Choosing sugar-free pet food helps prevent obesity and dental issues, promoting overall health and longevity. Sweetened pet foods may enhance flavor but often contain added sugars that can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance. Prioritizing sugar-free options supports balanced nutrition and reduces the risk of chronic diseases in pets.
Table of Comparison
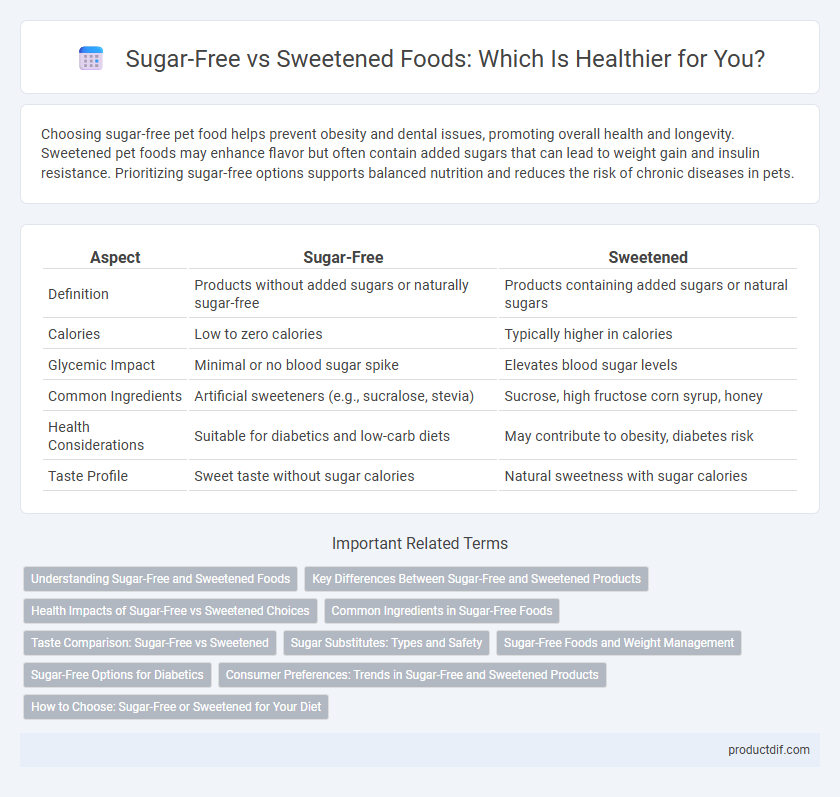
| Aspect | Sugar-Free | Sweetened |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Products without added sugars or naturally sugar-free | Products containing added sugars or natural sugars |
| Calories | Low to zero calories | Typically higher in calories |
| Glycemic Impact | Minimal or no blood sugar spike | Elevates blood sugar levels |
| Common Ingredients | Artificial sweeteners (e.g., sucralose, stevia) | Sucrose, high fructose corn syrup, honey |
| Health Considerations | Suitable for diabetics and low-carb diets | May contribute to obesity, diabetes risk |
| Taste Profile | Sweet taste without sugar calories | Natural sweetness with sugar calories |
Understanding Sugar-Free and Sweetened Foods
Sugar-free foods contain artificial or natural non-caloric sweeteners such as stevia, erythritol, or sucralose, which provide sweetness without increasing blood sugar levels, making them ideal for diabetics and calorie-conscious consumers. Sweetened foods, on the other hand, are typically formulated with added sugars like sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup, or honey, contributing to higher calorie content and potential risks for obesity and metabolic diseases. Understanding the differences in sugar content and glycemic impact between sugar-free and sweetened products helps consumers make informed dietary choices based on health goals and nutritional needs.
Key Differences Between Sugar-Free and Sweetened Products
Sugar-free products contain artificial or natural non-nutritive sweeteners like stevia, erythritol, or sucralose, which provide sweetness without adding calories or impacting blood sugar levels. Sweetened products typically use sugar or high-fructose corn syrup, contributing to higher calorie content and increased glycemic response. Key differences include their effects on insulin, calorie intake, and suitability for diabetics or those managing weight.
Health Impacts of Sugar-Free vs Sweetened Choices
Choosing sugar-free alternatives significantly reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and obesity compared to sweetened options laden with high fructose corn syrup or sucrose. Artificial sweeteners in sugar-free products do not raise blood glucose levels, making them safer for individuals with insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome. Long-term consumption of sweetened foods is linked to increased inflammation and cardiovascular disease, whereas sugar-free choices often contribute to better weight management and overall metabolic health.
Common Ingredients in Sugar-Free Foods
Common ingredients in sugar-free foods often include natural sweeteners such as stevia, erythritol, and monk fruit extract, which provide sweetness without the calories of sugar. Sugar alcohols like xylitol and sorbitol are frequently used for their bulking properties and low glycemic impact. These ingredients allow sugar-free products to maintain sweetness while supporting blood sugar management and dental health.
Taste Comparison: Sugar-Free vs Sweetened
Sugar-free products often use artificial or natural sweeteners like stevia or erythritol to mimic the sweetness of sugar without the calories, but they can sometimes have a slightly different aftertaste compared to sweetened options. Sweetened foods with sucrose or high-fructose corn syrup generally provide a more familiar, rich sweetness that many consumers prefer. Taste preferences vary, with some individuals favoring the cleaner, less cloying profile of sugar-free alternatives while others find sweetened products more satisfying and flavorful.
Sugar Substitutes: Types and Safety
Sugar substitutes used in sugar-free foods include natural options like stevia and monk fruit, as well as artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin. These substitutes vary in sweetness intensity, calorie content, and metabolic effects, with many approved by regulatory agencies like the FDA for safety when consumed within recommended limits. Studies indicate that while sugar substitutes are generally safe, individual responses and potential gastrointestinal effects should be considered when incorporating them into a diet.
Sugar-Free Foods and Weight Management
Sugar-free foods help reduce calorie intake, supporting weight management by eliminating added sugars that contribute to excess fat storage. These products often use sugar substitutes like stevia or erythritol, which provide sweetness without the glycemic impact of traditional sugars. Incorporating sugar-free options into a balanced diet can aid in controlling blood sugar levels and promoting healthier body weight.
Sugar-Free Options for Diabetics
Sugar-free options for diabetics are designed to maintain blood glucose levels without causing spikes, utilizing sweeteners like stevia, erythritol, or monk fruit that do not raise insulin levels. These alternatives support glycemic control and reduce the risk of complications associated with high sugar intake. Choosing sugar-free products enables diabetics to enjoy sweet flavors while managing their condition effectively.
Consumer Preferences: Trends in Sugar-Free and Sweetened Products
Consumer preferences increasingly favor sugar-free products due to growing health awareness and concerns about sugar-related illnesses such as diabetes and obesity. Market data reveals a significant rise in demand for sugar-free beverages and snacks, driven by younger, health-conscious demographics seeking lower-calorie alternatives. Despite this, sweetened products remain popular due to taste preferences and emotional connections, highlighting a diverse market where convenience and flavor balance influence purchasing decisions.
How to Choose: Sugar-Free or Sweetened for Your Diet
Choosing between sugar-free and sweetened options depends on your dietary goals and health conditions; sugar-free products often contain artificial or natural non-nutritive sweeteners suitable for reducing calorie intake and managing blood sugar levels. Sweetened items provide natural sugars or added sugars that can offer quick energy but may contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance if consumed excessively. Evaluating nutritional labels for sugar content, glycemic index, and ingredient sources helps tailor your diet to support metabolic health and personal preferences.
Sugar-Free vs Sweetened Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com