Closed-cell insulation offers higher R-values per inch and superior moisture resistance, making it ideal for areas prone to dampness. Open-cell insulation provides better sound absorption and flexibility, allowing for easier installation in irregular spaces. Choosing between these types depends on the specific building requirements, budget considerations, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
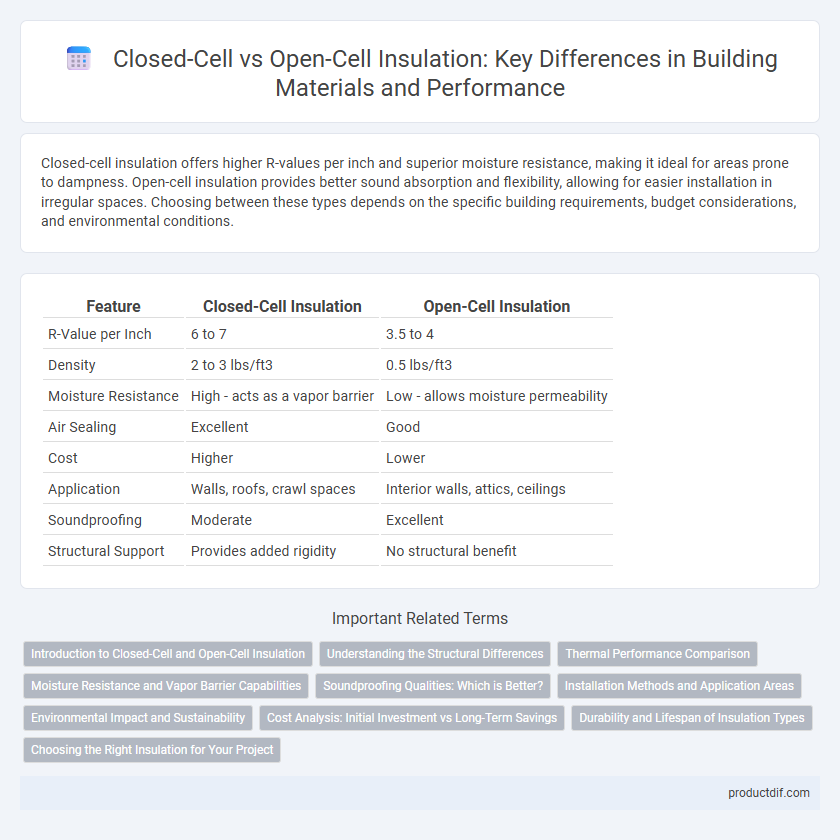
| Feature | Closed-Cell Insulation | Open-Cell Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| R-Value per Inch | 6 to 7 | 3.5 to 4 |
| Density | 2 to 3 lbs/ft3 | 0.5 lbs/ft3 |
| Moisture Resistance | High - acts as a vapor barrier | Low - allows moisture permeability |
| Air Sealing | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application | Walls, roofs, crawl spaces | Interior walls, attics, ceilings |
| Soundproofing | Moderate | Excellent |
| Structural Support | Provides added rigidity | No structural benefit |
Introduction to Closed-Cell and Open-Cell Insulation
Closed-cell insulation consists of rigid foam cells that are tightly packed, providing high thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for exterior walls and roofing applications. Open-cell insulation features a spongy texture with air pockets that allow vapor permeability, enhancing soundproofing and flexibility within interior walls and attics. Both insulation types offer unique benefits, with closed-cell delivering superior energy efficiency and structural strength, while open-cell delivers cost-effectiveness and breathability.
Understanding the Structural Differences
Closed-cell insulation consists of rigid cells tightly packed together, providing higher density and superior moisture resistance compared to open-cell insulation, which has a more flexible structure with cells that are open and less dense. The closed-cell variant delivers enhanced thermal insulation values (R-values), structural rigidity, and vapor barrier properties, making it ideal for exterior applications and areas prone to water exposure. Open-cell insulation, characterized by its breathability and sound absorption qualities, is better suited for interior walls and spaces requiring moisture control.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Closed-cell insulation offers higher thermal resistance (R-value) per inch, typically ranging from R-6 to R-7, compared to open-cell insulation's R-3.5 to R-4, making it more effective at reducing heat transfer. Its dense structure provides superior air sealing and moisture resistance, enhancing overall thermal performance in building envelopes. Open-cell insulation, while less efficient in thermal resistance, allows for better vapor permeability, suitable for specific applications requiring breathability.
Moisture Resistance and Vapor Barrier Capabilities
Closed-cell insulation offers superior moisture resistance due to its dense structure, effectively preventing water infiltration and acting as a built-in vapor barrier. Open-cell insulation, with its porous composition, allows moisture to pass through more easily and requires an additional vapor barrier for optimal protection. The enhanced vapor barrier capabilities of closed-cell insulation make it ideal for environments prone to high humidity or water exposure.
Soundproofing Qualities: Which is Better?
Closed-cell insulation offers superior soundproofing qualities compared to open-cell insulation due to its higher density and rigid structure, which effectively blocks airborne noise and reduces sound transmission. Open-cell insulation, being softer and more porous, excels at absorbing sound within a space but does not provide as much noise blocking between rooms or external sources. For applications requiring maximum soundproofing, especially in walls and floors, closed-cell insulation is generally the better choice.
Installation Methods and Application Areas
Closed-cell insulation is typically installed using spray foam techniques that create a dense, moisture-resistant barrier ideal for exterior walls, roofs, and below-grade foundations, offering superior structural support and energy efficiency. Open-cell insulation is applied as a spray or in batts, allowing it to expand and fill cavities in interior walls and attics where sound absorption and ventilation are prioritized. The choice between these materials depends on application requirements such as moisture control, thermal performance, and structural reinforcement.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Closed-cell insulation has a higher R-value per inch and provides superior moisture resistance, but it often contains blowing agents with higher global warming potential, impacting environmental sustainability negatively. Open-cell insulation uses fewer chemical blowing agents and generally has lower embodied carbon, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint and improved indoor air quality by allowing vapor permeability. Sustainable building projects prioritize open-cell insulation for its lower environmental impact, despite its lower density and insulation value compared to closed-cell options.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-Term Savings
Closed-cell insulation requires a higher initial investment due to its denser material and specialized installation process but offers superior thermal resistance and moisture barriers, translating to greater long-term energy savings. Open-cell insulation has a lower upfront cost and faster installation but tends to have lower R-values and less effective moisture control, possibly increasing heating and cooling expenses over time. Evaluating project scope and budget constraints is crucial to determining which insulation type delivers the optimal balance of upfront cost and lifecycle energy efficiency.
Durability and Lifespan of Insulation Types
Closed-cell insulation offers superior durability compared to open-cell insulation due to its rigid structure and resistance to moisture absorption, extending its lifespan significantly in harsh environments. Open-cell insulation, while effective for soundproofing and flexibility, tends to degrade faster and is more susceptible to mold and water damage, reducing its overall longevity. Selecting closed-cell insulation ensures longer-term performance and reliability in building applications where durability is critical.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Project
Closed-cell insulation offers a higher R-value per inch, making it ideal for projects requiring superior thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties. Open-cell insulation provides excellent sound absorption and is more cost-effective, suitable for interior applications with moderate insulation needs. Selecting the right insulation depends on project-specific factors such as climate, budget, and desired energy efficiency.
closed-cell insulation vs open-cell insulation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com