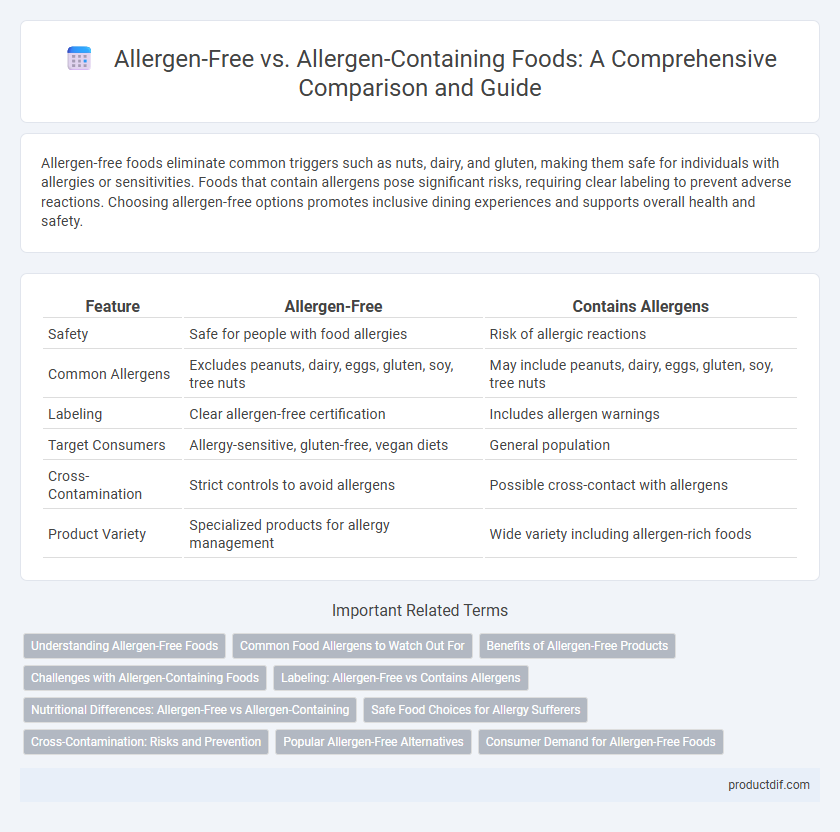
Allergen-free foods eliminate common triggers such as nuts, dairy, and gluten, making them safe for individuals with allergies or sensitivities. Foods that contain allergens pose significant risks, requiring clear labeling to prevent adverse reactions. Choosing allergen-free options promotes inclusive dining experiences and supports overall health and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Allergen-Free | Contains Allergens |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Safe for people with food allergies | Risk of allergic reactions |
| Common Allergens | Excludes peanuts, dairy, eggs, gluten, soy, tree nuts | May include peanuts, dairy, eggs, gluten, soy, tree nuts |
| Labeling | Clear allergen-free certification | Includes allergen warnings |
| Target Consumers | Allergy-sensitive, gluten-free, vegan diets | General population |
| Cross-Contamination | Strict controls to avoid allergens | Possible cross-contact with allergens |
| Product Variety | Specialized products for allergy management | Wide variety including allergen-rich foods |
Understanding Allergen-Free Foods
Allergen-free foods are specifically formulated to exclude common allergens such as peanuts, tree nuts, dairy, eggs, gluten, soy, fish, and shellfish, ensuring safety for individuals with food allergies. These products undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to prevent cross-contamination, enhancing consumer trust and compliance with regulatory standards. Clear labeling and ingredient transparency are essential in helping consumers accurately identify allergen-free options and avoid adverse allergic reactions.
Common Food Allergens to Watch Out For
Common food allergens to watch out for include peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish, which affect millions worldwide. Allergen-free products are specifically formulated to avoid these ingredients, reducing the risk of allergic reactions. Reading labels carefully and understanding cross-contamination risks are essential for managing and preventing exposure to allergens in food.
Benefits of Allergen-Free Products
Allergen-free products significantly reduce the risk of allergic reactions, making them essential for individuals with food allergies or sensitivities. These products promote safer dining experiences and enhance overall health by eliminating common allergens such as nuts, gluten, dairy, and soy. Choosing allergen-free options supports inclusive nutrition and peace of mind for consumers with dietary restrictions.
Challenges with Allergen-Containing Foods
Allergen-containing foods pose significant challenges for food manufacturers due to the risk of cross-contamination and the need for strict labeling compliance to protect consumers with food allergies. Managing allergen presence requires rigorous cleaning protocols, dedicated equipment, and comprehensive staff training to prevent unintended exposure. Failure to control allergens can lead to severe allergic reactions, legal liabilities, and loss of consumer trust.
Labeling: Allergen-Free vs Contains Allergens
Clear labeling distinguishes allergen-free products from those containing allergens, providing essential information for consumers with food allergies. Allergen-free labels identify items free from common allergens such as peanuts, dairy, gluten, soy, and shellfish, reducing the risk of allergic reactions. Labels indicating the presence of allergens use bold or highlighted text to warn consumers, ensuring safe food choices and compliance with regulatory standards like the FDA and EU food labeling laws.
Nutritional Differences: Allergen-Free vs Allergen-Containing
Allergen-free foods often have modified ingredient profiles that may result in lower protein content and altered vitamin levels compared to allergen-containing counterparts. Products containing common allergens like nuts or dairy typically provide higher amounts of essential fatty acids, calcium, and certain B vitamins. Consumers must balance nutritional needs with allergen risks, choosing fortified allergen-free options or diverse diets to maintain adequate nutrient intake.
Safe Food Choices for Allergy Sufferers
Safe food choices for allergy sufferers require careful identification of allergen-free products to prevent adverse reactions such as anaphylaxis. Labels indicating absence of common allergens like peanuts, gluten, dairy, and shellfish are crucial in ensuring consumer safety. Choosing certified allergen-free foods reduces cross-contamination risks and supports dietary compliance for individuals with multiple food allergies.
Cross-Contamination: Risks and Prevention
Cross-contamination poses significant risks for allergen-free food products, as even trace amounts of allergens like peanuts, gluten, or shellfish can trigger severe reactions. Implementing stringent cleaning protocols, dedicated equipment, and thorough staff training are essential prevention strategies in food production and handling environments. Accurate labeling and supplier verification further minimize the risk of allergen cross-contact, ensuring consumer safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
Popular Allergen-Free Alternatives
Popular allergen-free alternatives include almond milk, coconut yogurt, and gluten-free oats, providing safe options for individuals with nut, dairy, or gluten sensitivities. These substitutes maintain texture and flavor while eliminating common allergens such as peanuts, dairy, wheat, and soy. Choosing allergen-free products reduces the risk of allergic reactions and supports inclusive dining experiences.
Consumer Demand for Allergen-Free Foods
Consumer demand for allergen-free foods has surged as awareness of food allergies and intolerances grows, driving market expansion and innovation in product offerings. Products labeled allergen-free, such as gluten-free, nut-free, or dairy-free options, cater to a wide audience seeking safe and inclusive dietary choices. This trend encourages manufacturers to implement strict allergen control measures and transparent labeling to build consumer trust and meet regulatory standards.
Allergen-free vs Contains allergens Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com