Whole30 emphasizes a strict 30-day elimination of sugar, grains, dairy, and legumes to reset eating habits and identify food sensitivities, while Paleo allows more flexibility over time by focusing on foods presumed to be available to Paleolithic humans, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and lean meats. Paleo permits certain natural sweeteners and occasional dairy, whereas Whole30 strictly prohibits these to promote gut health and reduce inflammation. Both diets prioritize whole, unprocessed foods but differ in duration and flexibility, making them suited for varying health goals and lifestyle preferences.
Table of Comparison
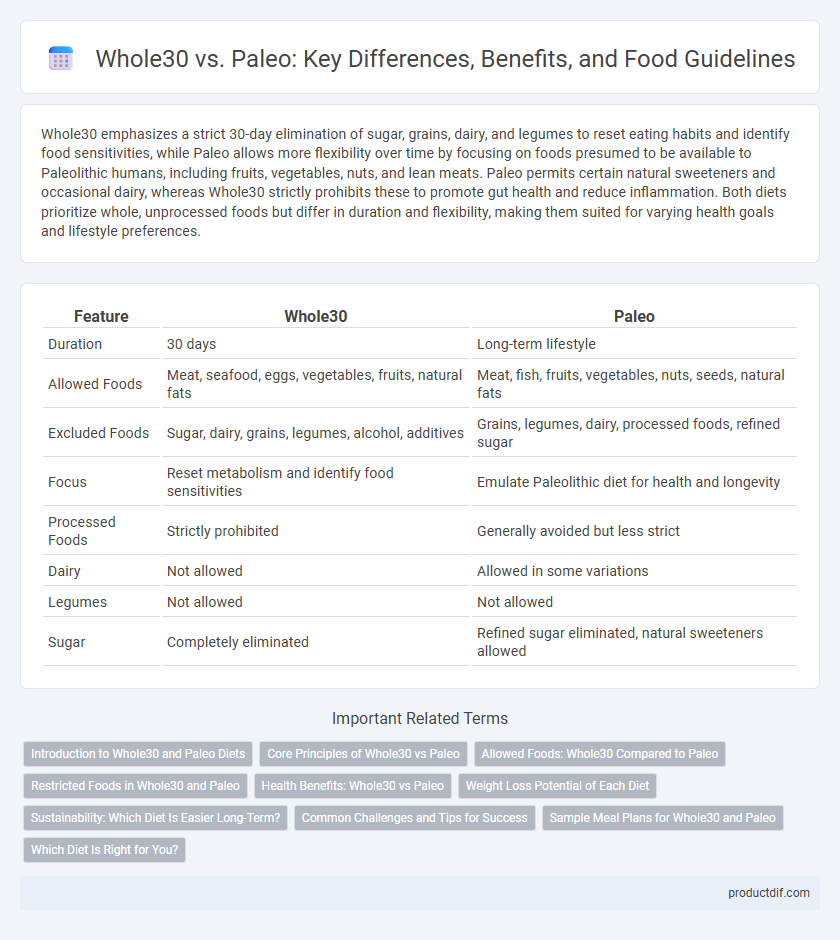
| Feature | Whole30 | Paleo |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 30 days | Long-term lifestyle |
| Allowed Foods | Meat, seafood, eggs, vegetables, fruits, natural fats | Meat, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, natural fats |
| Excluded Foods | Sugar, dairy, grains, legumes, alcohol, additives | Grains, legumes, dairy, processed foods, refined sugar |
| Focus | Reset metabolism and identify food sensitivities | Emulate Paleolithic diet for health and longevity |
| Processed Foods | Strictly prohibited | Generally avoided but less strict |
| Dairy | Not allowed | Allowed in some variations |
| Legumes | Not allowed | Not allowed |
| Sugar | Completely eliminated | Refined sugar eliminated, natural sweeteners allowed |
Introduction to Whole30 and Paleo Diets
The Whole30 diet emphasizes a 30-day elimination of sugar, alcohol, grains, legumes, dairy, and processed foods to reset the body's health and identify food sensitivities. The Paleo diet focuses on consuming foods presumed to be available to Paleolithic humans, such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while excluding modern agricultural products like grains and dairy. Both diets prioritize whole, unprocessed foods but differ in duration and specific food restrictions.
Core Principles of Whole30 vs Paleo
Whole30 emphasizes a strict 30-day elimination of sugar, alcohol, grains, legumes, dairy, and certain additives to reset the body's health and identify food sensitivities, while Paleo centers on consuming foods presumed to mirror those of Paleolithic ancestors, including lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Whole30 prohibits all forms of sweeteners and processed foods entirely during the program, promoting short-term detoxification, whereas Paleo allows natural sweeteners like honey and focuses on sustainable long-term dietary lifestyle. Both diets avoid grains and processed foods, but Whole30 is more rigid with a fixed duration, while Paleo provides flexible guidelines for ongoing consumption.
Allowed Foods: Whole30 Compared to Paleo
Whole30 emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods including vegetables, fruits, lean meats, seafood, eggs, and healthy fats, strictly eliminating grains, legumes, dairy, added sugars, and alcohol for 30 days. Paleo diet allows similar foods but permits natural sweeteners like honey, certain dairy products like grass-fed butter, and occasionally legumes and carbohydrates such as sweet potatoes. Whole30 is more restrictive, aiming for a reset by avoiding all potentially inflammatory foods during the program, whereas Paleo is a broader lifestyle approach focused on eating foods presumed to be available to Paleolithic ancestors.
Restricted Foods in Whole30 and Paleo
Whole30 restricts all forms of added sugar, grains, dairy, legumes, and alcohol for a strict 30-day reset, eliminating foods that could cause inflammation or digestive issues. Paleo excludes grains, legumes, dairy, and processed foods but allows natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup, offering more flexibility in sugar intake. Both diets focus on whole, unprocessed foods but differ primarily in their stance on sweeteners and the strictness of food elimination.
Health Benefits: Whole30 vs Paleo
Whole30 emphasizes a strict 30-day elimination of processed foods, sugar, grains, dairy, and legumes to reset metabolism and reduce inflammation, resulting in improved digestion and energy levels. Paleo encourages consumption of lean meats, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds while excluding processed food, emphasizing nutrient density and stable blood sugar, which supports weight loss and cardiovascular health. Both diets promote gut health and reduce chronic disease risk, but Whole30's structured timeframe offers a targeted detox approach compared to Paleo's long-term lifestyle focus.
Weight Loss Potential of Each Diet
Whole30 emphasizes a 30-day reset eliminating sugar, grains, dairy, and legumes, promoting rapid weight loss primarily through calorie reduction and improved food quality. Paleo allows more flexibility with natural, unprocessed foods including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and lean meats, supporting sustainable weight loss by balancing macronutrients and reducing processed food intake. Studies indicate both diets can lead to weight loss, but Whole30's strict elimination phase often results in quicker initial results, while Paleo's long-term approach may better support gradual and maintainable fat loss.
Sustainability: Which Diet Is Easier Long-Term?
Whole30 emphasizes short-term elimination and strict adherence for 30 days, making long-term sustainability challenging due to its rigid restrictions. Paleo promotes a broader range of food choices and encourages lifestyle flexibility, which supports easier adaptation and maintenance over time. Emphasizing nutrient-dense whole foods, Paleo's emphasis on variety and balance aligns better with sustainable, long-term healthy eating habits.
Common Challenges and Tips for Success
Whole30 and Paleo share common challenges such as navigating social situations and avoiding hidden sugars or processed ingredients. Success tips include meal planning, preparing Whole30-approved snacks, and gradually eliminating non-compliant foods to ease the transition. Prioritizing nutrient-dense foods like vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports adherence to both dietary approaches.
Sample Meal Plans for Whole30 and Paleo
Whole30 sample meal plans emphasize strict elimination of sugar, grains, dairy, and legumes, focusing on whole foods like eggs, vegetables, lean meats, and fruits for a 30-day reset. Paleo meal plans incorporate a broader variety of nutrient-dense foods, including nuts, seeds, and natural sweeteners like honey, while maintaining exclusion of processed foods, grains, and dairy. Both diets prioritize high protein and fiber intake but differ in allowable ingredients and duration, with Whole30 being more restrictive and time-bound.
Which Diet Is Right for You?
Whole30 emphasizes a strict 30-day elimination of sugar, grains, dairy, and legumes to reset eating habits and identify food sensitivities, making it ideal for those seeking a short-term detox. The Paleo diet allows more flexibility, promoting whole foods like meats, vegetables, nuts, and fruits while excluding processed foods and refined sugars, suited for individuals aiming for long-term sustainable eating patterns. Choosing between Whole30 and Paleo depends on your health goals, dietary preferences, and commitment to either a structured reset or lifestyle adaptation.
Whole30 vs Paleo Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com