Membrane roofing offers a lightweight, flexible solution that provides excellent waterproofing and ease of installation, ideal for flat or low-slope roofs, while built-up roofing (BUR) consists of multiple layers of bitumen and reinforcing fabrics, delivering exceptional durability and resistance to heavy foot traffic. Membrane roofing materials such as TPO, EPDM, and PVC resist UV rays and chemical exposure, making them energy-efficient and low-maintenance options. Built-up roofing systems excel in long-term performance and fire resistance but require more labor-intensive installation and regular maintenance to ensure longevity.
Table of Comparison
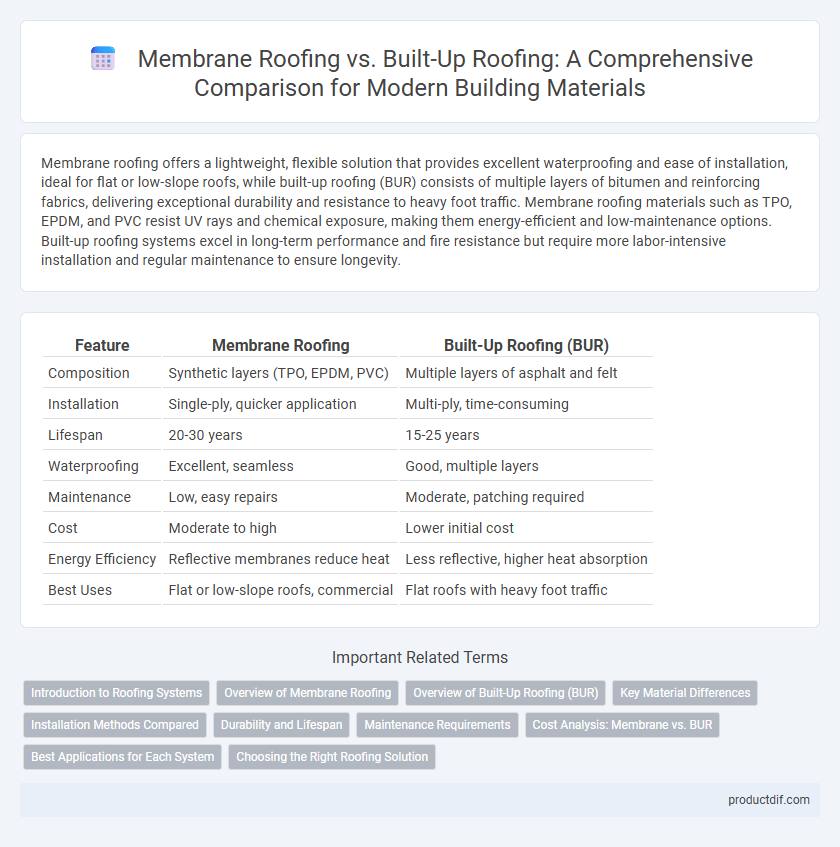
| Feature | Membrane Roofing | Built-Up Roofing (BUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Synthetic layers (TPO, EPDM, PVC) | Multiple layers of asphalt and felt |
| Installation | Single-ply, quicker application | Multi-ply, time-consuming |
| Lifespan | 20-30 years | 15-25 years |
| Waterproofing | Excellent, seamless | Good, multiple layers |
| Maintenance | Low, easy repairs | Moderate, patching required |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower initial cost |
| Energy Efficiency | Reflective membranes reduce heat | Less reflective, higher heat absorption |
| Best Uses | Flat or low-slope roofs, commercial | Flat roofs with heavy foot traffic |
Introduction to Roofing Systems
Membrane roofing systems consist of synthetic materials like TPO, EPDM, and PVC, providing a lightweight, flexible, and watertight solution ideal for flat or low-slope roofs. Built-up roofing (BUR) involves multiple layers of bitumen and reinforcing fabrics, creating a durable, robust barrier that excels in heavy-duty applications. Both systems offer distinct advantages depending on factors such as climate, roof structure, and maintenance requirements.
Overview of Membrane Roofing
Membrane roofing consists of flexible sheets made from synthetic materials such as TPO, EPDM, or PVC, designed to provide waterproofing and durability for flat or low-slope roofs. This roofing membrane is lightweight, UV-resistant, and offers excellent puncture resistance, making it a popular choice for commercial buildings. Installation involves mechanically fastening or adhering the membrane to the roof deck, ensuring seamless protection against water infiltration and weather elements.
Overview of Built-Up Roofing (BUR)
Built-Up Roofing (BUR) consists of multiple layers of bitumen alternated with reinforcing fabrics, creating a durable, waterproof membrane ideal for flat or low-slope roofs. BUR systems are valued for their excellent resistance to weather, UV radiation, and mechanical damage, offering a lifespan of 15 to 30 years with proper maintenance. The multi-ply construction provides superior insulation and thermal performance compared to single-layer membrane roofing alternatives.
Key Material Differences
Membrane roofing utilizes synthetic sheets such as TPO, EPDM, or PVC that offer flexibility and resistance to UV radiation and chemicals, making them ideal for low-slope roofs. Built-up roofing (BUR) consists of multiple layers of bitumen and reinforcing fabrics, providing durability and heavy-duty protection through its layered composition. The choice between membrane and built-up roofing depends on factors like climate resilience, material lifespan, and installation complexity.
Installation Methods Compared
Membrane roofing installation involves laying large sheets of synthetic materials like TPO, EPDM, or PVC that are mechanically fastened, adhered, or ballasted, providing a continuous, waterproof barrier. Built-up roofing (BUR) relies on multiple layers of bitumen alternated with reinforcing fabrics, applied in hot or cold processes, creating a thick, layered surface that enhances durability and resistance. Membrane roofing offers quicker installation and fewer seams, while BUR requires longer curing times but delivers superior fire resistance and impact protection.
Durability and Lifespan
Membrane roofing systems, such as TPO, EPDM, and PVC, provide exceptional durability through flexible, weather-resistant materials that withstand UV rays, chemical exposure, and temperature fluctuations, often lasting 20 to 30 years with proper maintenance. Built-up roofing (BUR), composed of multiple layers of bitumen and reinforcing fabrics, offers robust protection against heavy foot traffic and mechanical damage, typically delivering a lifespan of 15 to 25 years depending on climatic conditions and installation quality. Both membrane and built-up roofing systems demand routine inspections and timely repairs to maximize their longevity and performance in diverse environmental settings.
Maintenance Requirements
Membrane roofing requires less frequent maintenance due to its flexible, durable materials such as TPO or EPDM, which resist cracking and UV damage. Built-up roofing demands regular inspections and upkeep to address potential issues like blistering, punctures, and water pooling caused by layers of tar and gravel. Proper maintenance scheduling for membrane roofing often results in lower long-term costs compared to the labor-intensive upkeep of built-up roofing systems.
Cost Analysis: Membrane vs. BUR
Membrane roofing typically offers lower initial installation costs compared to built-up roofing (BUR), due to fewer labor hours and lightweight materials. BUR systems require more intensive labor and multiple layers of bitumen and felt, increasing both material and labor expenses. Over the long term, membrane roofing often reduces maintenance and repair costs, making it a more cost-effective option for many commercial and residential projects.
Best Applications for Each System
Membrane roofing systems, such as TPO, EPDM, and PVC, excel in commercial flat or low-slope roofs due to their lightweight, flexibility, and ease of installation, ideal for energy-efficient and waterproof solutions. Built-up roofing (BUR) offers superior durability and multilayer protection, making it best suited for heavy-traffic areas and older buildings requiring proven longevity and resistance to weather elements. Choosing between these systems depends on specific project requirements, including roof slope, budget, climate, and expected roof lifespan.
Choosing the Right Roofing Solution
Membrane roofing systems, such as TPO and EPDM, offer superior flexibility, energy efficiency, and ease of installation, making them ideal for flat or low-slope roofs prone to weather exposure. Built-up roofing (BUR), composed of multiple bitumen layers and reinforcing fabrics, provides excellent durability and waterproofing, often preferred for heavy traffic roofs requiring robust protection. Selecting the right roofing solution depends on factors like building design, climate conditions, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and lifespan.
Membrane Roofing vs Built-Up Roofing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com