Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control by vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a water bath, ensuring even doneness and enhanced flavor retention. Conventional cooking methods rely on direct heat, which can lead to uneven cooking and moisture loss, impacting texture and taste. Sous vide maximizes juiciness and tenderness, making it ideal for meats and delicate vegetables, while conventional techniques provide faster results and a crispy exterior.
Table of Comparison
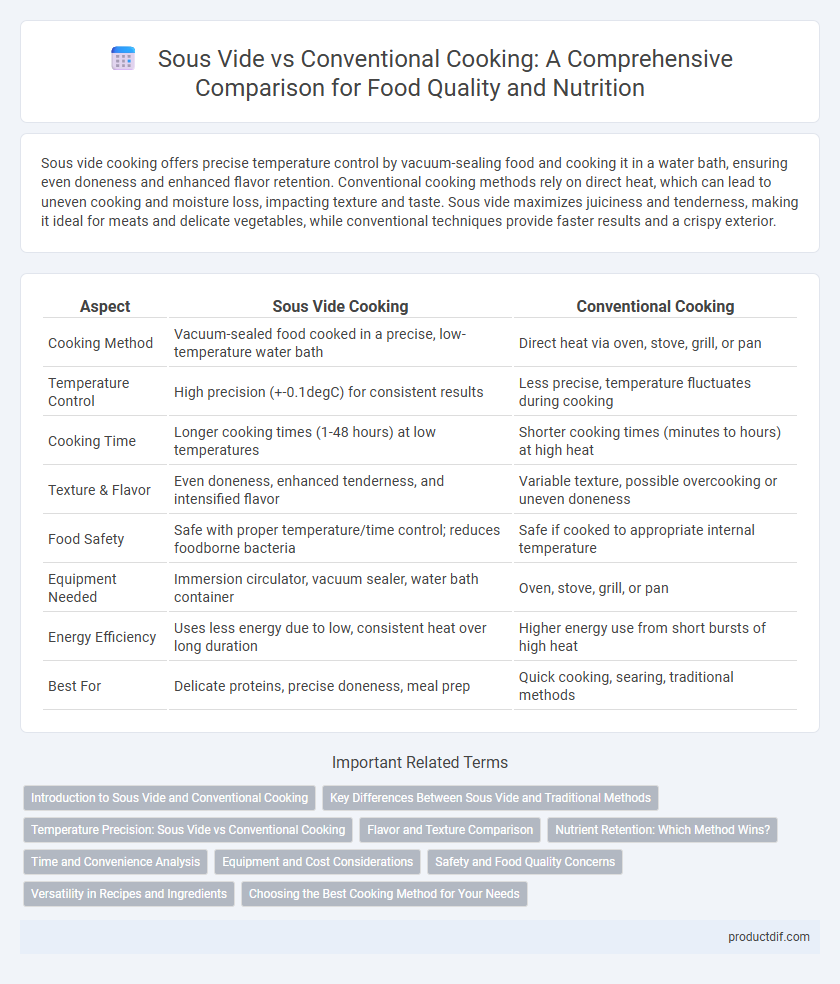
| Aspect | Sous Vide Cooking | Conventional Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vacuum-sealed food cooked in a precise, low-temperature water bath | Direct heat via oven, stove, grill, or pan |
| Temperature Control | High precision (+-0.1degC) for consistent results | Less precise, temperature fluctuates during cooking |
| Cooking Time | Longer cooking times (1-48 hours) at low temperatures | Shorter cooking times (minutes to hours) at high heat |
| Texture & Flavor | Even doneness, enhanced tenderness, and intensified flavor | Variable texture, possible overcooking or uneven doneness |
| Food Safety | Safe with proper temperature/time control; reduces foodborne bacteria | Safe if cooked to appropriate internal temperature |
| Equipment Needed | Immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, water bath container | Oven, stove, grill, or pan |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses less energy due to low, consistent heat over long duration | Higher energy use from short bursts of high heat |
| Best For | Delicate proteins, precise doneness, meal prep | Quick cooking, searing, traditional methods |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Conventional Cooking
Sous vide cooking involves sealing food in vacuum bags and cooking it at precise low temperatures in a water bath, preserving moisture and enhancing flavor. Conventional cooking methods, such as grilling, roasting, or frying, use direct heat at higher temperatures, often resulting in uneven cooking and moisture loss. Sous vide offers consistent doneness and texture, while conventional techniques provide faster cooking and characteristic browning or caramelization.
Key Differences Between Sous Vide and Traditional Methods
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control by sealing food in vacuum bags and cooking it in a water bath, ensuring even doneness and retaining moisture, while traditional methods rely on direct heat that can lead to uneven cooking and moisture loss. Sous vide preserves nutrients and flavors more effectively due to low-temperature, long-time cooking, whereas conventional methods often cause nutrient degradation from high heat exposure. The technique also allows for greater consistency and repeatability, contrasting with the variability found in grilling, roasting, or pan-frying.
Temperature Precision: Sous Vide vs Conventional Cooking
Sous vide cooking offers unparalleled temperature precision by circulating water at a consistent, exact temperature typically within +-0.1degC, ensuring uniform doneness throughout the food. Conventional cooking methods rely on less precise heat sources like ovens or stovetops, which often fluctuate and create hot spots, leading to uneven cooking. This precise temperature control in sous vide reduces the risk of overcooking or undercooking, enhancing texture and flavor retention in meats, vegetables, and seafood.
Flavor and Texture Comparison
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control, resulting in consistently tender textures and enhanced, evenly developed flavors by cooking food in vacuum-sealed bags. Conventional cooking methods often expose food to direct heat, which can create uneven doneness and potential moisture loss, impacting both texture and flavor intensity. The sous vide process retains juices and natural aromas better, offering a superior flavor profile and a delicate, melt-in-the-mouth texture compared to traditional cooking techniques.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Wins?
Sous vide cooking retains more nutrients than conventional methods by cooking food at lower, precise temperatures in airtight bags, minimizing nutrient loss caused by oxidation and overcooking. Traditional techniques like boiling and frying expose food to higher heat and water, which often lead to leaching of water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and folate. Studies show sous vide preserves up to 25-30% more vitamins and antioxidants, enhancing the overall nutritional quality of meals.
Time and Convenience Analysis
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, resulting in evenly cooked food with minimal supervision, while conventional cooking requires constant attention and frequent adjustments. The extended cooking time of sous vide, often ranging from one to several hours, is balanced by its convenience of hands-off preparation and consistent results. Conventional methods typically involve shorter cooking durations but demand active involvement, increasing the risk of overcooking or uneven textures.
Equipment and Cost Considerations
Sous vide cooking requires specialized equipment such as immersion circulators and vacuum sealers, which can be initially expensive but offer precise temperature control and consistency. Conventional cooking relies on standard kitchen appliances like ovens and stovetops, often incurring lower upfront costs but sacrificing uniformity in heat distribution. Long-term investment in sous vide gear can lead to energy efficiency and reduced food waste, balancing out the higher initial expenditure.
Safety and Food Quality Concerns
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control that minimizes the risk of bacterial growth, ensuring enhanced food safety compared to conventional methods that rely on higher heat and longer cooking times. This method preserves moisture and nutrients more effectively, resulting in superior texture and flavor retention. Conventional cooking carries a higher risk of uneven cooking, which can lead to foodborne illnesses and degradation of food quality.
Versatility in Recipes and Ingredients
Sous vide cooking offers exceptional versatility by allowing precise temperature control, making it ideal for delicate proteins, vegetables, and even eggs, ensuring consistent texture and flavor. Conventional cooking methods provide broader adaptability for fast searing, roasting, and sauteing, accommodating a wide range of ingredient textures and rapid cooking times. Combining sous vide with traditional techniques enhances recipe flexibility, achieving perfect doneness alongside rich, caramelized browning.
Choosing the Best Cooking Method for Your Needs
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, ensuring consistent results and enhanced flavor retention, ideal for tender meats and delicate dishes. Conventional cooking provides faster preparation and versatility, suitable for a wide range of recipes and textures. Selecting the best method depends on factors like time availability, desired texture, and equipment accessibility.
sous vide vs conventional cooking Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com