Functional foods offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition by containing bioactive compounds that may improve overall well-being and reduce disease risk. Conventional foods primarily provide essential nutrients for daily energy and growth without added health-promoting properties. Consumers seeking targeted health advantages often choose functional foods to support specific bodily functions or health conditions.
Table of Comparison
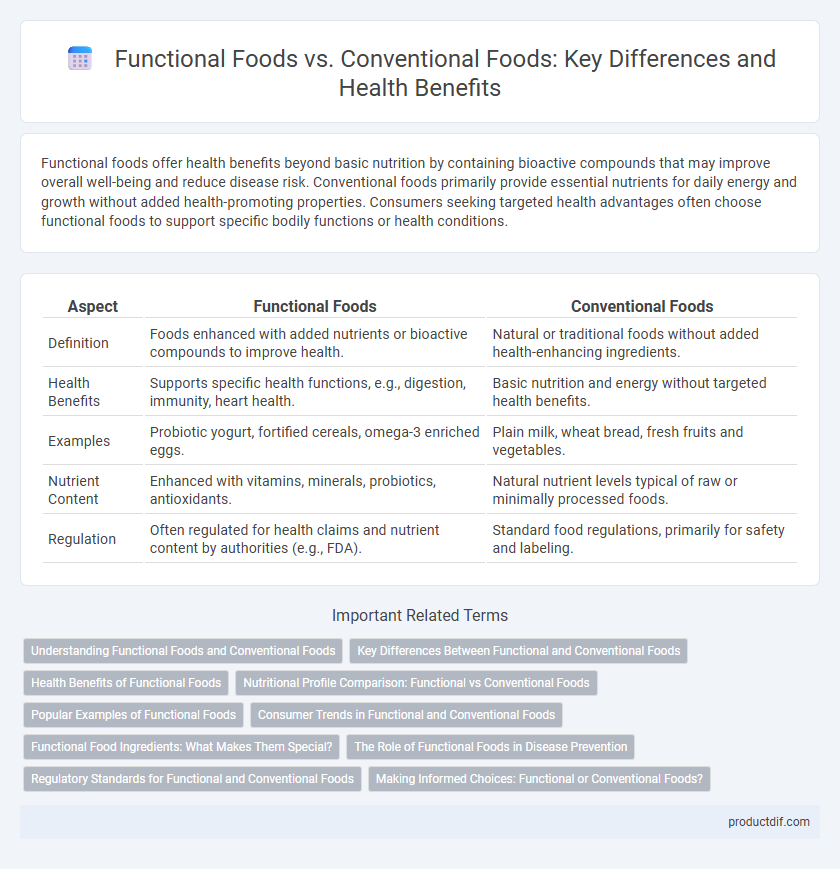
| Aspect | Functional Foods | Conventional Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Foods enhanced with added nutrients or bioactive compounds to improve health. | Natural or traditional foods without added health-enhancing ingredients. |
| Health Benefits | Supports specific health functions, e.g., digestion, immunity, heart health. | Basic nutrition and energy without targeted health benefits. |
| Examples | Probiotic yogurt, fortified cereals, omega-3 enriched eggs. | Plain milk, wheat bread, fresh fruits and vegetables. |
| Nutrient Content | Enhanced with vitamins, minerals, probiotics, antioxidants. | Natural nutrient levels typical of raw or minimally processed foods. |
| Regulation | Often regulated for health claims and nutrient content by authorities (e.g., FDA). | Standard food regulations, primarily for safety and labeling. |
Understanding Functional Foods and Conventional Foods
Functional foods are fortified or enriched with bioactive compounds that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, such as probiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants. Conventional foods primarily supply essential nutrients required for daily energy and growth but lack added bioactive components designed to prevent disease or promote optimal health. Understanding the distinction helps consumers make informed dietary choices to support specific health goals or manage chronic conditions.
Key Differences Between Functional and Conventional Foods
Functional foods contain bioactive compounds that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, such as probiotics, antioxidants, and vitamins aimed at disease prevention and health promotion. Conventional foods primarily serve as sources of essential nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals without targeted health-enhancing properties. The key differences lie in the purpose of consumption, with functional foods designed to improve specific physiological functions, while conventional foods support general dietary needs.
Health Benefits of Functional Foods
Functional foods provide enhanced health benefits by containing bioactive compounds such as probiotics, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids, which support immune function, reduce inflammation, and improve cardiovascular health. Unlike conventional foods, functional foods are specifically designed to promote optimal wellness and prevent chronic diseases through nutrient fortification and natural ingredients. Regular consumption of functional foods like yogurt, fortified cereals, and enriched beverages contributes to improved metabolic health and better disease management outcomes.
Nutritional Profile Comparison: Functional vs Conventional Foods
Functional foods offer enhanced nutritional profiles with added bioactive compounds such as probiotics, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids that promote health beyond basic nutrition. Conventional foods primarily provide essential macronutrients and micronutrients without the supplementary health benefits found in functional foods. Studies reveal that the enriched nutrient density in functional foods supports improved immune function, cardiovascular health, and digestive wellness compared to standard conventional food products.
Popular Examples of Functional Foods
Functional foods such as yogurt with probiotics, fortified cereals rich in vitamins and minerals, and omega-3 enriched eggs provide targeted health benefits beyond basic nutrition, enhancing digestion, immunity, and heart health. These foods contain bioactive compounds like antioxidants, fibers, and phytochemicals that are absent or less concentrated in conventional foods. Popular examples include kefir for gut health, plant sterol-enhanced margarines for cholesterol reduction, and green tea as a powerful antioxidant source.
Consumer Trends in Functional and Conventional Foods
Consumer trends reveal a growing preference for functional foods enriched with probiotics, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids due to their perceived health benefits and disease prevention capabilities. Conventional foods remain popular for their affordability and familiarity but face increasing competition as health-conscious consumers seek products supporting immune function and gut health. Market data from 2024 indicates a 12% annual growth in functional food sales, driven by demand for natural ingredients and clean-label products.
Functional Food Ingredients: What Makes Them Special?
Functional food ingredients contain bioactive compounds such as antioxidants, probiotics, and omega-3 fatty acids that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition. These components support immune function, improve gut health, and reduce inflammation, distinguishing them from conventional food ingredients primarily focused on essential nutrients. The presence of vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals in functional foods contributes to disease prevention and overall well-being.
The Role of Functional Foods in Disease Prevention
Functional foods contain bioactive compounds such as antioxidants, probiotics, and phytochemicals that actively contribute to disease prevention by enhancing immune function and reducing inflammation. These foods, including fortified cereals, yogurt with probiotics, and omega-3 enriched products, support cardiovascular health and lower the risk of chronic conditions like diabetes and cancer. In contrast, conventional foods primarily provide basic nutrition without targeted health benefits beyond essential nutrients.
Regulatory Standards for Functional and Conventional Foods
Functional foods are subject to stricter regulatory standards compared to conventional foods due to their added health benefits and bioactive compounds. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EFSA require comprehensive scientific evidence to substantiate health claims associated with functional foods, including safety assessments and ingredient transparency. Conventional foods generally follow basic safety and labeling regulations without the need for claims validation, resulting in less rigorous oversight.
Making Informed Choices: Functional or Conventional Foods?
Functional foods, enriched with bioactive compounds like probiotics, antioxidants, or omega-3 fatty acids, offer targeted health benefits beyond basic nutrition, making them ideal for addressing specific dietary needs or health conditions. Conventional foods provide essential nutrients naturally without modification or fortification, serving as the foundation of a balanced diet and supporting overall health through whole, unprocessed ingredients. Evaluating personal health goals, nutrient requirements, and lifestyle preferences is crucial when deciding between functional and conventional foods to ensure informed, effective dietary choices.
Functional foods vs Conventional foods Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com