AAC blocks offer superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties compared to traditional clay bricks, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency and easier handling during construction. Clay bricks provide higher compressive strength and better moisture resistance, making them suitable for load-bearing structures and damp environments. The choice between AAC blocks and clay bricks depends on specific project requirements such as structural demands, thermal performance, and budget considerations.
Table of Comparison
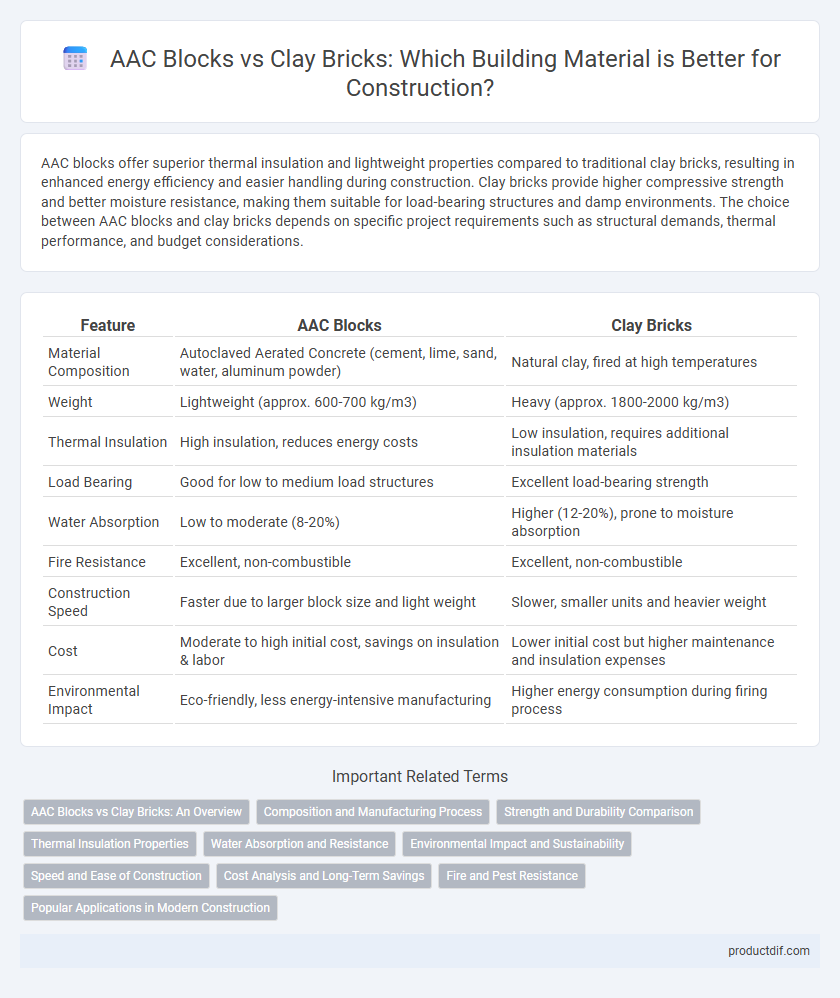
| Feature | AAC Blocks | Clay Bricks |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (cement, lime, sand, water, aluminum powder) | Natural clay, fired at high temperatures |
| Weight | Lightweight (approx. 600-700 kg/m3) | Heavy (approx. 1800-2000 kg/m3) |
| Thermal Insulation | High insulation, reduces energy costs | Low insulation, requires additional insulation materials |
| Load Bearing | Good for low to medium load structures | Excellent load-bearing strength |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate (8-20%) | Higher (12-20%), prone to moisture absorption |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent, non-combustible | Excellent, non-combustible |
| Construction Speed | Faster due to larger block size and light weight | Slower, smaller units and heavier weight |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost, savings on insulation & labor | Lower initial cost but higher maintenance and insulation expenses |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, less energy-intensive manufacturing | Higher energy consumption during firing process |
AAC Blocks vs Clay Bricks: An Overview
AAC blocks offer superior thermal insulation, lightweight properties, and faster construction compared to traditional clay bricks, which are denser and require longer curing times. AAC blocks provide better fire resistance and soundproofing, making them ideal for energy-efficient buildings and modern construction standards. Clay bricks, while durable and widely available, tend to have higher moisture absorption and lower insulation values relative to AAC blocks.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
AAC blocks consist primarily of cement, lime, silica sand, water, and aluminum powder, which acts as a foaming agent to create air pockets, while clay bricks are made by molding natural clay and then firing it at high temperatures in a kiln. The manufacturing process of AAC blocks involves mixing, casting, autoclaving, and cutting, resulting in lightweight, aerated construction units, whereas clay bricks undergo shaping, drying, and high-temperature firing stages that produce dense, durable blocks. The inclusion of aluminum powder in AAC blocks leads to a porous structure with thermal insulation properties, contrasting with the solid, dense composition of traditional clay bricks.
Strength and Durability Comparison
AAC blocks exhibit higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to traditional clay bricks, offering enhanced load-bearing capacity while reducing structural weight. Their cellular structure provides superior thermal insulation and resistance to cracking, contributing to long-term durability under varying environmental conditions. Clay bricks, though dense and strong, are more prone to moisture absorption and weathering, which can affect their longevity in harsh climates.
Thermal Insulation Properties
AAC blocks exhibit superior thermal insulation properties compared to clay bricks due to their porous structure, which significantly reduces heat transfer. This results in better energy efficiency for buildings, lowering cooling and heating costs in various climates. The lightweight nature of AAC blocks also contributes to enhanced thermal resistance, making them an ideal choice for sustainable construction.
Water Absorption and Resistance
AAC blocks exhibit significantly lower water absorption rates compared to traditional clay bricks, enhancing their resistance to moisture-related damage and reducing the risk of dampness in structures. The porous cellular structure of AAC blocks allows for better breathability while maintaining superior water resistance, making them ideal for humid environments. In contrast, clay bricks tend to absorb more water, which can lead to weakening over time and increased maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
AAC blocks significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing industrial waste and consuming less energy during manufacturing compared to clay bricks, which require extensive kiln firing and deplete topsoil. AAC blocks offer superior thermal insulation, decreasing energy consumption in buildings and enhancing sustainability through improved energy efficiency. Clay bricks generate higher CO2 emissions and involve resource-intensive extraction processes, making AAC blocks the more eco-friendly choice in sustainable construction.
Speed and Ease of Construction
AAC blocks offer significantly faster construction speed compared to clay bricks due to their larger size and lightweight nature, reducing mortar usage and labor effort. Their uniform shape and smooth surface simplify alignment and cutting, enhancing ease of installation on-site. Clay bricks, being smaller and heavier, require more time and precision, leading to slower progress and increased construction complexity.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Savings
AAC blocks offer significant cost savings compared to clay bricks due to their lightweight nature, which reduces transportation and labor expenses. Their superior thermal insulation properties lower energy consumption for heating and cooling, resulting in long-term utility cost reductions. Although the initial price of AAC blocks may be higher, the overall lifecycle savings make them a more economical choice for sustainable construction projects.
Fire and Pest Resistance
AAC blocks offer superior fire resistance due to their lightweight, aerated structure, which can withstand temperatures up to 1,200degC without structural damage, significantly outperforming traditional clay bricks. Clay bricks provide moderate fire resistance but are more vulnerable to thermal cracking under extreme heat conditions. AAC blocks also exhibit enhanced pest resistance as their porous composition deters termites and other pests, whereas clay bricks may be more susceptible to insect infestation if not properly treated.
Popular Applications in Modern Construction
AAC blocks are widely used in modern construction for residential and commercial buildings due to their lightweight nature, thermal insulation, and fire resistance. Clay bricks remain popular for load-bearing walls, traditional facades, and landscaping projects because of their durability and aesthetic appeal. The choice between AAC blocks and clay bricks often depends on project requirements such as energy efficiency, structural strength, and architectural style.
AAC blocks vs Clay bricks Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com