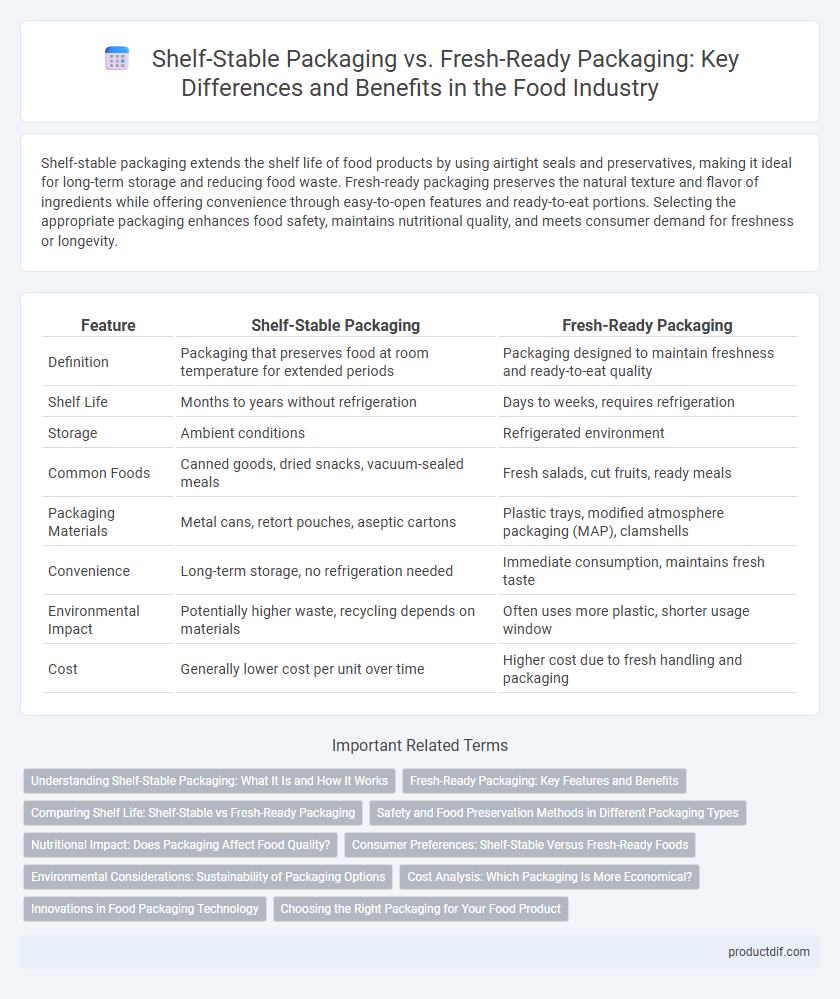
Shelf-stable packaging extends the shelf life of food products by using airtight seals and preservatives, making it ideal for long-term storage and reducing food waste. Fresh-ready packaging preserves the natural texture and flavor of ingredients while offering convenience through easy-to-open features and ready-to-eat portions. Selecting the appropriate packaging enhances food safety, maintains nutritional quality, and meets consumer demand for freshness or longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shelf-Stable Packaging | Fresh-Ready Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Packaging that preserves food at room temperature for extended periods | Packaging designed to maintain freshness and ready-to-eat quality |
| Shelf Life | Months to years without refrigeration | Days to weeks, requires refrigeration |
| Storage | Ambient conditions | Refrigerated environment |
| Common Foods | Canned goods, dried snacks, vacuum-sealed meals | Fresh salads, cut fruits, ready meals |
| Packaging Materials | Metal cans, retort pouches, aseptic cartons | Plastic trays, modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), clamshells |
| Convenience | Long-term storage, no refrigeration needed | Immediate consumption, maintains fresh taste |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially higher waste, recycling depends on materials | Often uses more plastic, shorter usage window |
| Cost | Generally lower cost per unit over time | Higher cost due to fresh handling and packaging |
Understanding Shelf-Stable Packaging: What It Is and How It Works
Shelf-stable packaging preserves food by using airtight seals, moisture barriers, and oxygen absorbers to prevent spoilage and microbial growth without refrigeration. Common methods include vacuum-sealing, retort processing, and aseptic packaging, which extend shelf life while maintaining nutritional value. These technologies enable distribution and storage at room temperature, reducing food waste and increasing convenience for consumers.
Fresh-Ready Packaging: Key Features and Benefits
Fresh-ready packaging preserves the natural taste and nutritional value of food products while extending shelf life without the need for refrigeration. Key features include airtight seals, oxygen scavengers, and innovative barrier materials that prevent contamination and spoilage. This packaging enhances convenience for consumers by offering ready-to-eat options that maintain freshness and safety during distribution and storage.
Comparing Shelf Life: Shelf-Stable vs Fresh-Ready Packaging
Shelf-stable packaging extends the shelf life of food products from several weeks to months by using airtight, vacuum-sealed, or retort techniques that prevent microbial growth and oxidation. Fresh-ready packaging, designed to preserve freshness for shorter periods, typically maintains product quality for days to a few weeks through modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) or refrigeration. Comparing shelf life reveals that shelf-stable packaging offers significantly longer storage without refrigeration, making it ideal for long-term distribution, while fresh-ready packaging prioritizes taste and texture for immediate consumption.
Safety and Food Preservation Methods in Different Packaging Types
Shelf-stable packaging utilizes advanced barrier materials and vacuum sealing to inhibit microbial growth and oxygen exposure, significantly extending product shelf life while maintaining safety without refrigeration. Fresh-ready packaging employs modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) and humidity control to preserve the texture and nutritional quality of perishable items, ensuring freshness and reducing spoilage risks. Both packaging types implement strict quality control and sanitation protocols to safeguard against contamination and uphold food safety standards throughout distribution.
Nutritional Impact: Does Packaging Affect Food Quality?
Shelf-stable packaging utilizes techniques like vacuum sealing and oxygen absorbers to maintain nutrient integrity over extended periods, minimizing vitamin and antioxidant loss. Fresh-ready packaging often incorporates modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) to preserve freshness and nutritional content by reducing oxidation and microbial growth. While both methods impact food quality differently, optimized packaging technologies aim to retain maximum nutritional value by controlling environmental factors such as light, oxygen, and moisture exposure.
Consumer Preferences: Shelf-Stable Versus Fresh-Ready Foods
Consumer preferences between shelf-stable and fresh-ready foods vary based on convenience, taste, and storage needs, with shelf-stable packaging offering longer durability and reduced spoilage risk. Fresh-ready packaging appeals to those prioritizing natural flavors and immediate consumption, often perceived as healthier due to minimal processing. Market trends indicate a growing demand for hybrid options combining the convenience of shelf-stable with the sensory appeal of fresh-ready foods.
Environmental Considerations: Sustainability of Packaging Options
Shelf-stable packaging often employs materials like metal cans, glass jars, and multilayer laminates that enhance product longevity but pose challenges in recycling and environmental impact. Fresh-ready packaging typically uses biodegradable or compostable films and recyclable plastics designed to reduce carbon footprint and waste accumulation. Evaluating sustainability involves considering resource consumption, end-of-life recyclability, and the packaging's role in minimizing food waste during storage and transportation.
Cost Analysis: Which Packaging Is More Economical?
Shelf-stable packaging generally offers a lower cost per unit due to extended product shelf life, reducing waste and storage expenses for retailers and consumers. Fresh-ready packaging tends to have higher costs related to refrigeration, shorter shelf life, and faster turnover requirements, increasing logistics and spoilage risks. Economic viability depends on product type and distribution scale, with shelf-stable options favored for long-term storage and fresh-ready preferred for premium, convenience-oriented markets.
Innovations in Food Packaging Technology
Shelf-stable packaging utilizes advanced barrier films and vacuum sealing to extend the product's shelf life without refrigeration, significantly reducing food waste and transportation costs. Fresh-ready packaging incorporates modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) and smart sensors to preserve freshness and monitor spoilage in real-time, enhancing consumer confidence and convenience. Innovations such as biodegradable materials and nanotechnology coatings are revolutionizing both packaging types by improving sustainability and food safety standards.
Choosing the Right Packaging for Your Food Product
Shelf-stable packaging extends product shelf life by using airtight seals and preservatives, ideal for non-perishable foods like canned goods and snacks. Fresh-ready packaging preserves freshness and nutritional value through advanced materials and technologies, perfect for perishable items like salads and fresh-cut fruits. Selecting the right packaging depends on your product's perishability, target market, and distribution channels to maintain quality and consumer appeal.
Shelf-stable packaging vs Fresh-ready packaging Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com