Mass customization in apparel offers personalized fit and style tailored to individual preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing waste by producing only what is needed. Unlike mass production, which emphasizes large-scale manufacturing of standardized clothing at lower per-unit costs, mass customization leverages advanced technologies to balance efficiency with uniqueness. This approach empowers brands to meet diverse consumer demands while maintaining competitive pricing and faster turnaround times.
Table of Comparison
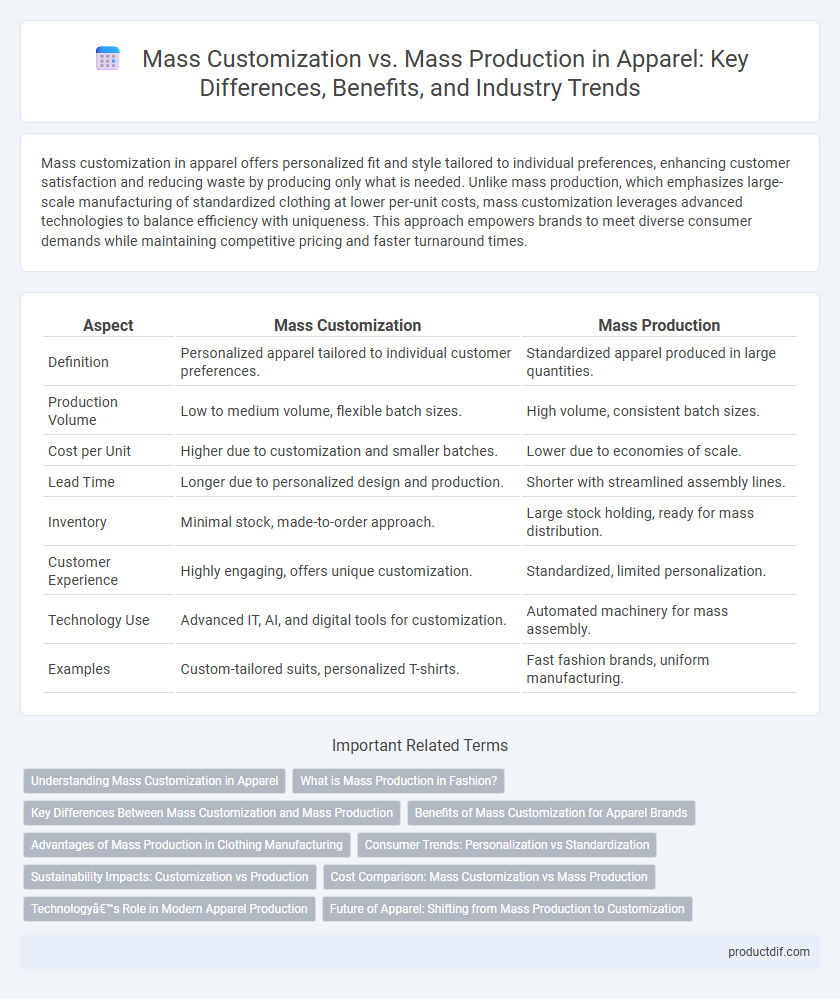
| Aspect | Mass Customization | Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personalized apparel tailored to individual customer preferences. | Standardized apparel produced in large quantities. |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume, flexible batch sizes. | High volume, consistent batch sizes. |
| Cost per Unit | Higher due to customization and smaller batches. | Lower due to economies of scale. |
| Lead Time | Longer due to personalized design and production. | Shorter with streamlined assembly lines. |
| Inventory | Minimal stock, made-to-order approach. | Large stock holding, ready for mass distribution. |
| Customer Experience | Highly engaging, offers unique customization. | Standardized, limited personalization. |
| Technology Use | Advanced IT, AI, and digital tools for customization. | Automated machinery for mass assembly. |
| Examples | Custom-tailored suits, personalized T-shirts. | Fast fashion brands, uniform manufacturing. |
Understanding Mass Customization in Apparel
Mass customization in apparel integrates advanced technologies such as 3D body scanning and AI-driven design to deliver personalized garments tailored to individual measurements and style preferences. This approach reduces inventory waste and enhances customer satisfaction by offering unique, made-to-order products instead of standardized mass-produced clothing. Brands leveraging mass customization gain competitive advantages through increased consumer engagement and sustainable manufacturing practices.
What is Mass Production in Fashion?
Mass production in fashion involves manufacturing large quantities of standardized clothing items using assembly line techniques and automated processes. This approach enables brands to achieve economies of scale, reduce unit costs, and quickly supply consistent designs to global markets. However, it often limits personalization and leads to overproduction concerns within the apparel industry.
Key Differences Between Mass Customization and Mass Production
Mass customization in apparel allows consumers to personalize designs, sizes, and materials, resulting in unique products tailored to individual preferences, whereas mass production focuses on high-volume manufacturing of standardized items with limited variation. The key differences lie in production flexibility, with mass customization requiring adaptable manufacturing systems and longer lead times, while mass production emphasizes efficiency, lower costs, and faster turnaround through repetitive processes. Supply chain complexity is higher in mass customization due to diverse inputs and order variability, contrasting with the streamlined, predictable logistics of mass production.
Benefits of Mass Customization for Apparel Brands
Mass customization empowers apparel brands to offer personalized products that cater to individual customer preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. This approach reduces inventory costs and minimizes waste by producing items on demand rather than in bulk. By leveraging advanced technologies like 3D body scanning and AI-driven design, brands can achieve faster product cycles and differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
Advantages of Mass Production in Clothing Manufacturing
Mass production in clothing manufacturing enables large-scale output with consistent quality, significantly lowering production costs per unit through economies of scale. This method ensures faster turnaround times, meeting high consumer demand efficiently while maintaining standardized sizing and design. Furthermore, mass production supports widespread distribution channels, enhancing market accessibility and brand visibility.
Consumer Trends: Personalization vs Standardization
Consumers increasingly demand personalized apparel that reflects their individual style and fit preferences, driving the growth of mass customization in the fashion industry. Mass customization leverages technologies like 3D body scanning and advanced manufacturing to deliver unique products at scale, contrasting with traditional mass production's focus on standardized sizes and designs. This shift aligns with trends towards sustainable consumption and enhanced customer engagement, as personalized apparel reduces waste and boosts brand loyalty.
Sustainability Impacts: Customization vs Production
Mass customization in apparel significantly reduces material waste and overproduction by tailoring products to individual consumer preferences, promoting sustainable consumption patterns. In contrast, mass production often leads to excess inventory, increased waste, and higher energy use due to large-scale manufacturing and unsold stock disposal. Sustainable apparel brands increasingly adopt mass customization to minimize environmental impacts while meeting customer demand efficiently.
Cost Comparison: Mass Customization vs Mass Production
Mass customization in apparel typically incurs higher per-unit costs due to individualized design and smaller production runs, whereas mass production benefits from economies of scale, significantly lowering expenses through bulk material purchasing and automated processes. Although upfront investments in flexible manufacturing systems raise customization costs, adaptive technologies and digital platforms are rapidly reducing these expenses, narrowing the cost gap. The trade-off between customization and cost efficiency remains a critical consideration for brands balancing customer personalization with large-scale affordability.
Technology’s Role in Modern Apparel Production
Technology drives the shift from mass production to mass customization in apparel by enabling advanced digital design, 3D body scanning, and automated manufacturing processes that tailor garments to individual preferences. Computer-aided design (CAD) software and AI-powered pattern making reduce material waste and accelerate production timelines while ensuring personalized fit and style. Integration of IoT devices and smart factories streamlines supply chains, enhancing responsiveness to consumer demand and minimizing inventory costs.
Future of Apparel: Shifting from Mass Production to Customization
The future of apparel manufacturing is rapidly shifting from mass production to mass customization, driven by advancements in 3D body scanning, AI-driven design tools, and on-demand manufacturing technologies. This transition enables brands to offer unique, personalized garments that reduce inventory waste and align with consumer demand for individuality and sustainability. As digital fabrication and automated cutting become mainstream, customization will enhance supply chain efficiency while meeting the growing market for tailored apparel experiences.
Mass Customization vs Mass Production Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com