Grass-fed beef offers a leaner nutritional profile with higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants compared to grain-fed beef. Grain-fed beef tends to have more marbling, resulting in a richer flavor and tender texture favored in many culinary applications. Choosing between grass-fed and grain-fed beef depends on preferences for taste, nutritional benefits, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
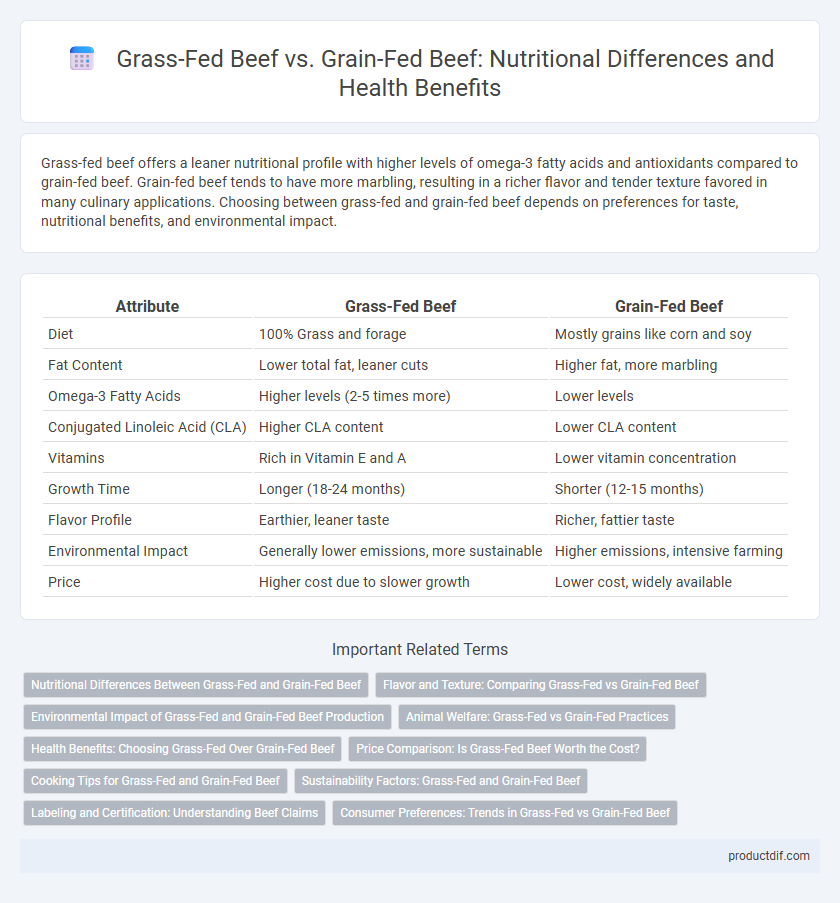
| Attribute | Grass-Fed Beef | Grain-Fed Beef |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | 100% Grass and forage | Mostly grains like corn and soy |
| Fat Content | Lower total fat, leaner cuts | Higher fat, more marbling |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Higher levels (2-5 times more) | Lower levels |
| Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) | Higher CLA content | Lower CLA content |
| Vitamins | Rich in Vitamin E and A | Lower vitamin concentration |
| Growth Time | Longer (18-24 months) | Shorter (12-15 months) |
| Flavor Profile | Earthier, leaner taste | Richer, fattier taste |
| Environmental Impact | Generally lower emissions, more sustainable | Higher emissions, intensive farming |
| Price | Higher cost due to slower growth | Lower cost, widely available |
Nutritional Differences Between Grass-Fed and Grain-Fed Beef
Grass-fed beef contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), and antioxidants like vitamin E compared to grain-fed beef. The lower fat content in grass-fed beef contributes to reduced saturated fat and increased levels of beneficial nutrients, supporting cardiovascular health. Grain-fed beef typically has more total fat and omega-6 fatty acids, which can affect the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio important for inflammation regulation.
Flavor and Texture: Comparing Grass-Fed vs Grain-Fed Beef
Grass-fed beef offers a distinct, robust flavor profile with a leaner texture due to the animal's natural diet, resulting in a slightly tougher but more nutrient-dense meat. Grain-fed beef is characterized by a richer, buttery taste and marbled texture, which enhances tenderness and juiciness through higher fat content. Both types appeal differently depending on culinary preferences, with grass-fed preferred for earthy flavor and grain-fed favored for smooth, tender mouthfeel.
Environmental Impact of Grass-Fed and Grain-Fed Beef Production
Grass-fed beef production generally has a lower carbon footprint per acre due to improved soil health and carbon sequestration from grazing practices, though it requires more land compared to grain-fed systems. Grain-fed beef tends to produce higher greenhouse gas emissions per pound of meat because of intensive feed crop cultivation and concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs) that increase methane and nitrous oxide outputs. Sustainable grazing management in grass-fed systems can mitigate environmental impacts, while grain-fed production often contributes to deforestation, water pollution, and heavy fossil fuel use in feed crop production.
Animal Welfare: Grass-Fed vs Grain-Fed Practices
Grass-fed beef typically comes from cattle raised on pasture with access to natural grazing, promoting better animal welfare through more natural behaviors and conditions. Grain-fed beef cattle are often confined to feedlots where their diet is supplemented with grains, which can lead to increased stress and health issues. Choosing grass-fed beef supports farming practices that prioritize open spaces and reduced reliance on antibiotics, enhancing overall animal welfare.
Health Benefits: Choosing Grass-Fed Over Grain-Fed Beef
Grass-fed beef contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), and antioxidants like vitamin E compared to grain-fed beef, supporting heart health and reducing inflammation. Its lower fat content and improved fatty acid profile contribute to better cholesterol levels and reduced risk of chronic diseases. Consumers opting for grass-fed beef benefit from a more nutrient-dense protein source that aligns with healthier dietary choices.
Price Comparison: Is Grass-Fed Beef Worth the Cost?
Grass-fed beef typically costs 20-50% more than grain-fed beef due to higher production costs and longer raising periods. Consumers often find the premium worth it for perceived benefits like improved flavor, higher omega-3 fatty acids, and ethical farming practices. However, price sensitivity varies, making grass-fed beef a preferred choice mainly among health-conscious and environmentally aware buyers.
Cooking Tips for Grass-Fed and Grain-Fed Beef
Grass-fed beef requires lower cooking temperatures and shorter cooking times to preserve its lean texture and natural flavors, making it ideal for quick searing or medium-rare preparation. Grain-fed beef, with its higher fat content, benefits from slower cooking methods like braising or roasting to enhance tenderness and juiciness. Resting both types of beef after cooking helps redistribute juices, resulting in a more succulent bite.
Sustainability Factors: Grass-Fed and Grain-Fed Beef
Grass-fed beef production often results in lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to grain-fed beef, as cattle graze on pasturelands that can sequester carbon in soil. Grain-fed beef typically requires more intensive resource inputs, such as water and fossil fuels, due to feed crop cultivation and feedlot management. Sustainable practices in grass-fed systems also promote biodiversity and soil health, making them a more eco-friendly choice.
Labeling and Certification: Understanding Beef Claims
Grass-fed beef labeling often requires certification from organizations like the American Grassfed Association, ensuring cattle are raised on pasture without grain supplementation. Grain-fed beef labels typically indicate feedlot finishing with grains like corn or soy, influencing marbling and flavor profiles. Consumers should verify claims through credible certifications to distinguish feeding practices and assess product authenticity.
Consumer Preferences: Trends in Grass-Fed vs Grain-Fed Beef
Consumer preferences for grass-fed beef have surged due to perceived health benefits, including higher omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, as well as environmental sustainability concerns. Grain-fed beef remains popular for its consistent marbling and tenderness, appealing to taste-driven consumers and cost-conscious buyers. Market trends indicate a growing niche for premium grass-fed products, while grain-fed beef dominates mainstream demand owing to established supply chains and affordability.
Grass-Fed Beef vs Grain-Fed Beef Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com