Single glazing consists of one layer of glass, offering minimal insulation and higher heat transfer, leading to increased energy costs. Double glazing features two glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space, providing superior thermal insulation, noise reduction, and enhanced security. Choosing double glazing over single glazing significantly improves energy efficiency and indoor comfort in buildings.
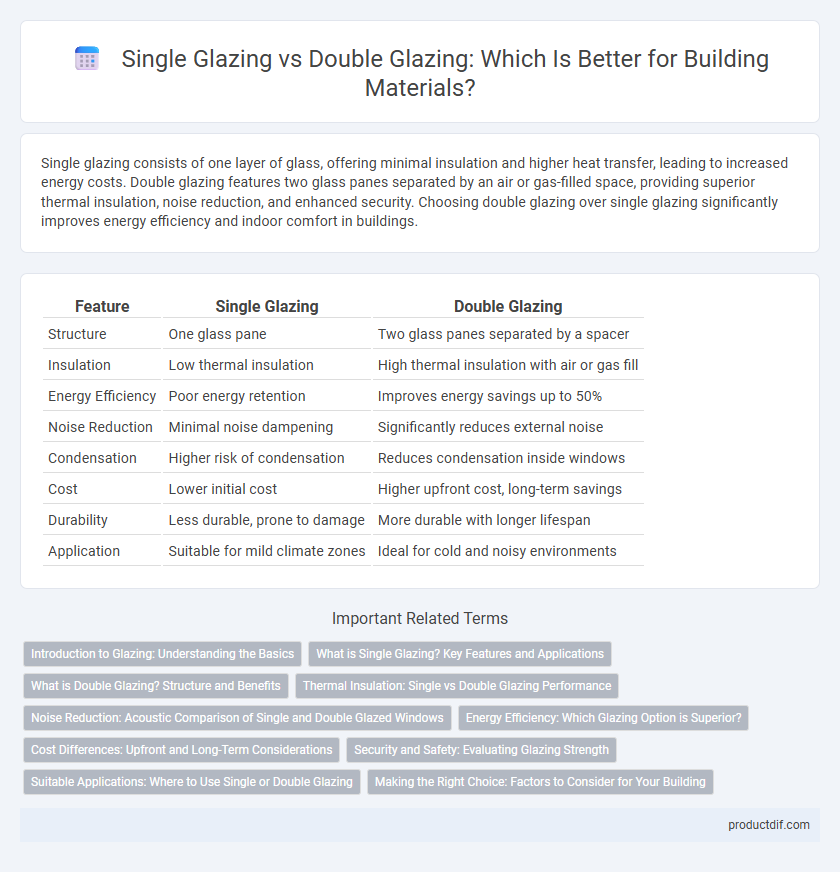
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single Glazing | Double Glazing |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | One glass pane | Two glass panes separated by a spacer |
| Insulation | Low thermal insulation | High thermal insulation with air or gas fill |
| Energy Efficiency | Poor energy retention | Improves energy savings up to 50% |
| Noise Reduction | Minimal noise dampening | Significantly reduces external noise |
| Condensation | Higher risk of condensation | Reduces condensation inside windows |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost, long-term savings |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to damage | More durable with longer lifespan |
| Application | Suitable for mild climate zones | Ideal for cold and noisy environments |
Introduction to Glazing: Understanding the Basics
Single glazing consists of a single pane of glass, providing minimal insulation and heat retention in building materials. Double glazing incorporates two glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or inert gas, significantly improving thermal performance and reducing noise transmission. Understanding these fundamental differences is essential for making informed decisions about energy efficiency and comfort in construction projects.
What is Single Glazing? Key Features and Applications
Single glazing consists of a single pane of glass, offering basic insulation and soundproofing properties suitable for mild climates and interior applications. Key features include lower cost, simple installation, and limited thermal efficiency compared to double glazing. Common applications involve interior partitions, decorative windows, and older buildings where historical appearance is prioritized.
What is Double Glazing? Structure and Benefits
Double glazing consists of two glass panes separated by a gas-filled space, typically argon, which enhances thermal insulation and soundproofing in buildings. The structure reduces heat transfer, lowers energy bills, and improves indoor comfort by minimizing external noise and condensation. This advanced window system significantly boosts energy efficiency and property value compared to single glazing.
Thermal Insulation: Single vs Double Glazing Performance
Double glazing significantly enhances thermal insulation by incorporating two glass panes separated by an air or inert gas-filled gap, which reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency. Single glazing, consisting of a single glass pane, allows more heat loss and gain, leading to higher energy consumption for heating or cooling. The insulating properties of double glazing contribute to maintaining indoor temperature stability and reducing utility costs compared to single glazing.
Noise Reduction: Acoustic Comparison of Single and Double Glazed Windows
Double glazed windows provide superior noise reduction compared to single glazed windows by incorporating two layers of glass separated by an air or gas-filled gap, which acts as an effective sound barrier. The acoustic insulation levels of double glazing typically reduce noise transmission by 25-35 decibels, whereas single glazing usually achieves only around 15 decibels of noise reduction. This significant difference in soundproofing performance makes double glazed windows the preferred choice for urban environments and noise-sensitive settings.
Energy Efficiency: Which Glazing Option is Superior?
Double glazing offers superior energy efficiency compared to single glazing by significantly reducing heat transfer through windows, which lowers heating and cooling costs. The air or gas-filled space between the two panes in double glazing acts as an insulating barrier, minimizing thermal exchange and enhancing indoor comfort. Single glazing lacks this insulating layer, resulting in higher energy consumption and less effective temperature regulation.
Cost Differences: Upfront and Long-Term Considerations
Single glazing typically costs significantly less upfront than double glazing, making it a budget-friendly choice for initial installation. However, double glazing offers better insulation, leading to lower energy bills and reduced heating and cooling expenses over time. Evaluating long-term savings against initial expenditure is crucial for deciding between single and double glazing in building projects.
Security and Safety: Evaluating Glazing Strength
Single glazing typically consists of a single pane of glass, making it more susceptible to breakage and easier for intruders to penetrate, thus offering lower security and safety. Double glazing features two layers of glass with an air or gas-filled gap, significantly enhancing the strength and resistance to impact, reducing the likelihood of burglary and accidental injuries. The added durability of double glazing also improves thermal insulation, indirectly contributing to safety by minimizing risks related to temperature fluctuations.
Suitable Applications: Where to Use Single or Double Glazing
Single glazing is suitable for interior spaces or mild climates where insulation and noise reduction are not critical, such as internal doors, decorative windows, or temporary structures. Double glazing is ideal for external windows in residential and commercial buildings, especially in regions with extreme temperatures or high noise levels, providing superior thermal insulation and soundproofing. Choosing between single and double glazing depends on the required energy efficiency, noise control, and budget constraints for the specific building application.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider for Your Building
Single glazing offers lower initial costs but lacks in thermal insulation and noise reduction compared to double glazing, which provides enhanced energy efficiency and soundproofing. Consider climate, budget, and long-term energy savings when choosing between single and double glazing for building windows. Double glazing also improves property value and reduces condensation risks, making it a sustainable investment for modern constructions.
Single Glazing vs Double Glazing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com