Zero-waste packaging reduces environmental impact by using biodegradable, compostable, or reusable materials, minimizing landfill waste and pollution. Traditional packaging often relies on single-use plastics and non-recyclable materials, contributing significantly to global plastic waste. Adopting zero-waste solutions supports sustainable food systems and promotes resource conservation throughout the supply chain.
Table of Comparison
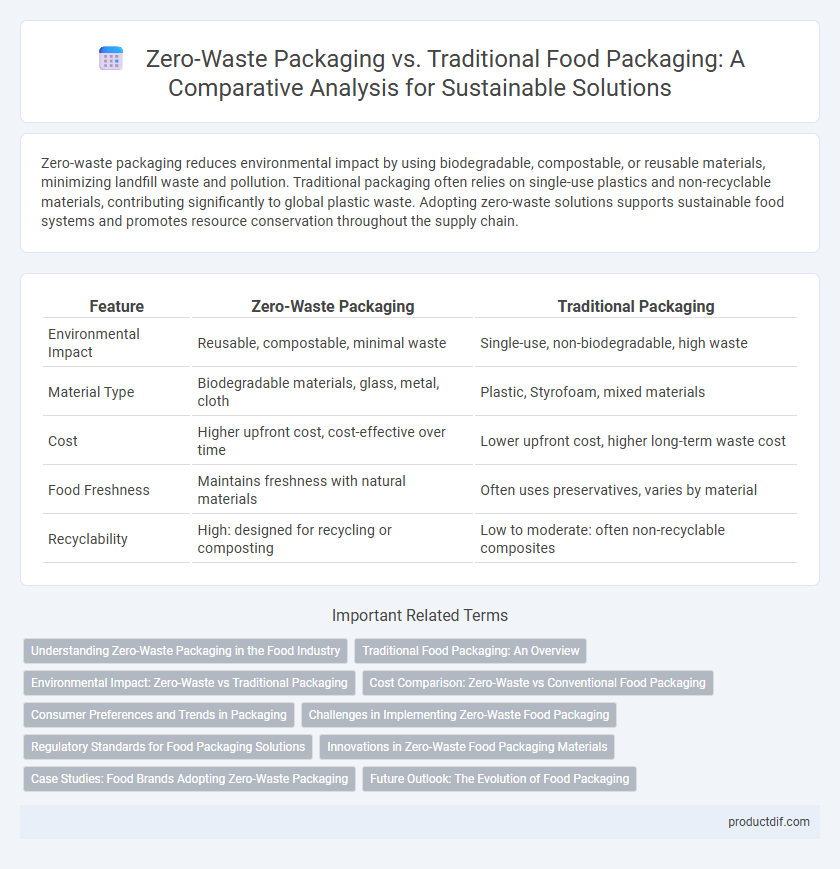
| Feature | Zero-Waste Packaging | Traditional Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Reusable, compostable, minimal waste | Single-use, non-biodegradable, high waste |
| Material Type | Biodegradable materials, glass, metal, cloth | Plastic, Styrofoam, mixed materials |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, cost-effective over time | Lower upfront cost, higher long-term waste cost |
| Food Freshness | Maintains freshness with natural materials | Often uses preservatives, varies by material |
| Recyclability | High: designed for recycling or composting | Low to moderate: often non-recyclable composites |
Understanding Zero-Waste Packaging in the Food Industry
Zero-waste packaging in the food industry utilizes materials designed for complete reuse, composting, or recycling to minimize environmental impact and reduce landfill waste. Unlike traditional packaging often made from single-use plastics and non-recyclable components, zero-waste alternatives include biodegradable wraps, edible containers, and refillable jars that maintain product freshness while promoting sustainability. Embracing zero-waste packaging aligns with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions and regulatory pressures targeting plastic pollution reduction.
Traditional Food Packaging: An Overview
Traditional food packaging primarily relies on materials such as plastic, glass, aluminum, and paperboard, designed for durability and convenience. These materials often contribute significantly to environmental pollution due to limited recyclability and high carbon footprints during production and disposal. Despite its widespread use, traditional packaging poses challenges in sustainability, driving increased demand for eco-friendly alternatives.
Environmental Impact: Zero-Waste vs Traditional Packaging
Zero-waste packaging significantly reduces plastic pollution and carbon emissions by utilizing biodegradable or reusable materials, minimizing landfill waste. Traditional packaging often relies on single-use plastics and non-recyclable materials, contributing to resource depletion and elevated greenhouse gas emissions. Switching to zero-waste packaging supports sustainable supply chains and promotes circular economy principles in the food industry.
Cost Comparison: Zero-Waste vs Conventional Food Packaging
Zero-waste packaging often requires higher upfront investment due to sustainable materials like biodegradable plastics or reusable containers, which can increase initial costs compared to conventional packaging made from cheap plastics or cardboard. Over time, zero-waste solutions reduce expenses related to waste disposal, regulatory fees, and environmental fines, potentially lowering total cost of ownership. Traditional packaging benefits from established supply chains and economies of scale, offering lower upfront costs but higher long-term environmental and waste management expenses.
Consumer Preferences and Trends in Packaging
Consumer preferences increasingly favor zero-waste packaging due to growing environmental awareness and demand for sustainable food solutions. Market trends reveal a significant rise in the adoption of biodegradable, compostable, and reusable materials compared to traditional plastic and non-recyclable packaging. Brands leveraging eco-friendly packaging strategies experience higher consumer loyalty and positive brand perception in the competitive food industry.
Challenges in Implementing Zero-Waste Food Packaging
Implementing zero-waste food packaging faces challenges such as high production costs and limited availability of biodegradable materials compared to traditional plastic packaging. The need for robust supply chains and consumer acceptance also slows widespread adoption. Regulatory hurdles and the lack of standardized composting infrastructure further complicate efforts to scale zero-waste packaging solutions.
Regulatory Standards for Food Packaging Solutions
Regulatory standards for zero-waste packaging in the food industry prioritize compostability, recyclability, and the absence of toxic chemicals to ensure food safety and environmental sustainability. Traditional packaging often faces stricter regulations related to material composition and food contact safety, frequently mandating extensive testing for contaminants like BPA or phthalates. Compliance with agencies such as the FDA, EFSA, and ISO 18604 ensures that zero-waste packaging solutions meet both performance criteria and environmental regulations, driving innovation in sustainable food packaging.
Innovations in Zero-Waste Food Packaging Materials
Innovations in zero-waste food packaging materials include biodegradable bioplastics derived from plant starches and algae-based films that decompose naturally without harming the environment. Edible packaging made from seaweed and rice paper offers sustainable alternatives that reduce landfill waste and plastic pollution. Advances in compostable coatings and recyclable fiber-based containers also enhance product freshness while supporting circular economy principles in the food industry.
Case Studies: Food Brands Adopting Zero-Waste Packaging
Food brands such as Loop and Lush have successfully integrated zero-waste packaging by using reusable containers and biodegradable materials, significantly reducing plastic waste in their supply chains. Studies show Loop's partnership with major companies like Nestle led to a 25% decrease in single-use packaging within two years, proving the economic viability and environmental impact of zero-waste initiatives. Lush reports that their zero-waste packaging strategies have cut over 2 million plastic bottles annually, highlighting a scalable model for sustainable packaging in the food industry.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Food Packaging
Zero-waste packaging is projected to dominate the future of food packaging due to increasing consumer demand for sustainability and stringent environmental regulations. Innovations in biodegradable materials and edible packaging are accelerating, reducing reliance on single-use plastics and minimizing landfill waste. Traditional packaging is expected to evolve by integrating recyclable components and smart technology to enhance food preservation and traceability, aligning with global carbon reduction goals.
Zero-Waste Packaging vs Traditional Packaging Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com