CMUs (Concrete Masonry Units) offer superior strength, fire resistance, and faster installation compared to traditional bricks, making them ideal for load-bearing walls and large-scale construction. Bricks provide excellent aesthetic appeal, durability, and better insulation properties, suitable for residential and decorative projects. Choosing between CMU and brick depends on factors like budget, structural requirements, and design preferences.
Table of Comparison
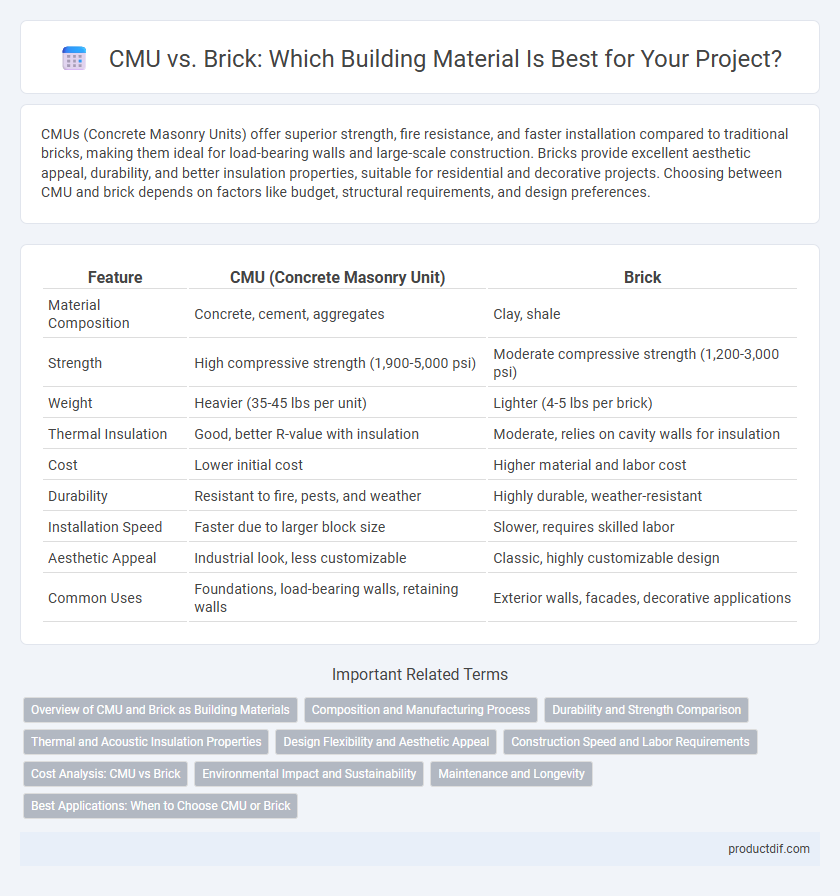
| Feature | CMU (Concrete Masonry Unit) | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Concrete, cement, aggregates | Clay, shale |
| Strength | High compressive strength (1,900-5,000 psi) | Moderate compressive strength (1,200-3,000 psi) |
| Weight | Heavier (35-45 lbs per unit) | Lighter (4-5 lbs per brick) |
| Thermal Insulation | Good, better R-value with insulation | Moderate, relies on cavity walls for insulation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher material and labor cost |
| Durability | Resistant to fire, pests, and weather | Highly durable, weather-resistant |
| Installation Speed | Faster due to larger block size | Slower, requires skilled labor |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Industrial look, less customizable | Classic, highly customizable design |
| Common Uses | Foundations, load-bearing walls, retaining walls | Exterior walls, facades, decorative applications |
Overview of CMU and Brick as Building Materials
CMU (Concrete Masonry Unit) is a versatile building material known for its strength, durability, and fire resistance, commonly used in load-bearing walls and foundations. Brick offers excellent thermal mass and aesthetic appeal, often favored for exterior facades and decorative finishes. Both materials provide long-term structural integrity, with CMU offering faster construction and brick delivering classic architectural value.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) are composed primarily of Portland cement, aggregates such as sand and gravel, and water, mixed and poured into molds before curing under controlled conditions. Bricks consist mainly of natural clay or shale, formed by shaping the material and then firing it at high temperatures in a kiln to achieve hardness and durability. The manufacturing of CMUs involves a hydraulic press and accelerated curing techniques, whereas brick production relies on traditional molding and prolonged kiln firing for strength and color development.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) offer superior durability with enhanced resistance to weathering, fire, and pests compared to traditional brick, making them ideal for load-bearing applications. CMUs typically exhibit higher compressive strength, often ranging between 1,900 to 3,000 psi, whereas common bricks average about 1,600 to 2,700 psi. Their uniform size and structure contribute to consistent strength and increased longevity in construction projects requiring robust materials.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
CMU (concrete masonry units) offer superior thermal mass that helps regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing and slowly releasing heat, making them more energy-efficient than traditional brick. Brick walls provide enhanced acoustic insulation due to their dense, solid composition, effectively reducing noise transmission between spaces. When selecting building materials, CMU is preferred for thermal performance, while brick excels in soundproofing applications.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) offer superior design flexibility due to their variety of shapes, sizes, and finishes, allowing for customized architectural expressions and structural versatility. Brick provides a timeless aesthetic appeal with its rich textures, colors, and traditional patterning, enhancing visual warmth and historic character in building facades. The choice between CMU and brick depends on balancing the need for customizable design complexity with the desired classic or modern visual impact.
Construction Speed and Labor Requirements
Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) enable faster construction speeds due to their larger size and modular design, reducing the number of units needed per wall area compared to bricks. Labor requirements for CMU installation are generally lower because fewer individual units need handling and mortar application, allowing for quicker assembly and reduced workforce fatigue. In contrast, brickwork demands more skilled labor and longer installation times due to smaller unit size and intricate bonding patterns.
Cost Analysis: CMU vs Brick
Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) typically offer a lower initial cost per square foot compared to brick, making them a budget-friendly option for large-scale construction projects. Brick, while more expensive upfront due to material and labor costs, provides higher durability and lower maintenance expenses over time. Cost analysis should factor in long-term value, including energy efficiency and potential repair costs, where CMU often requires more frequent upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
CMU (Concrete Masonry Units) typically have a lower embodied energy compared to traditional clay bricks, reducing their overall carbon footprint in construction. Bricks often require higher firing temperatures, resulting in more CO2 emissions during manufacturing, whereas CMUs can incorporate recycled materials and industrial byproducts, enhancing sustainability. Both materials offer durability, but CMUs generally promote better energy efficiency through improved thermal mass, contributing to greener building practices.
Maintenance and Longevity
Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) offer superior durability with minimal maintenance requirements compared to traditional brick, resisting cracking and weathering more effectively over time. Brick, while aesthetically pleasing, often demands regular upkeep such as repointing and sealing to prevent moisture penetration and deterioration. CMUs' reinforced structure and low absorption rate contribute to extended longevity, making them a cost-effective choice for long-term building performance.
Best Applications: When to Choose CMU or Brick
CMU (Concrete Masonry Units) are best suited for structural walls, retaining walls, and commercial buildings due to their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Brick is ideal for residential facades, decorative accents, and fire-resistant applications, offering superior aesthetic appeal and weather resistance. Choosing between CMU and brick depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, design preference, and budget constraints.
CMU vs Brick Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com