced antibiotics, higher omega-3 | More antibiotics, lower nutrient levels |
Understanding Free-Range and Confined Farming Systems
Free-range farming allows animals to roam outdoors, promoting natural behaviors and access to fresh air and sunlight, which can enhance animal welfare and product quality. Confined farming restricts animals to indoor spaces, maximizing space efficiency and controlling environmental factors but often raising concerns about animal stress and limited mobility. Understanding these systems helps consumers make informed choices about ethical practices and the environmental impact of their food sources.
Animal Welfare: Free-Range vs Confined
Free-range animals experience improved welfare through access to outdoor environments that allow natural behaviors such as foraging, dust bathing, and social interaction. Confined systems restrict movement and prevent expression of innate behaviors, leading to increased stress, injury, and susceptibility to disease. Animal welfare studies indicate free-range practices reduce the prevalence of welfare-related issues compared to intensive confinement methods.
Nutritional Differences in Free-Range vs Confined Products
Free-range products typically contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and antioxidants compared to confined counterparts due to increased access to natural diets and sunlight. Confinement systems often result in lower nutrient density and altered fatty acid profiles because of restricted movement and grain-based feed. Studies show free-range eggs and meat offer improved nutritional value, contributing to better heart health and immune function.
Environmental Impact: Free-Range Compared to Confined Methods
Free-range farming reduces soil degradation and enhances biodiversity by allowing animals to graze naturally, fostering healthier ecosystems compared to confined methods that often lead to concentrated waste and pollution. Confined animal feeding operations (CAFOs) contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, including methane and nitrous oxide, due to high-density waste accumulation and limited vegetation. Free-range systems promote better carbon sequestration through pasture maintenance, making them a more sustainable choice for lowering the environmental footprint of meat and dairy production.
Food Safety Considerations: Free-Range vs Confined
Free-range poultry often has lower risk of bacterial contamination such as Salmonella and Campylobacter due to better air circulation and reduced stress compared to confined systems. Confined animal feeding operations (CAFOs) may have higher pathogen loads and increased use of antibiotics, raising concerns about antimicrobial resistance and foodborne illness. Rigorous biosecurity measures and regular testing are critical in both systems to ensure food safety and minimize contamination risks.
Taste and Quality: Consumer Perceptions and Realities
Free-range poultry is often perceived to have superior taste and quality due to natural diets and increased exercise, which enhance muscle development and flavor complexity. Scientific analyses reveal that free-range eggs and meat contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants compared to confined counterparts. Consumer preferences increasingly favor free-range products, associating them with better texture, richer taste, and ethical farming practices.
Economic Factors: Cost Implications for Farmers and Consumers
Free-range farming typically incurs higher costs for farmers due to increased land requirements, labor, and feed management compared to confined systems, leading to elevated prices for consumers. Confined animal feeding operations benefit from economies of scale and efficient resource utilization, reducing production expenses but raising concerns about animal welfare. Market demand for ethically produced free-range products supports premium pricing, affecting affordability and accessibility in the food supply chain.
Labeling and Certification: Decoding Free-Range and Confined Claims
Free-range labeling on food products typically requires certification from organizations adhering to strict animal welfare standards, ensuring livestock access to outdoor spaces. Confined claims, often labeled as conventional or barn-raised, lack such rigorous certification and usually indicate animals are kept indoors with limited movement. Understanding certification logos like Certified Humane or Animal Welfare Approved helps consumers make informed choices between free-range and confined products based on verified ethical practices.
Ethical Considerations in Food Choices
Choosing free-range food products supports ethical animal welfare by allowing livestock natural behaviors and better living conditions compared to confined systems, which often involve overcrowding and restricted movement. Free-range practices typically result in lower stress levels and reduced incidence of disease among animals, promoting overall health and humane treatment. Consumers prioritizing ethics in food choices promote sustainable farming practices that respect animal rights and improve environmental outcomes.
Making an Informed Decision: Which Option is Right for You?
Choosing between free-range and confined food products depends on factors like animal welfare, nutritional content, and environmental impact. Free-range options often offer higher omega-3 fatty acids and lower saturated fat levels, while confined systems may provide more consistent pricing and availability. Understanding your priorities in health benefits, ethical considerations, and budget helps make an informed decision tailored to your lifestyle.
free-range vs confined Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com