Free-range eggs come from hens allowed to roam outdoors, providing access to fresh air and natural sunlight, which often results in better animal welfare and nutrient-rich eggs. Cage-free eggs come from hens that live indoors but are not confined to cages, offering more space than conventional battery cages but lacking outdoor access. Consumers seeking higher animal welfare standards and potentially healthier eggs often prefer free-range options over cage-free.
Table of Comparison
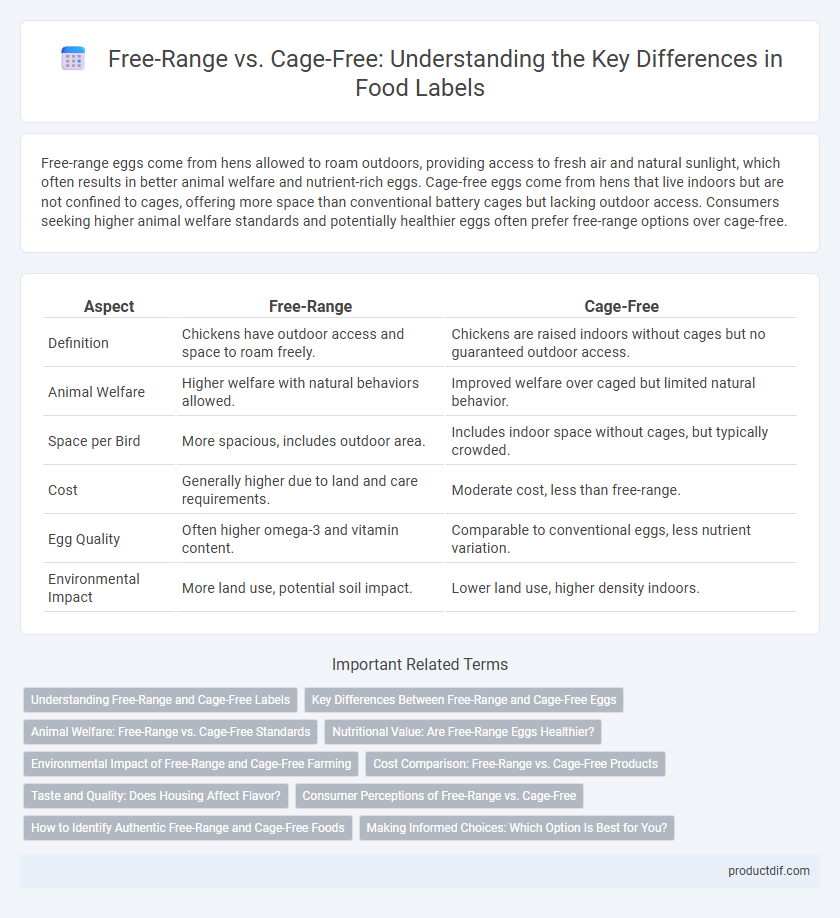
| Aspect | Free-Range | Cage-Free |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chickens have outdoor access and space to roam freely. | Chickens are raised indoors without cages but no guaranteed outdoor access. |
| Animal Welfare | Higher welfare with natural behaviors allowed. | Improved welfare over caged but limited natural behavior. |
| Space per Bird | More spacious, includes outdoor area. | Includes indoor space without cages, but typically crowded. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to land and care requirements. | Moderate cost, less than free-range. |
| Egg Quality | Often higher omega-3 and vitamin content. | Comparable to conventional eggs, less nutrient variation. |
| Environmental Impact | More land use, potential soil impact. | Lower land use, higher density indoors. |
Understanding Free-Range and Cage-Free Labels
Free-range eggs come from hens that have access to the outdoors, allowing natural behaviors like foraging and dust bathing, which improves animal welfare compared to confined conditions. Cage-free eggs are produced by hens raised indoors without cages, providing more space to move but lacking outdoor access, resulting in varying welfare standards. Understanding these labels helps consumers make informed choices based on animal welfare and product quality preferences.
Key Differences Between Free-Range and Cage-Free Eggs
Free-range eggs come from hens that have access to the outdoors, allowing them to roam freely and engage in natural behaviors, while cage-free eggs are laid by hens kept indoors without cages but do not necessarily have outdoor access. The space and environment significantly impact animal welfare, with free-range systems providing more room and opportunities for exercise compared to cage-free systems. Nutritionally, free-range eggs may contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins due to the hens' diverse diet and outdoor exposure.
Animal Welfare: Free-Range vs. Cage-Free Standards
Free-range standards require animals, particularly poultry, to have regular outdoor access, allowing natural behaviors like foraging and exercise, which significantly enhances animal welfare compared to cage-free systems. Cage-free poultry are housed indoors without restrictive cages but lack guaranteed outdoor exposure, limiting their ability to engage in natural activities and impacting overall well-being. Studies show free-range environments reduce stress and improve physical health indicators in animals, making free-range a superior choice for consumers prioritizing ethical treatment and animal welfare.
Nutritional Value: Are Free-Range Eggs Healthier?
Free-range eggs typically contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A and E, and antioxidants compared to cage-free eggs due to hens' access to natural forage and sunlight. Studies indicate that the nutritional profile of free-range eggs supports better heart health and immune function. However, both free-range and cage-free eggs provide essential protein and nutrients, making them healthier options than conventional eggs from caged hens.
Environmental Impact of Free-Range and Cage-Free Farming
Free-range farming allows chickens to roam outdoors, which promotes better soil health through natural fertilization and reduces the concentration of waste compared to cage-free systems confined indoors. Cage-free farming minimizes animal confinement but concentrates waste within barns, leading to higher ammonia emissions and potential water contamination risks. Studies indicate free-range systems generally have a lower environmental footprint by enhancing biodiversity and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
Cost Comparison: Free-Range vs. Cage-Free Products
Free-range eggs typically cost 20-30% more than cage-free eggs due to higher land and maintenance expenses associated with outdoor access for hens. Cage-free products benefit from more controlled environments, reducing operational costs but offering less space per bird. Consumers often pay a premium for free-range products because of perceived welfare advantages, impacting retail prices significantly.
Taste and Quality: Does Housing Affect Flavor?
Free-range eggs often have richer yolks and more vibrant flavors due to hens' varied diet and outdoor access, which enhances nutrient diversity. Cage-free eggs provide better quality than conventional caged eggs but may lack the flavor complexity from natural foraging. Studies indicate that hens' housing conditions influence egg taste and quality by affecting their nutrition and stress levels.
Consumer Perceptions of Free-Range vs. Cage-Free
Consumers often perceive free-range eggs as more humane and environmentally friendly compared to cage-free options, associating free-range with outdoor access and natural behaviors for hens. Surveys indicate that free-range labeling increases willingness to pay due to beliefs about better animal welfare and superior egg quality. However, confusion persists as many consumers lack clear knowledge about the specific standards differentiating free-range from cage-free practices.
How to Identify Authentic Free-Range and Cage-Free Foods
Authentic free-range and cage-free foods are identified by verifying certified labels from recognized organizations such as USDA Organic, Certified Humane, or Animal Welfare Approved, which ensure compliance with strict animal welfare standards. Consumers should look for clear packaging information detailing outdoor access for free-range poultry or the absence of cages in cage-free environments, supported by transparent farm audits. Ingredient lists and retailer sourcing policies further validate authenticity by confirming adherence to free-range and cage-free practices throughout the supply chain.
Making Informed Choices: Which Option Is Best for You?
Choosing between free-range and cage-free eggs depends on factors like animal welfare, nutritional content, and environmental impact. Free-range hens have outdoor access promoting natural behaviors, while cage-free hens live indoors with more space but limited outdoor exposure. Consumers prioritizing animal welfare and richer nutrient profiles may prefer free-range, whereas those seeking affordability and improved welfare over conventional caged eggs might opt for cage-free options.
Free-Range vs Cage-Free Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com