Bitumen offers excellent waterproofing and durability for roofing applications, but it can be prone to cracking and requires regular maintenance in extreme weather conditions. EPDM, a synthetic rubber membrane, provides superior flexibility, UV resistance, and longevity, making it ideal for flat roofs and harsh climates. Choosing between bitumen and EPDM depends on factors like budget, climate, and the specific demands of the building project.
Table of Comparison
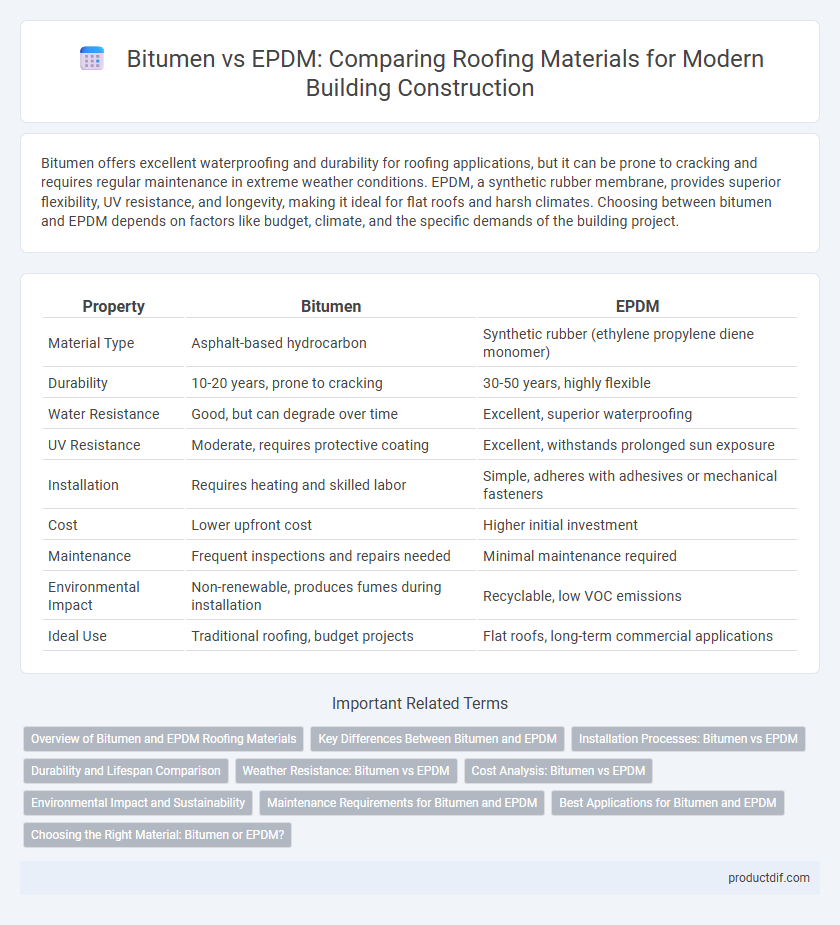
| Property | Bitumen | EPDM |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Asphalt-based hydrocarbon | Synthetic rubber (ethylene propylene diene monomer) |
| Durability | 10-20 years, prone to cracking | 30-50 years, highly flexible |
| Water Resistance | Good, but can degrade over time | Excellent, superior waterproofing |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, requires protective coating | Excellent, withstands prolonged sun exposure |
| Installation | Requires heating and skilled labor | Simple, adheres with adhesives or mechanical fasteners |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
| Maintenance | Frequent inspections and repairs needed | Minimal maintenance required |
| Environmental Impact | Non-renewable, produces fumes during installation | Recyclable, low VOC emissions |
| Ideal Use | Traditional roofing, budget projects | Flat roofs, long-term commercial applications |
Overview of Bitumen and EPDM Roofing Materials
Bitumen roofing is a traditional, asphalt-based material known for its waterproofing properties, durability, and cost-effectiveness, often used in low-slope roofs for commercial and residential buildings. EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) is a synthetic rubber roofing membrane celebrated for its superior flexibility, UV resistance, and longevity, making it ideal for various climate conditions. Both materials provide effective waterproofing but differ significantly in installation methods, environmental impact, and maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Bitumen and EPDM
Bitumen roofing relies on asphalt-based materials renowned for durability and waterproofing, while EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is a synthetic rubber membrane celebrated for flexibility and UV resistance. Bitumen systems are typically heavier and require heat or torch application, whereas EPDM offers easier installation through adhesive bonding or mechanical fastening. Longevity varies as bitumen roofs last 15-20 years with maintenance, whereas EPDM membranes can exceed 30 years due to superior weathering properties.
Installation Processes: Bitumen vs EPDM
Bitumen roofing requires heating and torching to adhere sheets, demanding skilled labor and careful fire safety measures while EPDM installation uses adhesive or mechanical fastening, allowing faster and less hazardous application. EPDM membranes offer flexibility and seamless coverage suitable for complex roof shapes, whereas bitumen's multi-layered torch-down system provides durable waterproofing but with longer curing time. The choice between bitumen and EPDM impacts labor intensity, installation speed, and safety protocols on construction sites.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Bitumen roofing typically offers a lifespan of 10 to 20 years, while EPDM roofing can last 30 to 50 years due to its superior resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering. EPDM's synthetic rubber composition provides enhanced elasticity and durability, reducing the risk of cracking and leaks over time compared to the more brittle bitumen layers. Maintenance requirements for EPDM are generally lower, contributing to its longer, more cost-effective service life in various climatic conditions.
Weather Resistance: Bitumen vs EPDM
EPDM roofing membranes demonstrate superior weather resistance compared to bitumen, offering exceptional durability against UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC. Bitumen, while effective in waterproofing, tends to become brittle and crack under prolonged exposure to sunlight and temperature fluctuations, which can lead to leaks and structural damage. EPDM's elastic properties maintain flexibility in harsh weather conditions, ensuring longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs in roofing and waterproofing applications.
Cost Analysis: Bitumen vs EPDM
Bitumen roofing typically costs between $3 to $5 per square foot, making it a more affordable option compared to EPDM, which ranges from $5 to $7 per square foot due to its synthetic composition and durability. Installation costs for bitumen are generally lower but may require more frequent maintenance and repairs over time, increasing long-term expenses. EPDM's higher initial cost is offset by its superior lifespan of 20-30 years and resistance to UV and weather damage, resulting in reduced repair and replacement costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bitumen roofing often contains petroleum-based materials that can release harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production and disposal, impacting air quality and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) is a synthetic rubber with a longer lifespan, is fully recyclable, and has a lower environmental footprint due to reduced energy consumption in manufacturing. Sustainability considerations favor EPDM for its durability, recyclability, and reduced toxic emissions compared to traditional bitumen roofing systems.
Maintenance Requirements for Bitumen and EPDM
Bitumen roofing requires regular inspections and periodic re-coating to prevent cracking and water infiltration, with maintenance intervals typically every 5 to 10 years. EPDM membranes offer lower maintenance demands due to their resistance to UV radiation and weathering, often lasting over 20 years with minimal upkeep. Proper cleaning and immediate repair of punctures are essential for both materials to extend their service life and ensure roof integrity.
Best Applications for Bitumen and EPDM
Bitumen excels in roofing applications requiring strong waterproofing and adhesion on flat or low-slope roofs, making it ideal for residential and commercial buildings exposed to harsh weather. EPDM is best suited for flexible, durable roofing membranes on commercial buildings and green roofs, offering superior resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures. Both materials are widely used in waterproofing foundations and basements, with bitumen preferred for its cost-effectiveness and EPDM valued for its elasticity and longevity.
Choosing the Right Material: Bitumen or EPDM?
Choosing the right roofing material depends on factors like durability, weather resistance, and installation complexity; bitumen offers excellent waterproofing and UV resistance, making it suitable for flat roofs with budget constraints, while EPDM provides superior flexibility, longevity, and resistance to extreme temperatures. Bitumen is typically easier to repair and more affordable, but EPDM's synthetic rubber composition ensures longer service life and minimal maintenance. Evaluating project requirements, climate conditions, and lifecycle costs helps determine whether bitumen or EPDM is the optimal choice for roofing applications.
Bitumen vs EPDM Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com