Fresh pet food offers high moisture content and natural flavors that appeal to pets, promoting better digestion and hydration. Flash-frozen pet food preserves nutrients and enzymes more effectively than traditional freezing methods, ensuring that the nutritional value remains intact over time. Choosing between fresh and flash-frozen options depends on convenience, shelf life, and the specific dietary needs of your pet.
Table of Comparison
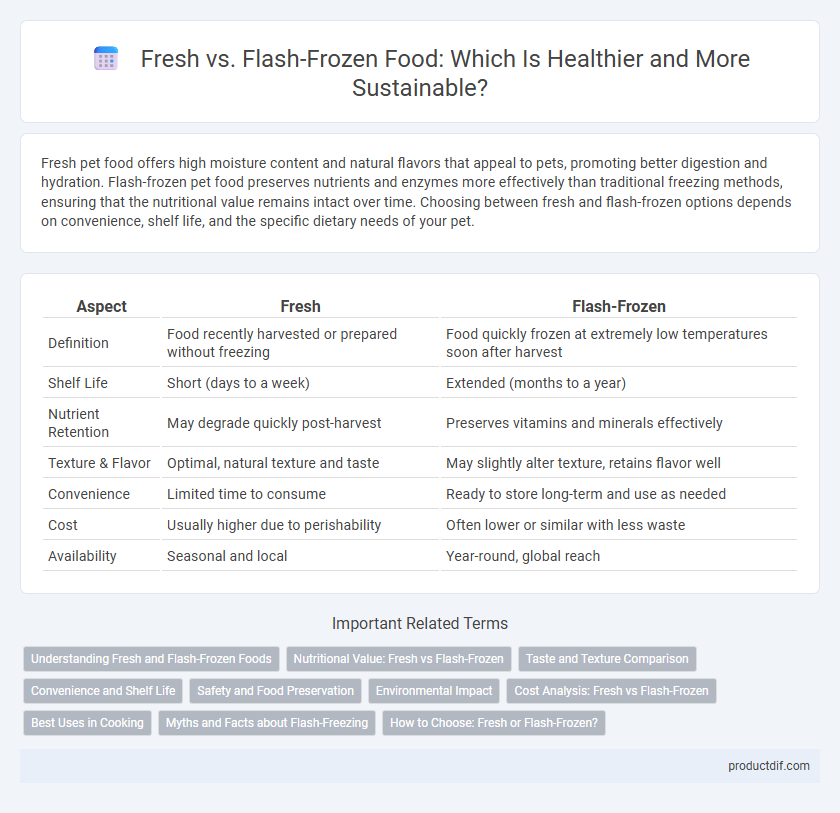
| Aspect | Fresh | Flash-Frozen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Food recently harvested or prepared without freezing | Food quickly frozen at extremely low temperatures soon after harvest |
| Shelf Life | Short (days to a week) | Extended (months to a year) |
| Nutrient Retention | May degrade quickly post-harvest | Preserves vitamins and minerals effectively |
| Texture & Flavor | Optimal, natural texture and taste | May slightly alter texture, retains flavor well |
| Convenience | Limited time to consume | Ready to store long-term and use as needed |
| Cost | Usually higher due to perishability | Often lower or similar with less waste |
| Availability | Seasonal and local | Year-round, global reach |
Understanding Fresh and Flash-Frozen Foods
Fresh foods retain their natural texture, flavor, and nutritional profile because they are consumed shortly after harvest or preparation. Flash-frozen foods undergo rapid freezing at extremely low temperatures to preserve nutrients and prevent ice crystal formation, maintaining quality similar to fresh produce. Understanding the differences in preservation methods helps consumers choose options that best meet their nutritional and convenience needs.
Nutritional Value: Fresh vs Flash-Frozen
Fresh fruits and vegetables often retain higher levels of certain vitamins like vitamin C and B vitamins immediately after harvest, but nutrient degradation begins soon after. Flash-freezing typically preserves nutritional value by rapidly locking in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants at peak ripeness, minimizing nutrient loss compared to prolonged storage of fresh produce. Studies show flash-frozen produce can equal or sometimes exceed fresh in nutrient retention, especially when fresh items are stored for extended periods before consumption.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Fresh produce typically offers superior taste and texture due to minimal processing and immediate consumption post-harvest, preserving natural flavors and crispness. Flash-frozen foods are rapidly frozen at peak ripeness, which helps lock in nutrients but may slightly alter texture, often resulting in a softer or less crisp mouthfeel after thawing. Consumers seeking maximum freshness prefer fresh options, while flash-frozen remains a convenient alternative that maintains much of the original flavor profile despite minor texture changes.
Convenience and Shelf Life
Fresh produce offers optimal taste and nutritional value but has a limited shelf life, often lasting only a few days when stored properly. Flash-frozen foods maintain most of their nutrients and flavor by rapidly freezing at ultra-low temperatures, significantly extending shelf life to several months or more. This method provides greater convenience for meal planning and reduces food waste by allowing consumers to store ingredients longer without spoilage.
Safety and Food Preservation
Fresh foods retain natural enzymes and nutrients but have a limited shelf life, increasing the risk of spoilage and bacterial growth if not consumed quickly. Flash-freezing preserves food by rapidly lowering temperature, which inhibits microbial activity and maintains nutritional value without the need for preservatives. Studies show flash-frozen fruits and vegetables can retain up to 90% of their vitamins, making them a safer option for long-term storage compared to fresh perishables.
Environmental Impact
Fresh produce generally requires more frequent transportation and refrigeration, leading to higher carbon emissions compared to flash-frozen items that are preserved at peak ripeness and transported in bulk. Flash-freezing reduces food waste by extending shelf life, thus minimizing the environmental impact associated with discarded produce. Energy consumption in flash-freezing is offset by decreased spoilage and transportation frequency, making it a more sustainable option in the food supply chain.
Cost Analysis: Fresh vs Flash-Frozen
Fresh produce often incurs higher costs due to transportation, limited shelf life, and spoilage rates, directly impacting retail pricing. Flash-frozen foods, preserved at peak ripeness through rapid freezing techniques, reduce waste and extend shelf life, offering more cost-efficient inventory management for retailers and consumers. Evaluating cost per nutrient retention reveals flash-frozen options provide affordable, high-quality alternatives without compromising nutritional value.
Best Uses in Cooking
Fresh ingredients provide optimal texture and flavor in dishes that require minimal cooking, such as salads, sushi, and raw preparations. Flash-frozen foods retain most of their nutrients and are ideal for soups, stews, and casseroles where cooking times are extended, allowing flavors to meld. Choosing between fresh and flash-frozen depends on the recipe's cooking method, desired texture, and nutrient preservation.
Myths and Facts about Flash-Freezing
Flash-freezing preserves the nutritional value and texture of fruits and vegetables more effectively than many assume, debunking the myth that only fresh produce retains quality. Scientific studies show that flash-frozen foods are often frozen at peak ripeness, locking in vitamins and minerals, while fresh produce can lose nutrients during transportation and storage. Consumers benefit from flash-frozen options as a convenient, long-lasting alternative without sacrificing taste or health benefits.
How to Choose: Fresh or Flash-Frozen?
Selecting between fresh and flash-frozen food depends on factors like nutritional value, convenience, and shelf life. Fresh produce retains maximum flavor and nutrients when consumed quickly, while flash-frozen items maintain freshness through rapid freezing, preserving vitamins and texture for extended periods. Consider usage frequency and storage capacity to determine whether fresh or flash-frozen better suits your dietary needs and lifestyle.
Fresh vs Flash-Frozen Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com