Upcycled ingredients reduce food waste by transforming by-products into nutritious components, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional ingredients that often require more resources to produce. These ingredients maintain high quality and meet food safety standards while supporting eco-friendly production methods. Choosing upcycled ingredients encourages innovation in food manufacturing and promotes environmental responsibility.
Table of Comparison
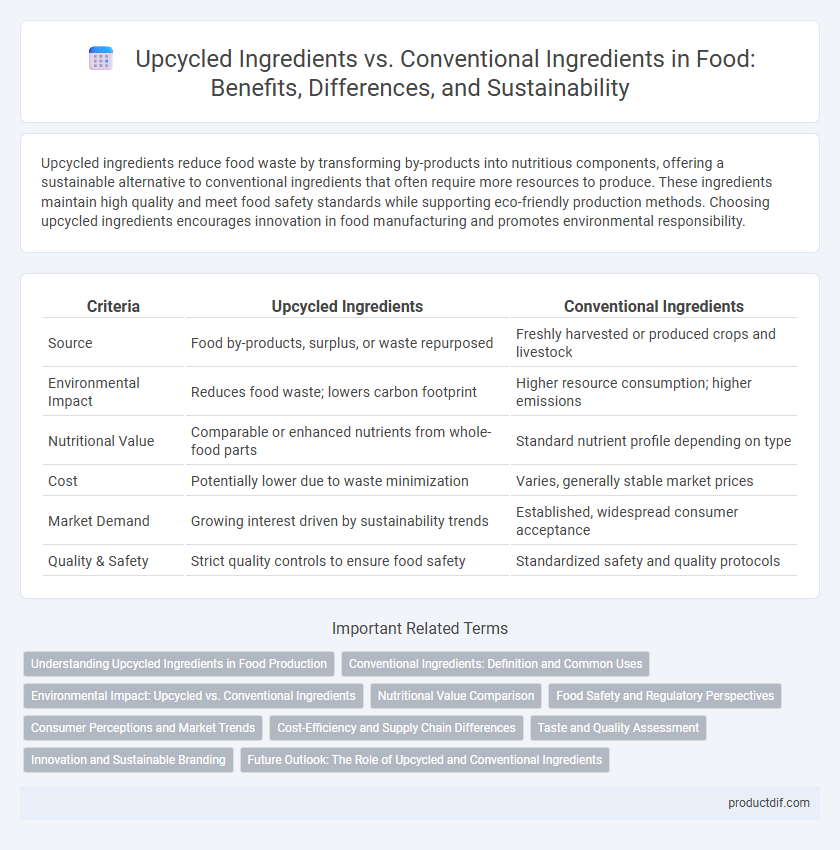
| Criteria | Upcycled Ingredients | Conventional Ingredients |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Food by-products, surplus, or waste repurposed | Freshly harvested or produced crops and livestock |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces food waste; lowers carbon footprint | Higher resource consumption; higher emissions |
| Nutritional Value | Comparable or enhanced nutrients from whole-food parts | Standard nutrient profile depending on type |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to waste minimization | Varies, generally stable market prices |
| Market Demand | Growing interest driven by sustainability trends | Established, widespread consumer acceptance |
| Quality & Safety | Strict quality controls to ensure food safety | Standardized safety and quality protocols |
Understanding Upcycled Ingredients in Food Production
Upcycled ingredients in food production are sourced from by-products or surplus materials that would otherwise go to waste, enhancing sustainability and resource efficiency. These ingredients maintain nutritional value and can reduce environmental impact compared to conventional ingredients that rely on primary agricultural inputs. Incorporating upcycled ingredients supports waste reduction initiatives while meeting consumer demand for eco-friendly and health-conscious food options.
Conventional Ingredients: Definition and Common Uses
Conventional ingredients refer to traditional food components sourced through standard agricultural practices without specific emphasis on resource recovery or waste reduction. Common uses of these ingredients include baking, cooking, and food manufacturing, where staples like wheat flour, sugar, and dairy are essential for creating a wide variety of products. These ingredients dominate global food supply chains due to their established availability and consistency in quality and flavor.
Environmental Impact: Upcycled vs. Conventional Ingredients
Upcycled ingredients significantly reduce environmental impact by minimizing food waste and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional ingredients, which often require extensive agricultural resources and generate substantial food loss. Utilizing upcycled ingredients conserves water and energy through the repurposing of byproducts and surplus materials that would otherwise be discarded. This sustainable approach promotes circular economy principles in food production, contrasting with the linear, resource-intensive practices typical of conventional food supply chains.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Upcycled ingredients often retain higher levels of fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants compared to conventional ingredients due to minimal processing and the use of by-products from food production. Studies indicate that upcycled foods can provide comparable or enhanced nutritional profiles while reducing food waste, supporting sustainable consumption. Nutrient density in upcycled ingredients frequently surpasses conventional counterparts, particularly in micronutrients and bioactive compounds essential for health.
Food Safety and Regulatory Perspectives
Upcycled ingredients undergo rigorous safety assessments to ensure compliance with food safety regulations, reducing waste without compromising quality. Conventional ingredients typically have established regulatory frameworks, while upcycled foods require evolving standards to address potential contamination risks and traceability challenges. Regulatory agencies emphasize transparency and stringent monitoring to safeguard consumer health in both upcycled and conventional ingredient markets.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Consumers increasingly favor upcycled ingredients due to their environmental benefits and sustainability claims, perceiving them as healthier and more ethical compared to conventional ingredients. Market trends show a rising demand for products featuring upcycled components, driven by growing awareness of food waste and resource conservation. Retailers and brands are leveraging these perceptions to differentiate their offerings and tap into the eco-conscious consumer segment.
Cost-Efficiency and Supply Chain Differences
Upcycled ingredients reduce food waste by utilizing by-products, lowering raw material costs compared to conventional ingredients. Their supply chain emphasizes local sourcing and shorter logistics, enhancing freshness and reducing transportation expenses. Conventional ingredients rely on established, large-scale supply chains with consistent volume but often incur higher environmental and waste-related costs.
Taste and Quality Assessment
Upcycled ingredients often retain unique flavors and nutrients sourced from food by-products, enhancing taste profiles with sustainable appeal while maintaining high-quality standards. Conventional ingredients typically offer consistent taste and texture due to standardized processing but may lack the complex flavor notes found in upcycled alternatives. Sensory evaluations frequently reveal that upcycled ingredients can match or exceed conventional ones in taste intensity and overall quality, supporting their growing use in innovative food products.
Innovation and Sustainable Branding
Upcycled ingredients transform food industry waste into valuable resources, driving innovation through sustainable sourcing and reducing environmental impact. Conventional ingredients often rely on traditional agriculture, which can contribute to higher carbon footprints and resource depletion. Embracing upcycled ingredients enhances sustainable branding by appealing to eco-conscious consumers and positioning brands as leaders in circular food systems.
Future Outlook: The Role of Upcycled and Conventional Ingredients
Upcycled ingredients are projected to play a pivotal role in the future of sustainable food production by reducing food waste and lowering environmental impact compared to conventional ingredients. Market trends indicate a growing consumer demand for eco-friendly and nutritious options, driving innovation and investment in upcycled food solutions. Conventional ingredients remain essential for baseline food production but will increasingly be complemented or replaced by upcycled alternatives as regulatory frameworks and supply chains adapt to sustainable practices.
Upcycled ingredients vs Conventional ingredients Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com