Drywall offers quicker installation and easier repairs compared to plaster, making it a cost-effective option for modern construction. Plaster provides superior durability, sound insulation, and a smooth, high-quality finish favored in traditional or historic buildings. Choosing between drywall and plaster depends on project requirements, budget constraints, and desired aesthetics.
Table of Comparison
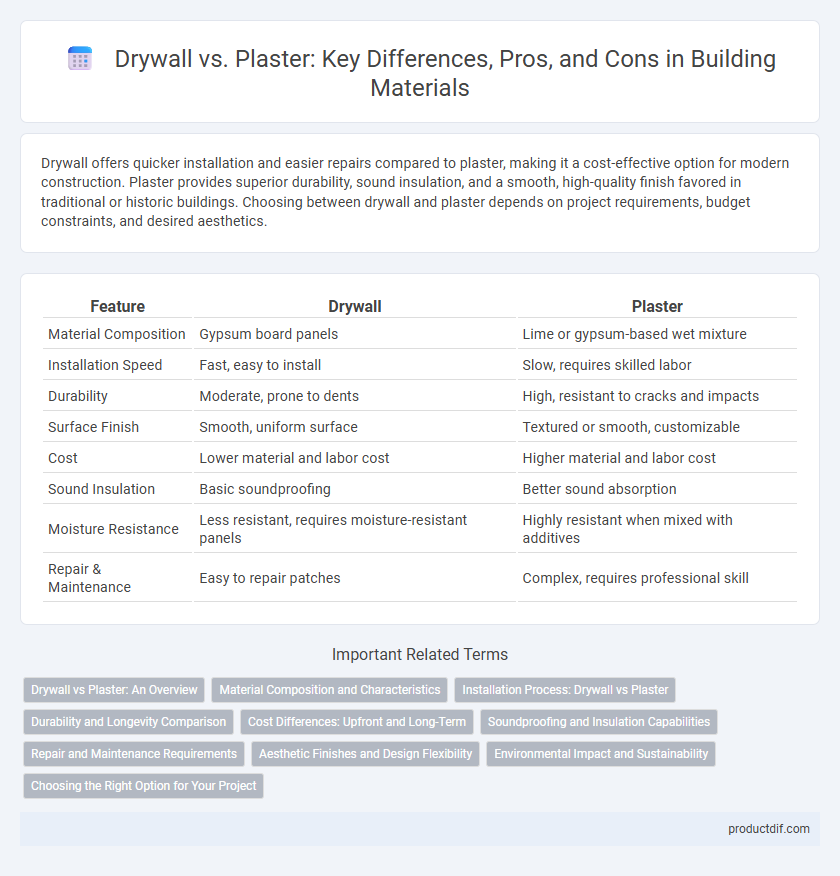
| Feature | Drywall | Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Gypsum board panels | Lime or gypsum-based wet mixture |
| Installation Speed | Fast, easy to install | Slow, requires skilled labor |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to dents | High, resistant to cracks and impacts |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform surface | Textured or smooth, customizable |
| Cost | Lower material and labor cost | Higher material and labor cost |
| Sound Insulation | Basic soundproofing | Better sound absorption |
| Moisture Resistance | Less resistant, requires moisture-resistant panels | Highly resistant when mixed with additives |
| Repair & Maintenance | Easy to repair patches | Complex, requires professional skill |
Drywall vs Plaster: An Overview
Drywall and plaster serve as popular wall finishes with distinct properties; drywall consists of gypsum panels attached to framing, offering quick installation and ease of repair, while plaster is a traditional material applied in multiple wet layers for a hard, durable surface. Drywall provides a cost-effective, uniform appearance and is favored in modern construction, whereas plaster offers superior soundproofing and a more textured, rich aesthetic preferred in historic restorations. Understanding the differences in installation, durability, and finish quality is essential for selecting the appropriate wall material for residential or commercial projects.
Material Composition and Characteristics
Drywall consists primarily of gypsum plaster sandwiched between two thick sheets of paper, offering a lightweight and easy-to-install option widely used in modern construction. Plaster is composed of lime or cement mixed with sand and water, creating a dense, durable surface that provides superior soundproofing and a smooth, hard finish. While drywall provides quicker installation and repair, plaster's material composition results in greater strength and moisture resistance suitable for high-traffic or humid environments.
Installation Process: Drywall vs Plaster
Drywall installation typically involves attaching large panels of gypsum board to wall studs using screws or nails, followed by taping and mudding the joints for a smooth finish. Plaster application requires a multi-step process where wet plaster is applied in multiple coats over lath or a base, demanding skilled craftsmanship and longer drying times. Drywall offers faster and more straightforward installation, while plaster provides a more durable and customizable surface but with increased labor and time requirements.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Drywall offers moderate durability with resistance to cracks and easier repair, while plaster provides superior longevity due to its dense composition and ability to withstand wear and impacts. Plaster walls are less prone to dents and moisture damage, extending their lifespan significantly beyond drywall in high-traffic or humid environments. Choosing plaster over drywall can result in walls that maintain structural integrity and aesthetic appeal for decades longer.
Cost Differences: Upfront and Long-Term
Drywall offers lower upfront costs due to its quicker installation and less labor intensity compared to plaster, which requires skilled craftsmanship and more time. Over the long term, drywall may incur higher maintenance expenses since it is more susceptible to damage and repairs, while plaster's durability often reduces the frequency and cost of restorations. Homeowners should weigh initial affordability against potential longevity and upkeep expenses when choosing between these materials.
Soundproofing and Insulation Capabilities
Drywall offers moderate soundproofing and insulation properties, with standard panels providing basic thermal resistance and noise reduction. Plaster, especially multiple coats over metal lath, creates a denser barrier that significantly enhances soundproofing and thermal insulation by reducing sound transmission and heat loss. For superior acoustic and insulation performance, combining plaster with specialized insulation materials outperforms drywall alone in both noise control and energy efficiency.
Repair and Maintenance Requirements
Drywall requires simpler repair techniques, such as patching holes and sanding surfaces, making maintenance quicker and more cost-effective compared to plaster. Plaster repairs often involve more intricate processes, including matching texture and multiple drying stages, which can increase labor time and expense. Regular maintenance of plaster walls is essential to prevent cracking and water damage, while drywall is more resilient but can be prone to dents and moisture issues if not properly treated.
Aesthetic Finishes and Design Flexibility
Drywall offers smooth, uniform surfaces ideal for modern, minimalist aesthetics, allowing for seamless painting or wallpaper application, while plaster provides textured finishes with greater depth and character, suiting traditional or ornate designs. Plaster's moldability enables intricate architectural details like cornices and reliefs that drywall cannot replicate. The choice between drywall and plaster influences design flexibility, with plaster supporting more customized and artistic finishes compared to drywall's faster installation and clean look.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Drywall production consumes large amounts of natural gypsum and generates significant construction waste, raising concerns about resource depletion and landfill overflow. Plaster, typically made from lime or cement, offers better biodegradability and lower embodied energy, making it a more sustainable option in eco-friendly building projects. Recycling drywall materials and using eco-certified plasters can significantly reduce the environmental footprint associated with interior wall finishes.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Project
Drywall offers faster installation and easier repairs, making it ideal for modern construction and renovation projects requiring efficiency. Plaster provides superior durability and a smoother, more customizable finish, preferred for historic restorations or high-end interiors. Selecting between drywall and plaster depends on project timelines, budget constraints, and desired aesthetic outcomes.
Drywall vs Plaster Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com