Brick veneer offers a lightweight, cost-effective alternative to solid brick, providing the aesthetic appeal of traditional brickwork with easier installation and improved insulation properties. Solid brick, known for its durability and structural strength, delivers superior thermal mass and fire resistance, making it ideal for load-bearing walls. Choosing between brick veneer and solid brick depends on factors such as budget, climate, and construction requirements, balancing appearance with performance.
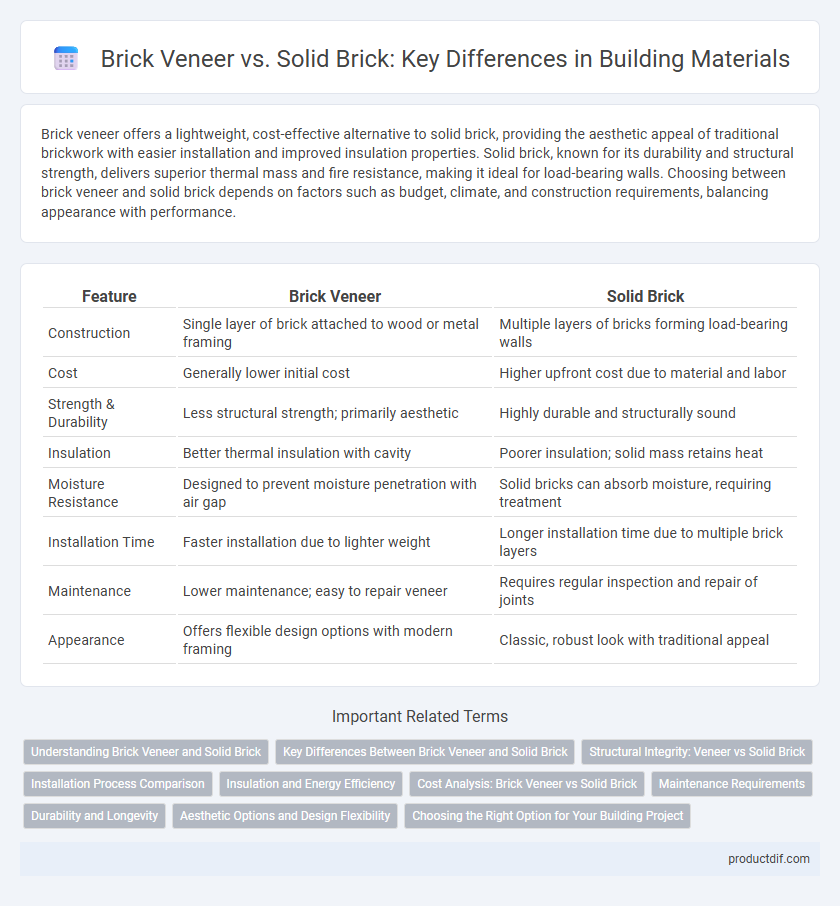
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Brick Veneer | Solid Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Single layer of brick attached to wood or metal framing | Multiple layers of bricks forming load-bearing walls |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost due to material and labor |
| Strength & Durability | Less structural strength; primarily aesthetic | Highly durable and structurally sound |
| Insulation | Better thermal insulation with cavity | Poorer insulation; solid mass retains heat |
| Moisture Resistance | Designed to prevent moisture penetration with air gap | Solid bricks can absorb moisture, requiring treatment |
| Installation Time | Faster installation due to lighter weight | Longer installation time due to multiple brick layers |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance; easy to repair veneer | Requires regular inspection and repair of joints |
| Appearance | Offers flexible design options with modern framing | Classic, robust look with traditional appeal |
Understanding Brick Veneer and Solid Brick
Brick veneer consists of a single layer of brick attached to the exterior of a framed structure, providing the aesthetic appeal of traditional brick while offering improved insulation and reduced cost. Solid brick, also known as traditional or structural brick, is a thick, load-bearing material made entirely of bricks, offering durability and superior thermal mass. Understanding the differences between brick veneer and solid brick is essential for selecting appropriate building materials based on budget, structural requirements, and climate considerations.
Key Differences Between Brick Veneer and Solid Brick
Brick veneer consists of a single layer of brick attached to a wood or metal frame, providing aesthetic appeal without structural support, whereas solid brick walls are made entirely of bricks, offering full structural strength and durability. Brick veneer is generally lighter, more cost-effective, and allows for better insulation and moisture control compared to the heavier, more labor-intensive solid brick construction. Thermal performance differs as brick veneer often requires additional insulation, while solid brick naturally provides greater thermal mass and fire resistance.
Structural Integrity: Veneer vs Solid Brick
Solid brick offers superior structural integrity due to its full-thickness construction, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity and durability compared to brick veneer, which consists of a single brick layer attached to a structural frame. Brick veneer relies on the underlying framing system for support, making it less robust under heavy loads or impact. Engineers prefer solid brick in applications requiring exceptional strength and long-term stability.
Installation Process Comparison
Brick veneer installation involves attaching a single layer of brick to a framed structure with a moisture barrier and air gap, which simplifies construction and reduces weight on the foundation. Solid brick requires laying multiple courses of full-depth bricks with mortar, demanding skilled labor and extended curing times for structural integrity. The veneer method offers faster installation and easier maintenance, while solid brick provides enhanced durability and thermal mass.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Brick veneer offers superior insulation and energy efficiency compared to solid brick due to its cavity design, which provides better thermal resistance by reducing heat transfer. The air gap between the veneer and structural wall acts as an insulating barrier, enhancing temperature regulation and lowering energy consumption. Solid bricks, while durable, have higher thermal conductivity, resulting in less effective insulation and increased energy costs for heating and cooling.
Cost Analysis: Brick Veneer vs Solid Brick
Brick veneer offers a cost-effective solution compared to solid brick due to lower material and labor expenses, as its thinner profile requires less brick and simpler installation. Solid brick, while more expensive upfront, provides greater durability and thermal mass, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and energy costs. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and energy efficiency, is crucial when choosing between brick veneer and solid brick for construction projects.
Maintenance Requirements
Brick veneer requires less maintenance compared to solid brick due to its single-layer design that reduces moisture absorption and cracking risks. Solid brick, being thicker and more porous, often demands regular repointing and sealing to prevent water damage and structural degradation. Proper upkeep of mortar joints in solid brick is essential to maintain durability and appearance over time.
Durability and Longevity
Brick veneer offers a durable facade that resists weathering and provides excellent moisture protection, while solid brick excels in structural strength and long-term resilience. Solid bricks typically have a lifespan exceeding 100 years due to their dense composition, making them ideal for load-bearing applications. Brick veneer, although generally less massive, enhances home durability through modern construction techniques that prevent thermal and moisture damage.
Aesthetic Options and Design Flexibility
Brick veneer offers greater aesthetic options and design flexibility compared to solid brick, allowing for a wide variety of colors, textures, and patterns that can closely mimic traditional brickwork while adapting to modern architectural styles. The thinner profile of brick veneer enables installation over different substrates, facilitating creative wall designs and shapes that solid brick's weight and construction methods typically restrict. This adaptability makes brick veneer a preferred choice for designers seeking both classic brick appeal and innovative visual customization.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Building Project
Brick veneer offers superior insulation and is lighter, reducing structural load and allowing faster installation, making it ideal for renovations or projects with weight constraints. Solid brick provides unmatched durability and thermal mass, enhancing energy efficiency and longevity, suitable for load-bearing walls in new constructions. Assess project requirements such as budget, climate, structural support, and aesthetic preferences to determine the optimal choice between brick veneer and solid brick.
Brick Veneer vs Solid Brick Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com