Garment dyeing involves dyeing fully constructed garments, offering a softer feel and unique color variations, ideal for casual and vintage-style apparel. Piece dyeing colors fabric rolls before garment construction, ensuring uniform shades and optimal color consistency for mass production. Choosing between garment dyeing and piece dyeing depends on the desired aesthetic, production scale, and fabric type.
Table of Comparison
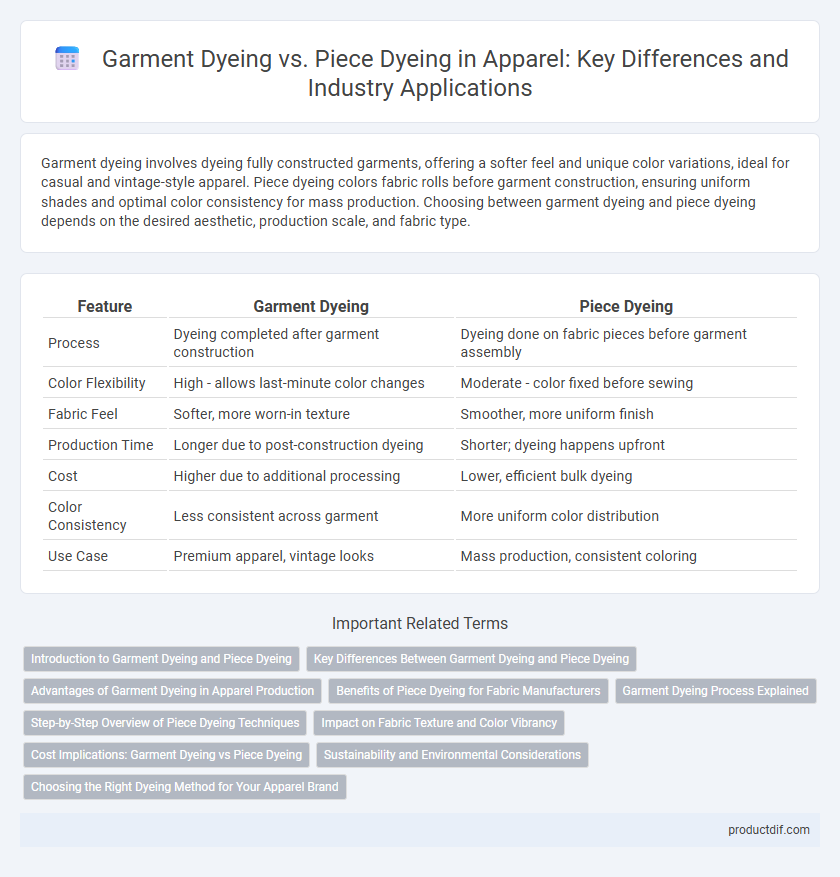
| Feature | Garment Dyeing | Piece Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dyeing completed after garment construction | Dyeing done on fabric pieces before garment assembly |
| Color Flexibility | High - allows last-minute color changes | Moderate - color fixed before sewing |
| Fabric Feel | Softer, more worn-in texture | Smoother, more uniform finish |
| Production Time | Longer due to post-construction dyeing | Shorter; dyeing happens upfront |
| Cost | Higher due to additional processing | Lower, efficient bulk dyeing |
| Color Consistency | Less consistent across garment | More uniform color distribution |
| Use Case | Premium apparel, vintage looks | Mass production, consistent coloring |
Introduction to Garment Dyeing and Piece Dyeing
Garment dyeing involves dyeing fully constructed apparel, resulting in unique color variations and a soft hand feel ideal for casual and fashion-forward garments. Piece dyeing colors fabric yarns or greige fabric before garment construction, ensuring consistent hues and efficient mass production. Selecting between garment dyeing and piece dyeing impacts fabric texture, color uniformity, and production timelines in apparel manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Garment Dyeing and Piece Dyeing
Garment dyeing involves coloring fully constructed garments, allowing for unique color effects, soft fabric texture, and flexibility in production runs, while piece dyeing colors yarns or fabrics before garment assembly, ensuring uniform and consistent color across large quantities. Garment dyeing is ideal for small batches and fashion flexibility, whereas piece dyeing suits mass production with precise color matching and better colorfastness. The dyeing stage, color uniformity, production scale, and fabric hand feel are key elements distinguishing garment dyeing from piece dyeing in apparel manufacturing.
Advantages of Garment Dyeing in Apparel Production
Garment dyeing offers superior color customization by allowing dyeing after the apparel is fully constructed, resulting in enhanced color uniformity and depth. This process reduces inventory risks by enabling flexibility to respond swiftly to market trends and demand fluctuations. Additionally, garment dyeing improves fabric softness and vintage aesthetic appeal, providing a unique texture that is highly valued in fashion-conscious apparel production.
Benefits of Piece Dyeing for Fabric Manufacturers
Piece dyeing offers fabric manufacturers significant flexibility by allowing precise color matching on finished fabric, reducing color inconsistencies compared to garment dyeing. This process enables efficient inventory management through dyeing large fabric batches in bulk, minimizing production downtime. Enhanced colorfastness and uniformity also contribute to superior quality control, making piece dyeing a preferred method in textile manufacturing.
Garment Dyeing Process Explained
Garment dyeing is a process where fabric is first cut and sewn into the final garment before being dyed, allowing for unique color variations and a softer, worn-in feel. This method enhances the fabric's texture and provides a vintage or distressed look that is difficult to achieve with traditional piece dyeing, where fabric is dyed prior to garment construction. Brands favor garment dyeing for its ability to produce one-of-a-kind hues and improved colorfastness on finished clothing items.
Step-by-Step Overview of Piece Dyeing Techniques
Piece dyeing involves dyeing fabric after it has been woven or knitted, allowing for uniform color application across the entire textile. The process begins with fabric preparation, including scouring and bleaching to remove impurities, followed by immersion in dye baths where specific temperatures and dwell times ensure penetration. After dyeing, the fabric undergoes washing, drying, and finishing treatments to enhance color fastness and texture, making piece dyeing ideal for creating solid-colored apparel with consistent hues.
Impact on Fabric Texture and Color Vibrancy
Garment dyeing enhances fabric texture by creating a softer, vintage look with subtle color variations, while piece dyeing offers consistent color saturation across the entire fabric, resulting in uniform vibrancy. The post-construction dyeing process of garment dyeing imparts a lived-in feel and depth to textures, whereas piece dyeing emphasizes color precision and durability due to dyeing before garment assembly. Choosing between these methods impacts both aesthetic appeal and fabric hand feel, influencing the final garment quality.
Cost Implications: Garment Dyeing vs Piece Dyeing
Garment dyeing often incurs higher production costs due to additional handling and labor required after garment construction, making it less cost-effective for large-volume orders. Piece dyeing, applied to fabric before garment assembly, typically reduces overall expenses by streamlining the dyeing process and minimizing waste in bulk production. Apparel manufacturers prioritize piece dyeing for budget efficiency and scalability, while garment dyeing remains favored for premium, custom or small-batch collections despite its cost implications.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Garment dyeing reduces water consumption and minimizes chemical waste by dyeing finished products, promoting sustainable apparel manufacturing processes. Piece dyeing requires dyeing fabric rolls before garment assembly, often leading to higher energy use and potential water pollution. Choosing garment dyeing aligns with eco-conscious practices by optimizing material use and lowering environmental impact in textile production.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Method for Your Apparel Brand
Garment dyeing offers enhanced color depth and unique vintage effects by dyeing fully assembled garments, ideal for brands seeking customization and soft handfeel. Piece dyeing, which colors fabric before garment construction, provides consistency and cost-efficiency, making it suitable for large-scale production with standardized color requirements. Selecting the right dyeing method depends on your brand's focus on aesthetic versatility, production volume, and budget constraints.
Garment dyeing vs Piece dyeing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com