GMO labeling provides transparency by informing consumers about the presence of genetically modified organisms in food products, helping them make informed choices. The Non-GMO Project offers third-party verification, ensuring products meet rigorous standards for GMO avoidance and promoting consumer trust. Both approaches support market demand for clear information on food sourcing and production methods.
Table of Comparison
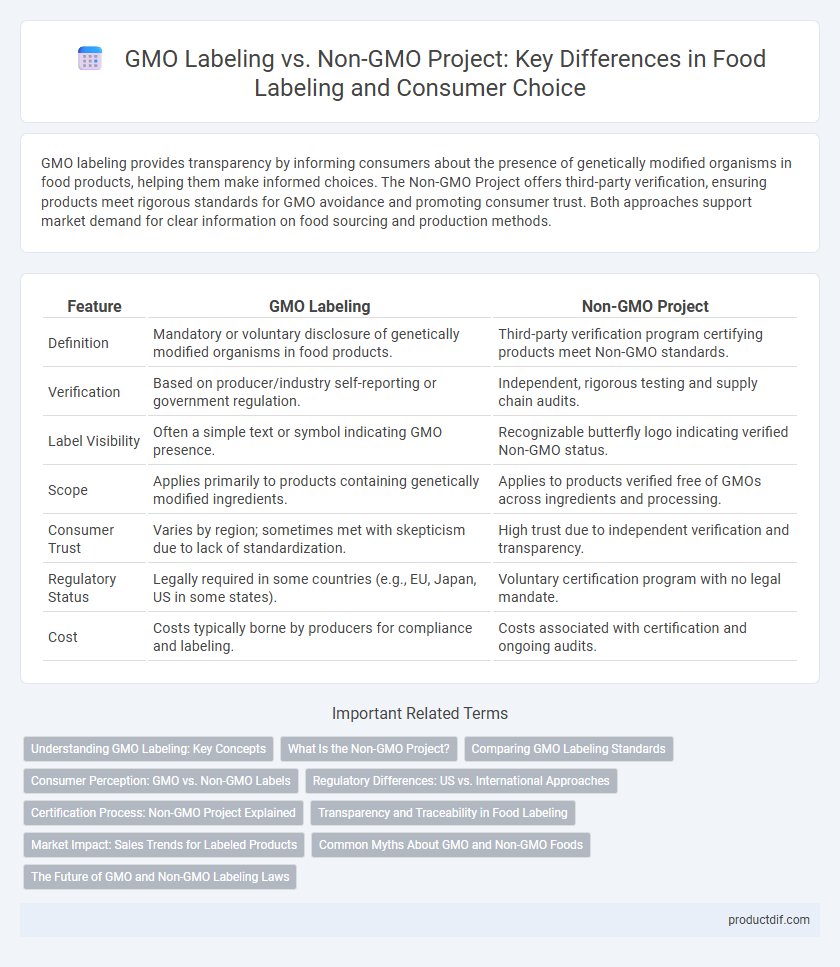
| Feature | GMO Labeling | Non-GMO Project |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mandatory or voluntary disclosure of genetically modified organisms in food products. | Third-party verification program certifying products meet Non-GMO standards. |
| Verification | Based on producer/industry self-reporting or government regulation. | Independent, rigorous testing and supply chain audits. |
| Label Visibility | Often a simple text or symbol indicating GMO presence. | Recognizable butterfly logo indicating verified Non-GMO status. |
| Scope | Applies primarily to products containing genetically modified ingredients. | Applies to products verified free of GMOs across ingredients and processing. |
| Consumer Trust | Varies by region; sometimes met with skepticism due to lack of standardization. | High trust due to independent verification and transparency. |
| Regulatory Status | Legally required in some countries (e.g., EU, Japan, US in some states). | Voluntary certification program with no legal mandate. |
| Cost | Costs typically borne by producers for compliance and labeling. | Costs associated with certification and ongoing audits. |
Understanding GMO Labeling: Key Concepts
Understanding GMO labeling involves recognizing key concepts such as genetically modified organisms, which are plants or animals altered using biotechnology to exhibit specific traits. The Non-GMO Project offers third-party verification and labeling for products that meet strict standards for GMO avoidance, providing consumers with transparency. Clear GMO labeling helps consumers make informed decisions by distinguishing between genetically engineered foods and those verified as non-GMO.
What Is the Non-GMO Project?
The Non-GMO Project is a nonprofit organization dedicated to verifying and labeling products that meet rigorous standards for being free from genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Their verification process involves detailed ingredient screening, traceability, and segregation to ensure transparency and integrity in food labeling. This label provides consumers with reliable information to make informed choices about non-GMO products.
Comparing GMO Labeling Standards
GMO labeling standards vary significantly between regulatory bodies and third-party certifications, impacting consumer transparency and trust. The U.S. mandatory GMO labeling, enforced by the National Bioengineered Food Disclosure Standard (NBFDS), requires disclosure of bioengineered ingredients but allows flexible formats, which some argue reduces clarity. In contrast, the Non-GMO Project offers a rigorous third-party verification with strict thresholds for GMO presence, emphasizing clear labeling and traceability, which many consumers and retailers prefer for non-GMO product assurance.
Consumer Perception: GMO vs. Non-GMO Labels
Consumer perception of GMO labeling often revolves around concerns about health, safety, and environmental impact, with many associating GMO labels with potential risks despite scientific consensus on their safety. Non-GMO Project Verified labels tend to evoke a sense of naturalness and trust, appealing to consumers who prioritize organic and pesticide-free products. Market research shows that products bearing non-GMO labels frequently achieve higher sales among health-conscious buyers seeking transparency and sustainability in food production.
Regulatory Differences: US vs. International Approaches
GMO labeling regulations in the US are overseen by the USDA's National Bioengineered Food Disclosure Standard, which requires disclosure of bioengineered ingredients but allows various labeling formats. Internationally, the European Union enforces stricter GMO labeling laws under Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011, mandating clear labeling of products containing more than 0.9% GMOs. The Non-GMO Project, a third-party verification organization in the US, offers voluntary labeling that emphasizes transparency but operates independently from government regulatory frameworks, contrasting with mandatory international mandates.
Certification Process: Non-GMO Project Explained
The Non-GMO Project certification process involves rigorous third-party verification to ensure products meet strict standards for GMO avoidance, including traceability and segregation practices throughout the supply chain. This certification requires comprehensive testing of high-risk ingredients for GMO content and ongoing annual audits to maintain compliance. Unlike general GMO labeling, the Non-GMO Project label provides consumers with verified transparency and assurance of non-GMO integrity.
Transparency and Traceability in Food Labeling
Transparency and traceability in food labeling are critical for consumers seeking clear information about genetically modified organisms (GMO) in their products. GMO labeling mandates provide regulated, standardized disclosures governed by government agencies, ensuring consistent information about ingredient origins and genetic alterations. In contrast, the Non-GMO Project emphasizes third-party verification with a transparent supply chain audit, offering detailed traceability and consumer confidence through its verified non-GMO certification standards.
Market Impact: Sales Trends for Labeled Products
Products labeled as GMO and Non-GMO Project Verified show distinct sales trends, with Non-GMO products experiencing faster growth due to increasing consumer demand for transparency and perceived health benefits. Market data reveals that Non-GMO labeled foods command a premium price and attract a loyal customer base, driving expansion across natural and organic retail sectors. In contrast, GMO-labeled products maintain stable sales in commodity markets but face challenges gaining traction among health-conscious buyers.
Common Myths About GMO and Non-GMO Foods
Common myths about GMO and non-GMO foods include misconceptions that GMOs are inherently unsafe or that non-GMO products are always healthier or more nutritious. Scientific consensus confirms that genetically modified organisms undergo rigorous testing for safety and nutritional equivalence, while non-GMO labeling primarily focuses on absence of genetic modification rather than overall health benefits. Consumers benefit from understanding labeling standards such as the Non-GMO Project Verified seal, which ensures products meet strict non-GMO criteria without implying superiority in safety or nutrition.
The Future of GMO and Non-GMO Labeling Laws
Evolving regulatory frameworks for GMO labeling emphasize transparency and consumer choice, with laws increasingly mandating clear disclosure of genetically modified ingredients. The Non-GMO Project's third-party verification continues to influence market demand by providing trusted certification beyond legal requirements. Advances in biotechnology and shifting public sentiment are driving legislative updates that balance innovation with stringent labeling standards worldwide.
GMO labeling vs non-GMO project Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com