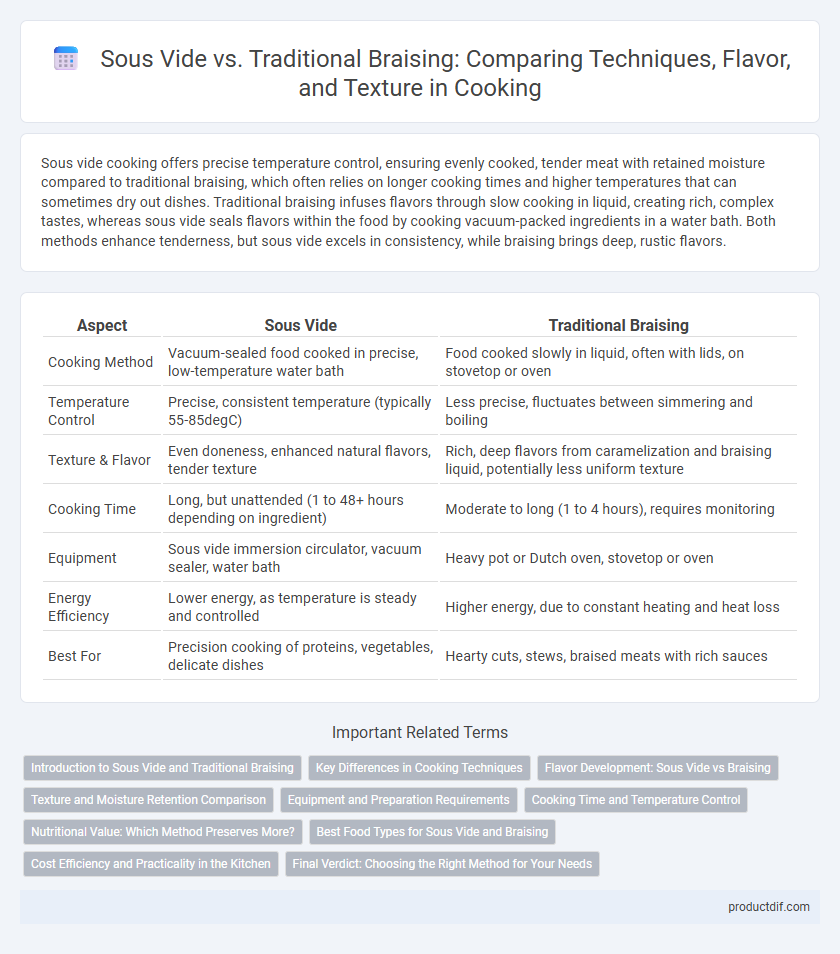
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, ensuring evenly cooked, tender meat with retained moisture compared to traditional braising, which often relies on longer cooking times and higher temperatures that can sometimes dry out dishes. Traditional braising infuses flavors through slow cooking in liquid, creating rich, complex tastes, whereas sous vide seals flavors within the food by cooking vacuum-packed ingredients in a water bath. Both methods enhance tenderness, but sous vide excels in consistency, while braising brings deep, rustic flavors.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Traditional Braising |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vacuum-sealed food cooked in precise, low-temperature water bath | Food cooked slowly in liquid, often with lids, on stovetop or oven |
| Temperature Control | Precise, consistent temperature (typically 55-85degC) | Less precise, fluctuates between simmering and boiling |
| Texture & Flavor | Even doneness, enhanced natural flavors, tender texture | Rich, deep flavors from caramelization and braising liquid, potentially less uniform texture |
| Cooking Time | Long, but unattended (1 to 48+ hours depending on ingredient) | Moderate to long (1 to 4 hours), requires monitoring |
| Equipment | Sous vide immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, water bath | Heavy pot or Dutch oven, stovetop or oven |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy, as temperature is steady and controlled | Higher energy, due to constant heating and heat loss |
| Best For | Precision cooking of proteins, vegetables, delicate dishes | Hearty cuts, stews, braised meats with rich sauces |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Traditional Braising
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a water bath at precise, low temperatures for extended periods, ensuring even doneness and flavor retention. Traditional braising combines searing and slow cooking in liquid, typically in a covered pot, to break down tough fibers in meats and develop rich, deep flavors. Both methods enhance tenderness but differ significantly in technique, temperature control, and texture outcomes.
Key Differences in Cooking Techniques
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath at a consistent low temperature, ensuring even doneness and moisture retention. Traditional braising combines searing food at high heat followed by slow cooking in a covered pot with liquid, allowing flavors to develop through evaporation and reduction. Sous vide offers precise temperature control and consistent texture, while braising emphasizes flavor complexity through browning and prolonged simmering.
Flavor Development: Sous Vide vs Braising
Sous vide cooking enhances flavor development by precisely controlling temperature, allowing meat and vegetables to retain their natural juices and intensify aromatics over extended cooking times. Traditional braising relies on slow cooking in liquid, which helps break down tough fibers while infusing the dish with rich, deep flavors from the braising liquid and aromatics. Sous vide offers consistent, tender results with enhanced intrinsic flavors, whereas braising imparts complex, layered flavors through caramelization and Maillard reactions in its moist heat environment.
Texture and Moisture Retention Comparison
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control, resulting in exceptionally tender textures and superior moisture retention compared to traditional braising, which can sometimes lead to uneven cooking and moisture loss due to higher heat exposure. The vacuum-sealed environment of sous vide locks in natural juices, preserving succulent flavors and preventing dryness often encountered in braising. While braising develops rich, complex flavors through slow simmering and caramelization, sous vide excels in maintaining consistent texture and juiciness throughout the food.
Equipment and Preparation Requirements
Sous vide cooking requires precise immersion circulators and vacuum sealers to maintain exact temperature control and airtight packaging, eliminating the need for constant monitoring. Traditional braising relies on heavy-duty pots or Dutch ovens and stovetop or oven heat, demanding attentive stirring and temperature adjustments throughout the cooking process. The investment in sous vide equipment promises consistent doneness and enhanced flavor infusion, while braising offers simplicity with readily available kitchen tools but less precision.
Cooking Time and Temperature Control
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control, typically between 130degF and 185degF, allowing food to cook evenly over extended periods, often several hours to days, depending on the recipe. Traditional braising uses higher temperatures, usually around 300degF in an oven or stovetop, with indirect heat and liquid to break down tough cuts, but it requires careful monitoring to prevent overcooking. The enhanced precision of sous vide results in consistent texture and doneness, while braising's variable heat can lead to less predictable outcomes and longer active supervision.
Nutritional Value: Which Method Preserves More?
Sous vide cooking preserves more nutrients compared to traditional braising by maintaining precise, lower temperatures and reducing nutrient loss through minimal water exposure. Vitamins like B-complex and C, which are heat-sensitive and water-soluble, remain more intact with sous vide due to sealed vacuum bags preventing leaching. Traditional braising, involving prolonged cooking in liquid at higher temperatures, often leads to greater degradation of these essential nutrients.
Best Food Types for Sous Vide and Braising
Sous vide excels with precise temperature control, making it ideal for delicate proteins like fish, poultry, and tender cuts of beef or pork, ensuring even cooking and retaining moisture. Traditional braising suits tougher cuts such as short ribs, brisket, and pork shoulder, where long, slow cooking breaks down connective tissue for rich, flavorful results. Both methods enhance texture and tenderness, but sous vide is preferred for consistency in lean meats while braising deepens flavor in tougher, collagen-rich cuts.
Cost Efficiency and Practicality in the Kitchen
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, reducing overcooking and food waste, which enhances cost efficiency compared to traditional braising that often requires longer cooking times and higher energy use. Sous vide equipment involves an initial investment but lowers labor costs by allowing unattended cooking, while traditional braising demands constant monitoring and larger energy consumption. Practicality in the kitchen favors sous vide for its consistency and ease of use, whereas traditional braising is simpler to execute without specialized tools but may lead to inconsistent results and greater time expenditure.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control and consistent results, making it ideal for perfectly tender and evenly cooked dishes. Traditional braising excels in developing deep flavors through slow cooking in liquid, suitable for rustic recipes and large cuts of meat. Selecting the right method depends on whether you prioritize exact doneness and texture or rich, complex flavors from extended simmering.
Sous vide vs Traditional braising Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com