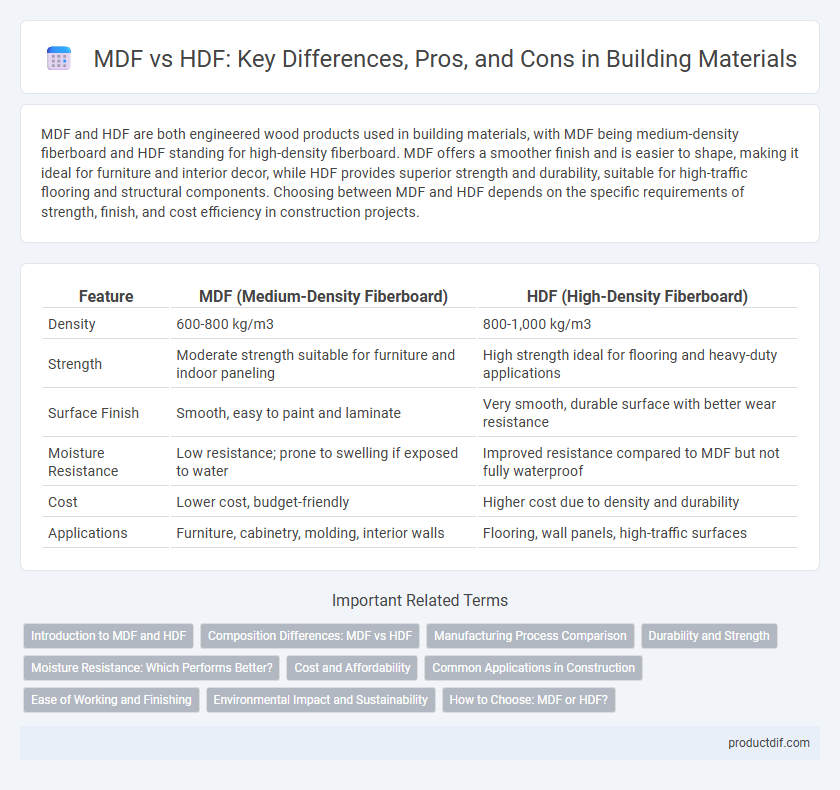
MDF and HDF are both engineered wood products used in building materials, with MDF being medium-density fiberboard and HDF standing for high-density fiberboard. MDF offers a smoother finish and is easier to shape, making it ideal for furniture and interior decor, while HDF provides superior strength and durability, suitable for high-traffic flooring and structural components. Choosing between MDF and HDF depends on the specific requirements of strength, finish, and cost efficiency in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) | HDF (High-Density Fiberboard) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 600-800 kg/m3 | 800-1,000 kg/m3 |
| Strength | Moderate strength suitable for furniture and indoor paneling | High strength ideal for flooring and heavy-duty applications |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, easy to paint and laminate | Very smooth, durable surface with better wear resistance |
| Moisture Resistance | Low resistance; prone to swelling if exposed to water | Improved resistance compared to MDF but not fully waterproof |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost due to density and durability |
| Applications | Furniture, cabinetry, molding, interior walls | Flooring, wall panels, high-traffic surfaces |
Introduction to MDF and HDF
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) and HDF (High Density Fiberboard) are engineered wood products made from wood fibers bonded with resin under heat and pressure. MDF offers a smooth surface ideal for painting and intricate designs, providing moderate density and strength commonly used in furniture and cabinetry. HDF, with higher density and hardness, is preferred for flooring and applications requiring enhanced durability and resistance to impact.
Composition Differences: MDF vs HDF
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) consists of wood fibers combined with resin and wax, pressed at lower density levels typically around 600-800 kg/m3. High Density Fiberboard (HDF) has a higher density, usually above 800 kg/m3, achieved by using finer wood fibers and applying greater pressure during processing. The compositional differences result in HDF exhibiting increased durability, hardness, and moisture resistance compared to MDF, making it more suitable for high-impact applications.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) is manufactured by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibers, combining them with wax and resin binders, and forming panels through high temperature and pressure in a hydraulic press. HDF (High Density Fiberboard) follows a similar procedure but undergoes greater fiber refinement, higher pressing pressures, and increased temperature, resulting in a denser and stronger panel. The difference in fiber compression and resin content in the manufacturing process directly impacts the durability, hardness, and application suitability of MDF and HDF products.
Durability and Strength
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) offers moderate durability and strength, making it suitable for interior applications like furniture and cabinetry where less structural load is expected. High Density Fiberboard (HDF) provides superior durability and higher density, resulting in greater strength and resistance to impact, making it ideal for high-traffic flooring and exterior uses. HDF's compact fiber composition enhances load-bearing capacity and moisture resistance compared to MDF.
Moisture Resistance: Which Performs Better?
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) outperforms Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF) in moisture resistance due to its denser composition and higher compression levels, making it less prone to swelling and warping when exposed to humidity. MDF tends to absorb moisture more readily, leading to significant expansion and potential structural damage in wet environments. For applications requiring superior water resistance, HDF is the preferred choice in building materials.
Cost and Affordability
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) typically costs less than HDF (High Density Fiberboard), making it a more affordable option for budget-conscious construction projects. The lower density and manufacturing process of MDF contribute to its reduced price, while HDF's higher density and strength result in increased material costs. For applications where cost efficiency is crucial and moderate durability suffices, MDF offers a better balance between price and performance.
Common Applications in Construction
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) is widely used for interior applications such as cabinetry, furniture, and decorative moldings due to its smooth surface and ease of machining. High Density Fiberboard (HDF) is favored for flooring panels and wall paneling where higher durability and resistance to impact are required. Both materials are engineered wood products but differ in density and strength, influencing their suitability for specific construction uses.
Ease of Working and Finishing
MDF offers superior ease of working due to its uniform density and smooth surface, making it ideal for precise cutting, drilling, and shaping without splintering. HDF, being denser and harder, provides a more durable finish but requires sharper tools and more effort during machining, potentially increasing production time. Both materials accept paint and veneer well, but MDF's softer composition allows for better adherence and finer surface finishing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) and HDF (High Density Fiberboard) differ significantly in environmental impact due to their raw material usage and manufacturing processes. MDF typically uses recycled wood fibers and adhesives with a higher formaldehyde content, leading to concerns about indoor air quality and VOC emissions, while HDF's denser structure allows for more efficient resource use and longer product lifespan, contributing to reduced waste. Sustainable production of both materials depends on sourcing certified wood fibers, low-emission resins, and adherence to eco-friendly manufacturing standards such as CARB or EUTR compliance.
How to Choose: MDF or HDF?
When deciding between MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) and HDF (High Density Fiberboard), consider the specific application and durability requirements. MDF offers a smoother surface ideal for painting and indoor furniture, while HDF provides higher density and strength suitable for flooring and heavy-use cabinetry. Evaluate factors such as moisture resistance, load-bearing capacity, and finish quality to determine the best board for your building material project.
MDF vs HDF Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com